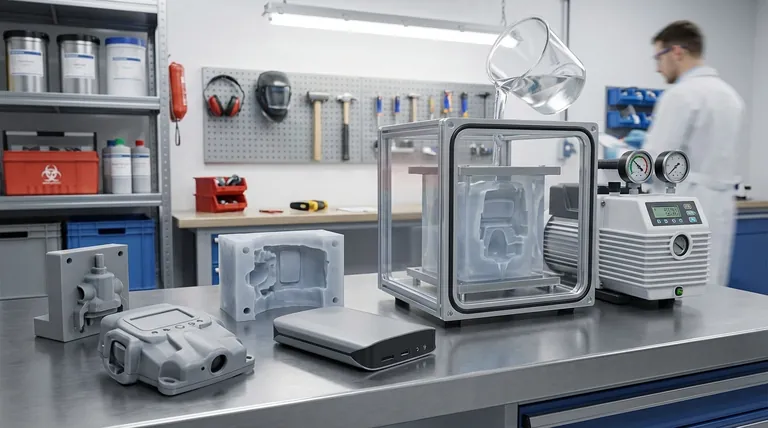
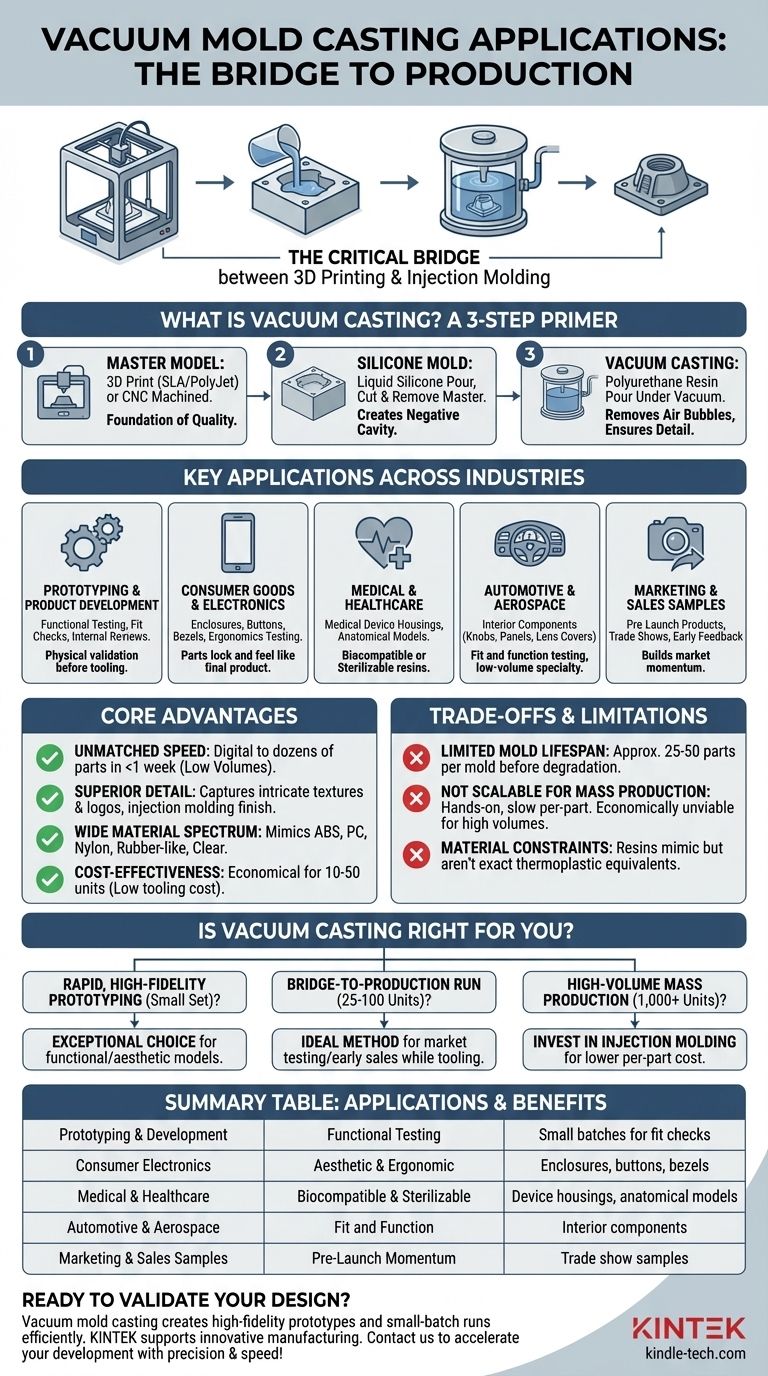
At its core, vacuum mold casting is an advanced manufacturing technique used to create small batches of high-fidelity, production-quality parts. It excels in applications ranging from functional prototyping and engineering validation to producing the first series of market-ready products, especially in the consumer electronics, medical device, and automotive industries.
Vacuum casting is best understood as the critical bridge between a single 3D-printed prototype and full-scale injection molding. It enables the rapid creation of dozens of parts that perfectly mimic the look, feel, and performance of a final product without the prohibitive cost of hard tooling.

What is Vacuum Casting? A Quick Primer
To understand its applications, it's essential to grasp the process. It's a three-step method that leverages a high-quality master model to create a flexible silicone mold.
The Master Model: The Foundation of Quality
The process begins with a "master model" or pattern. This is typically created using a high-resolution 3D printing method like SLA or PolyJet, or it can be CNC machined.
The final quality of the cast parts is directly dependent on the precision and surface finish of this master model.
Creating the Silicone Mold
The master model is suspended inside a casting box, and liquid silicone is poured around it. Once the silicone cures, it is carefully cut into two halves, and the master model is removed.
