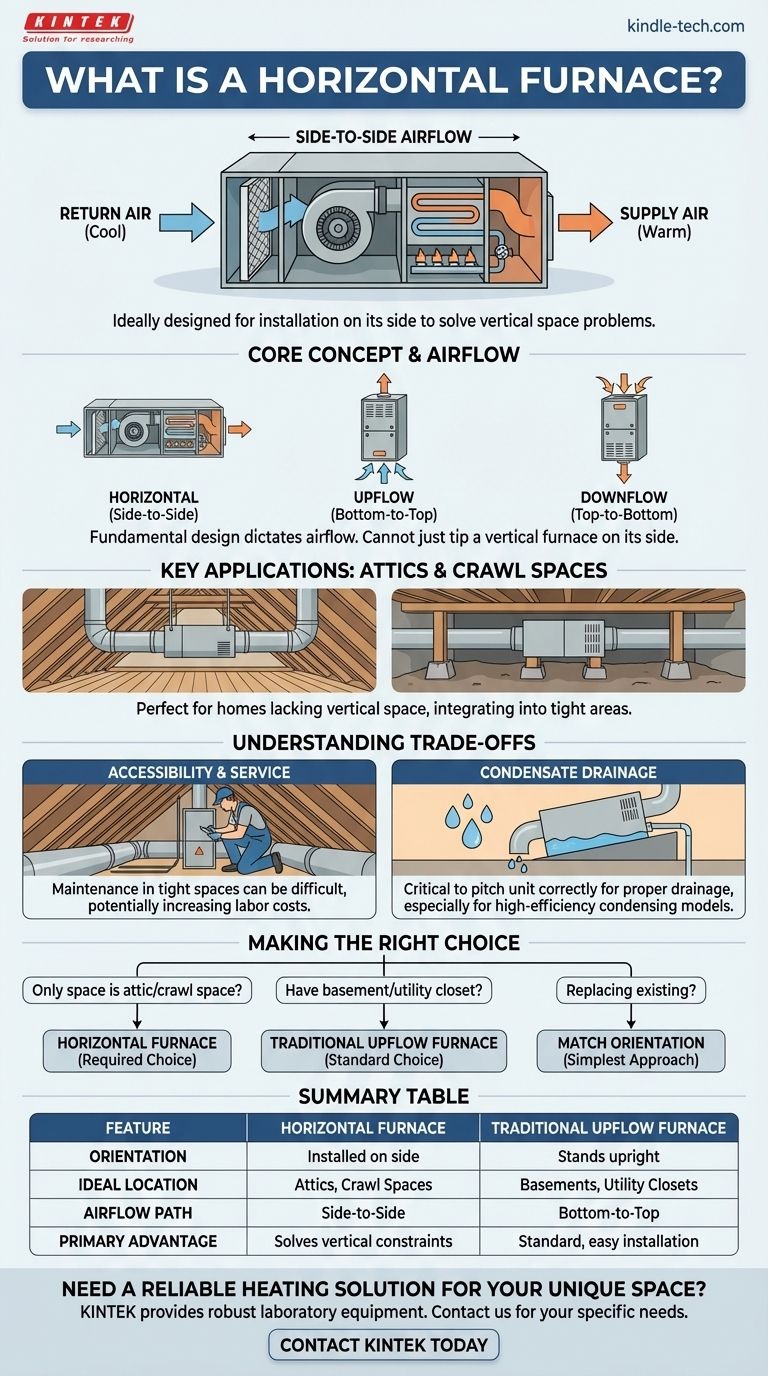
In simple terms, a horizontal furnace is a home heating unit specifically designed to be installed and operated on its side. Unlike traditional furnaces that stand upright, this model draws air in from one end, heats it, and pushes it out the other end in a straight, horizontal path.
The primary purpose of a horizontal furnace is to solve a space problem. It is the go-to solution for homes that lack the vertical space for a traditional furnace, making it ideal for installation in tight areas like attics and crawl spaces.

The Core Concept: Airflow and Orientation
A furnace's orientation is not an arbitrary choice; it's a fundamental design feature that dictates how it functions within your home's HVAC system.
How It Works: Side-to-Side Air Movement
A horizontal furnace is engineered for a specific airflow pattern. The return air (cooler air from your home) enters one side of the unit, passes through the filter and over the heat exchanger, and is then pushed out the other side as supply air (warm air) into your ductwork.
This is distinct from an upflow model (common in basements), which pulls air from the bottom and pushes it out the top, or a downflow model, which does the opposite.
Why the Design Is Deliberate
You cannot simply take a standard vertical furnace and tip it on its side. The internal components, from the blower to the burners and safety switches, are specifically positioned and secured to operate safely and efficiently in a horizontal configuration.
Using the wrong orientation can lead to serious performance issues, premature component failure, and significant safety hazards.
Key Applications for Horizontal Furnaces
The choice to use a horizontal furnace is almost always dictated by the architectural constraints of the building.
The Ideal Use Case: Attics and Crawl Spaces
The most common application is in homes without basements or dedicated utility closets. Low-ceiling environments like attics and crawl spaces simply do not have the vertical clearance for an upflow or downflow unit.
A horizontal furnace can be suspended from the rafters in an attic or set on blocks in a crawl space, integrating seamlessly with the ductwork in these otherwise unusable areas.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While they are an effective solution for specific situations, horizontal installations come with unique considerations.
Accessibility and Service
Installing, maintaining, and repairing a unit in a cramped attic or crawl space can be more difficult and time-consuming for an HVAC technician. This can sometimes translate to higher labor costs for service calls compared to an easily accessible basement unit.
Condensate Drainage
High-efficiency condensing furnaces produce water (condensate) as a byproduct of combustion. In a horizontal setup, ensuring this water drains properly is critical. The unit must be pitched correctly to allow gravity to feed the drain line, preventing water from pooling inside the furnace, which could cause rust and water damage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Home
Selecting the correct furnace orientation is fundamental to a properly functioning HVAC system.
- If your only available space is an attic or crawl space: A horizontal furnace is almost certainly the required and correct choice for your home.
- If you have a basement or a tall utility closet: A traditional upflow furnace is the standard and typically the most straightforward to install and service.
- If you are replacing an existing furnace: The simplest approach is to match the orientation of the old unit, as your ductwork is already configured for it.
Ultimately, the layout of your home will determine the right furnace configuration for you.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Horizontal Furnace | Traditional Upflow Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Orientation | Installed on its side | Stands upright |
| Ideal Location | Attics, Crawl Spaces | Basements, Utility Closets |
| Airflow Path | Side-to-Side | Bottom-to-Top |
| Primary Advantage | Solves vertical space constraints | Standard, easy-to-access installation |
Need a Reliable Heating Solution for Your Unique Space?
Choosing the right lab equipment, including specialized environmental systems, is crucial for your operations. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust and efficient laboratory equipment and consumables tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're setting up a new lab or upgrading your current systems, our experts can help you find the perfect solution.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's heating and environmental control requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- Why is a horizontal alumina tube furnace ideal for mixed gas corrosion at 650 °C? Ensure Pure Experimental Integrity



















