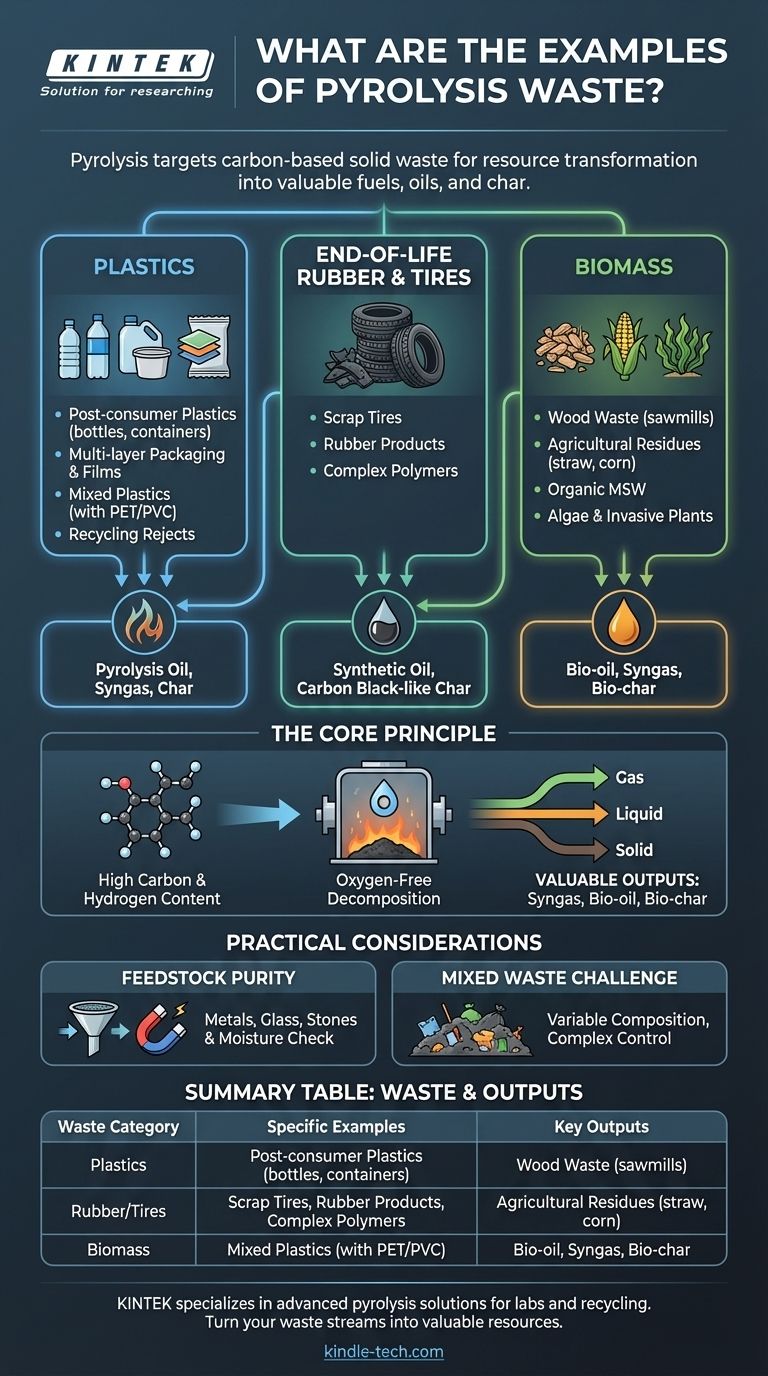
In essence, pyrolysis targets three primary categories of solid waste. These include various types of plastics, end-of-life rubber products like tires, and a wide range of organic materials known as biomass, such as wood and agricultural residues. The process is designed to handle carbon-based materials that are difficult to recycle through traditional mechanical means.
The core principle of pyrolysis is not merely waste disposal, but resource transformation. It selects waste streams rich in carbon and hydrogen to chemically decompose them in an oxygen-free environment, converting materials destined for a landfill into valuable fuels, oils, and char.
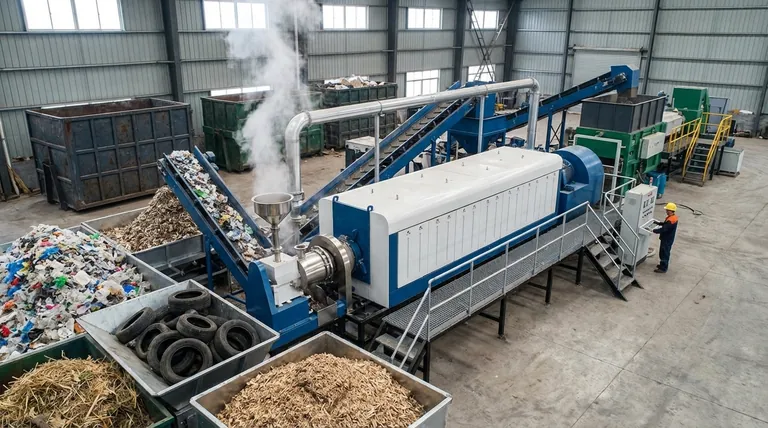

Deconstructing Pyrolysis-Suitable Waste
The viability of pyrolysis hinges on the chemical composition of the feedstock. Materials with high energy potential locked within their molecular structure are the ideal candidates for this thermal decomposition process.