This process leaves a hollow cavity inside the flexible mold that is a perfect negative impression of the original part.
The Casting Process Under Vacuum
The two halves of the silicone mold are reassembled, and the entire mold is placed inside a vacuum chamber. A two-part polyurethane resin is mixed and poured into the mold's cavity while under vacuum.
The vacuum is critical because it removes all air from the chamber and the mold itself, ensuring the liquid resin fills every tiny feature without creating air bubbles. The part then cures, often with the assistance of heat, before being de-molded.
Key Applications Across Industries
The unique combination of speed, quality, and material versatility makes vacuum casting indispensable for specific goals across many sectors.
Prototyping and Product Development
This is the most common application. Teams create a small batch of prototypes for functional testing, fit checks, and internal design reviews, allowing for physical validation before committing to expensive tooling.
Consumer Goods and Electronics
Vacuum casting is ideal for producing enclosures, casings, buttons, and bezels for new electronic devices. It allows designers to test ergonomics and aesthetics with parts that look and feel identical to the final product.
Medical and Healthcare
The process is used to create highly detailed medical device housings and anatomical models for surgical planning. The ability to use biocompatible or sterilizable resins is a significant advantage in this field.
Automotive and Aerospace
Engineers use vacuum casting to produce interior components like knobs, dashboard panels, and lens covers for concept cars or low-volume specialty vehicles. It's also used for fit and function testing of parts before mass production begins.
Marketing and Sales Samples
Companies rely on vacuum casting to create a run of pre-launch products for marketing photoshoots, trade shows, and early feedback from key customers. This builds market momentum before the final product is widely available.
The Core Advantages: Why Choose Vacuum Casting?
Understanding the benefits reveals why it's chosen for the applications listed above. The decision almost always comes down to a balance of speed, fidelity, and cost at a specific volume.
Unmatched Speed for Low Volumes
Once the master model is created, a silicone mold can be made in a day or two. Casting parts is also rapid, allowing a company to go from a digital design to dozens of physical parts in under a week.
Superior Detail and Surface Finish
Because the liquid resin is pulled into a flexible silicone mold under vacuum, it captures intricate textures, logos, and features with incredible precision. The resulting surface finish can be indistinguishable from injection molding.
A Wide Spectrum of Material Properties
A vast range of polyurethane resins can be used. These materials can be formulated to mimic the properties of common production plastics, including ABS, polycarbonate, and nylon.
They can also be flexible and rubber-like (simulating TPE), rigid, or perfectly clear, offering immense design freedom.
Cost-Effectiveness for Small Batches
The tooling cost for vacuum casting (the silicone mold) is a tiny fraction of the cost of a steel injection mold. For production runs of 10 to 50 units, it is almost always the most economical choice.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No process is perfect. Objectivity requires acknowledging where vacuum casting falls short, which is primarily a matter of scale.
Limited Mold Lifespan
A single silicone mold begins to degrade with use. You can typically expect to get only 25 to 50 parts from one mold before its fine details and dimensional accuracy begin to deteriorate.
Not Scalable for Mass Production
The process is hands-on and relatively slow on a per-part basis compared to automated methods. The cost per part does not decrease significantly with volume, making it economically unviable for hundreds or thousands of units.
Material Constraints
While the resins are excellent mimics, they are not the exact same thermoplastic materials used in injection molding. This can be a limiting factor for parts that require very specific thermal or chemical resistance properties found only in production-grade plastics.
Is Vacuum Casting the Right Choice for Your Project?
Use the following guidelines to determine if this process aligns with your goals.
- If your primary focus is rapid, high-fidelity prototyping: Vacuum casting is an exceptional choice for creating a small set of functional and aesthetic models for testing.
- If your primary focus is a bridge-to-production run: It is the ideal method for producing the first 25-100 units for market testing or early sales while your injection mold is being manufactured.
- If your primary focus is high-volume mass production (1,000+ units): You should invest in injection molding tooling, as the per-part cost will be substantially lower.
- If your primary focus is creating a single, simple concept model: A direct 3D print from a technology like FDM or SLA will likely be faster and more cost-effective.
Ultimately, vacuum casting provides an unparalleled ability to validate your design with production-quality parts before you make a major capital investment.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Prototyping & Product Development | Functional Testing & Design Validation | Creating small batches for fit checks and reviews |
| Consumer Electronics | Aesthetic & Ergonomic Testing | Producing enclosures, buttons, and bezels |
| Medical & Healthcare | Biocompatible & Sterilizable Parts | Medical device housings and anatomical models |
| Automotive & Aerospace | Fit and Function Testing | Interior components for concept cars |
| Marketing & Sales Samples | Pre-Launch Market Momentum | Trade show samples and customer feedback units |
Ready to Validate Your Design with Production-Quality Parts?
Vacuum mold casting is the ideal solution for creating high-fidelity prototypes and small-batch production runs without the high cost of injection molding. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables that support innovative manufacturing processes like vacuum casting.
Whether you're in consumer electronics, medical devices, or automotive development, our expertise can help you bridge the gap between prototyping and mass production efficiently.
Contact us today to discuss how vacuum casting can accelerate your product development cycle and bring your ideas to life with unmatched precision and speed!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of graphite molds during the hot pressing of LSLBO ceramics? Essential for High-Density Electrolytes
- What role does a high-purity graphite mold play during hot pressing? Optimize Boron Carbide Sintering at 1850°C
- What role do high-temperature pressure molds play in SiCp/Al fabrication? Enhancing Densification and Thermal Uniformity
- Why is hot press molding preferred over traditional solution casting? Expert Comparison for Polymer Electrolytes
- What technical requirements must specialized pressure-bearing molds meet? Optimize Sulfide Electrolyte Densification



















