In essence, the "high temperature method" is not a single process but a broad category of techniques that use controlled, elevated heat to induce a specific physical or chemical change in a material. These methods are common across various fields, from food preservation, known as High-Temperature–Short-Time (HTST) processing, to advanced materials science for creating high-performance components like those in Li-ion batteries.
The core principle is using thermal energy as a tool to drive a desired transformation—such as sterilization or material synthesis—while carefully managing temperature and duration to avoid degrading the subject material's essential qualities.

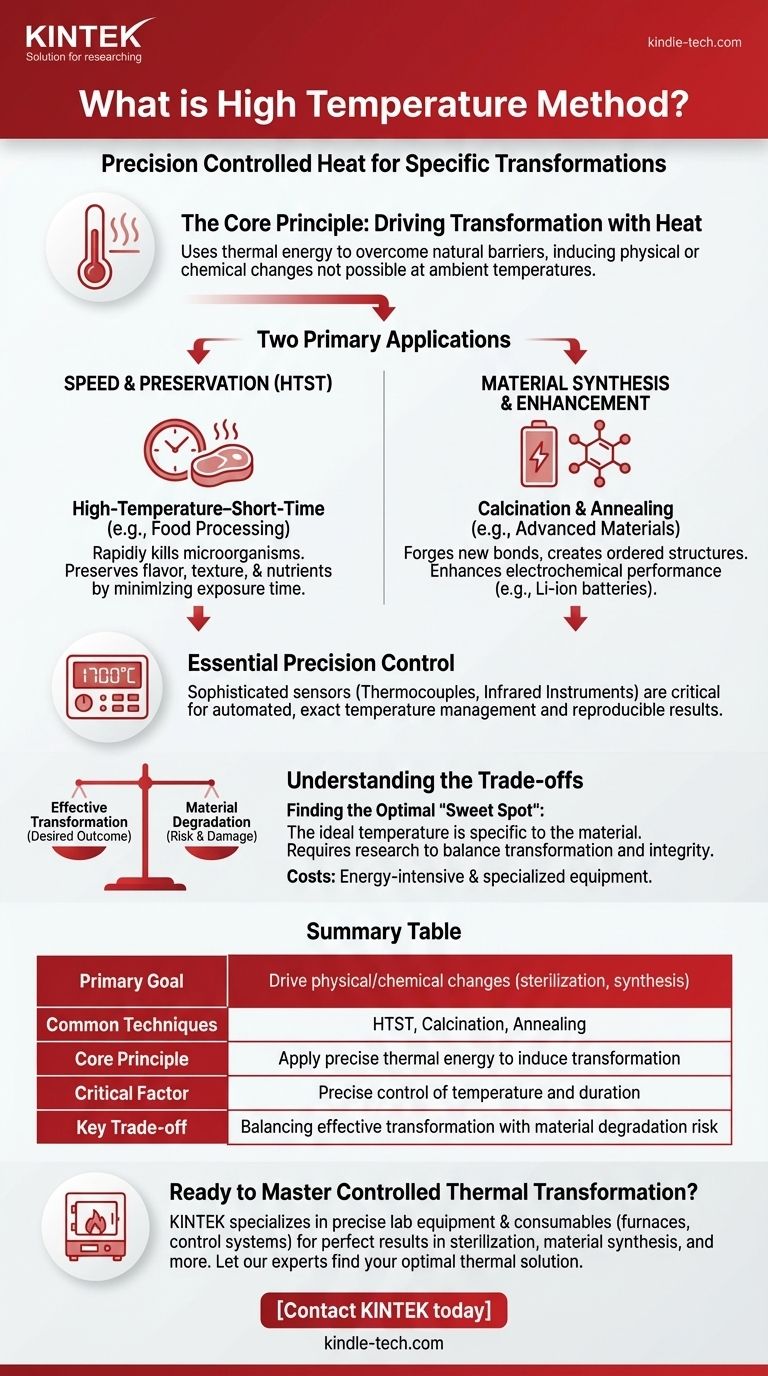
The Core Principle: Driving Transformation with Heat
The fundamental goal of any high temperature method is to supply enough energy, in the form of heat, to overcome a natural barrier. This allows for changes that would not occur, or would occur too slowly, at ambient temperatures.
Speed and Efficiency
In many applications, the goal is to complete a process as quickly as possible. Applying a very high temperature for a very short time can achieve the desired outcome while minimizing unwanted side effects.
A classic example is the HTST method in food processing. It rapidly kills harmful microorganisms without significantly altering the food's flavor, texture, or nutritional value, which would happen with prolonged heating.
Material Synthesis and Enhancement
In materials science, high temperatures are used to create new structures or modify existing ones. This process, often called calcination or annealing, can forge new chemical bonds and create highly ordered materials.
For instance, a high-temperature solid-state method can produce a uniform carbon coating on battery components, which dramatically enhances their electrochemical performance and longevity.
Precision Control is Essential
Achieving the desired outcome is impossible without precise control over the thermal environment. The process is not simply about making something "hot."
Modern systems use sophisticated sensors, such as thermocouples for lower ranges and infrared instruments for temperatures above 1700°C. This allows for automated and exact temperature management, which is critical for reproducible results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, high temperature methods are a balancing act. The same energy that drives a positive transformation can also cause damage if not applied correctly.
The Risk of Degradation
Every material has a temperature threshold beyond which it begins to break down. For food, this means a loss of quality. For an advanced chemical compound, it could mean complete structural failure.
The key is applying heat for the minimum duration required to achieve the goal, thereby preserving the material's integrity.
Finding the Optimal "Sweet Spot"
There is no universal "high temperature" that works for all applications. The optimal temperature is highly specific to the material being processed and the desired outcome.
Determining the ideal conditions for a new material often requires significant research and exploration to find the perfect balance between effective transformation and potential damage.
Energy and Equipment Costs
Maintaining very high temperatures is energy-intensive and requires specialized equipment built to withstand extreme thermal stress. These factors represent significant operational and capital costs that must be considered.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The right approach depends entirely on your end goal. The high temperature method is a means to an end, and your strategy should reflect the specific outcome you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is preservation or sterilization: Aim for a high-temperature, short-time (HTST) model to maximize the destructive effect on microbes while minimizing exposure time to preserve the core qualities of your product.
- If your primary focus is material creation or modification: Concentrate on controlled calcination or annealing to create specific crystalline structures or surface properties, understanding that extensive testing is needed to find the optimal temperature for your specific material.
Ultimately, mastering a high temperature method is about understanding heat not as a brute force, but as a precise instrument for controlled change.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Use heat to drive physical/chemical changes (e.g., sterilization, synthesis). |
| Common Techniques | High-Temperature-Short-Time (HTST), Calcination, Annealing. |
| Core Principle | Apply precise thermal energy to overcome barriers and induce transformation. |
| Critical Factor | Precise control of temperature and duration to avoid material degradation. |
| Key Trade-off | Balancing effective transformation with the risk of damaging the material. |
Ready to Master Controlled Thermal Transformation?
Choosing and implementing the right high temperature method is critical for your project's success. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables—from high-temperature furnaces to exact temperature control systems—that your laboratory needs to achieve perfect results in sterilization, material synthesis, and beyond.
Let our experts help you find the optimal thermal solution. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is a muffle furnace in the environment? Achieve Clean, Contaminant-Free Heating
- What is the alternative to a laboratory oven? Find the Right Heating Tool for Your Lab
- What is the difference between hot air oven and muffle furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Thermal Needs
- How do you clean a muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Ensure Safety and Longevity
- What is the working principle of laboratory muffle furnace? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing



