Plastics: From Packaging to Contaminants
Plastics are a primary target for pyrolysis due to their high hydrocarbon content.
Specific examples include post-consumer plastics, such as bottles and containers, and segregated plastics from municipal solid waste (MSW).
It is particularly effective for materials that challenge traditional recycling, like multi-layer packaging, films, and mixed plastics contaminated with materials like PET or PVC. Even the rejects from mechanical recycling facilities can be used as feedstock.
End-of-Life Tires and Rubber
Used tires represent a significant and problematic waste stream globally.
Pyrolysis offers a robust solution for recovering value from scrap tires and other rubber products. The process breaks down the complex polymers into valuable outputs like synthetic oil (pyrolysis oil) and a solid residue called bio-char, which is similar to carbon black.
Biomass: Organic and Agricultural Residues
Biomass refers to any material derived from organic, renewable sources. The key components that decompose during pyrolysis are cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin.
Common examples include wood waste from sawmills and construction, and agricultural waste like corn stover and straw.
The definition also extends to the organic fraction of municipal solid waste, dedicated energy crops, algae, and even invasive plant species like kudzu.
Why These Materials? The Underlying Principle
The selection of these waste types is not arbitrary. It is based on a clear chemical and economic objective: converting a liability into an asset.
High Carbon and Hydrogen Content
The common thread among plastics, rubber, and biomass is their composition. They are all rich in carbon and hydrogen, the fundamental building blocks of fuels.
The pyrolysis process heats these materials in the absence of oxygen, breaking the large, complex molecules (polymers) into smaller, more valuable ones.
The Goal: Value Recovery, Not Just Disposal
Unlike incineration, which primarily aims to reduce waste volume and recover heat, pyrolysis is a material recovery process.
The outputs—syngas (a combustible gas mixture), bio-oil (a liquid fuel), and bio-char (a stable, carbon-rich solid)—can be sold or used as fuel, soil amendments, or chemical feedstocks. This creates an economic incentive for waste management.
Understanding the Practical Considerations
While pyrolysis is versatile, it is not a magic bullet for all waste. The quality and consistency of the input material, or feedstock, directly impact the efficiency of the process and the quality of the outputs.
The Importance of Feedstock Purity
Preprocessing is a critical step. Non-pyrolyzable materials like metals, glass, and stones must be removed to prevent damage to the equipment and contamination of the final products.
Excessive moisture in the feedstock is also a major concern, as energy must be spent to evaporate the water before the pyrolysis reaction can begin, reducing the overall energy efficiency of the system.
The Challenge of Mixed Waste
Using a clean, homogenous feedstock like tires or a specific type of plastic is relatively straightforward.
However, processing mixed streams like municipal solid waste is more complex. The variability in composition can lead to inconsistent yields and qualities of the resulting oil, gas, and char, requiring more sophisticated operational controls.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal pyrolysis feedstock depends entirely on your primary objective, whether it's environmental remediation, resource recovery, or energy production.
- If your primary focus is resource recovery from plastics: Target post-consumer packaging, multi-layer films, and rejects from traditional recycling that would otherwise be landfilled.
- If your primary focus is managing bulky, problematic waste: End-of-life tires are an ideal and highly common feedstock for dedicated pyrolysis systems that produce valuable oil and carbon black.
- If your primary focus is sustainable energy from organic sources: Agricultural and forestry residues like straw, corn stover, and wood waste offer a renewable path to producing bio-oils and bio-char.
Ultimately, pyrolysis provides a powerful tool to redefine waste as a valuable resource in a circular economy.
Summary Table:
| Waste Category | Specific Examples | Key Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Plastics | Post-consumer bottles, multi-layer packaging, film, recycling rejects | Pyrolysis oil, syngas, char |
| Rubber/Tires | Scrap tires, end-of-life rubber products | Synthetic oil, carbon black-like char |
| Biomass | Wood waste, agricultural residues (straw, corn stover), algae | Bio-oil, syngas, bio-char |
Ready to turn your waste streams into valuable resources? KINTEK specializes in advanced pyrolysis solutions for laboratories and recycling facilities. Our equipment is designed to efficiently process plastics, tires, and biomass, helping you recover energy and materials while reducing landfill waste. Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab equipment and consumables can support your pyrolysis research and operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success



















