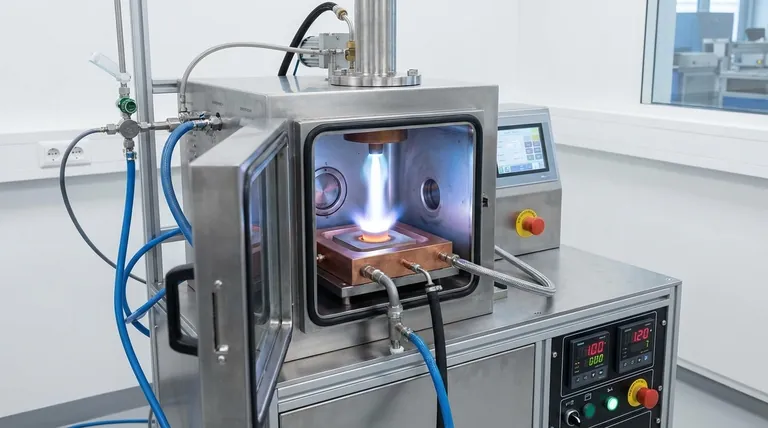
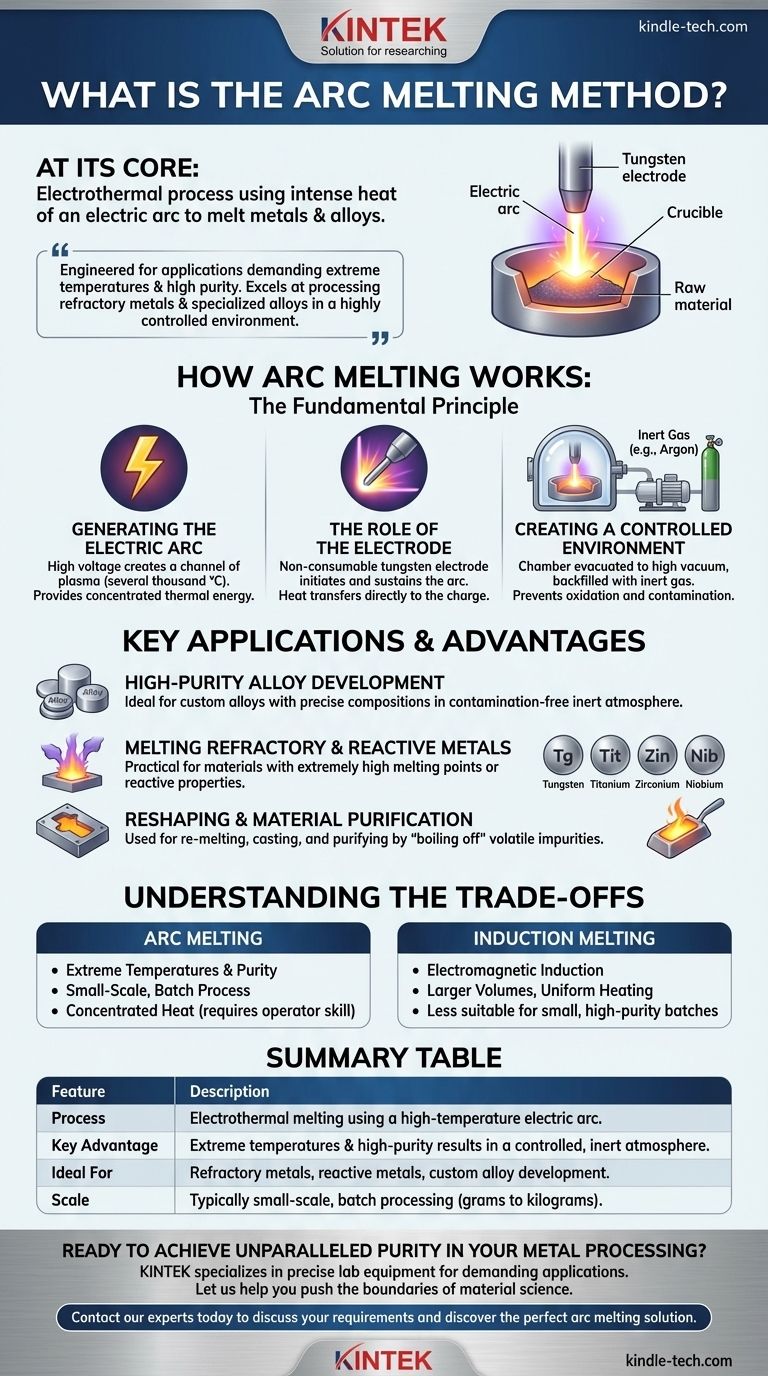
At its core, arc melting is an electrothermal process that uses the intense heat of an electric arc to melt metals and alloys. The arc, which is essentially a controlled, high-energy plasma discharge, is generated between electrodes or between a single electrode and the raw material. This process provides the direct thermal energy necessary to liquefy even the most resilient materials.
While many methods can melt metal, arc melting is specifically engineered for applications demanding extreme temperatures and high purity. It excels at processing refractory metals and creating specialized alloys in a highly controlled environment, free from atmospheric contamination.

The Fundamental Principle: How Arc Melting Works
To understand arc melting, it's best to break down its core components: the arc, the electrodes, and the environment. Each element is critical to achieving a successful melt.
Generating the Electric Arc
The heart of the process is the electric arc. Think of it as a continuous, controlled bolt of lightning.
When a high voltage is applied across a gap between two conductive points (the electrodes or electrode-and-material), it ionizes the gas in that gap, creating a channel of plasma. This plasma channel is incredibly hot—often reaching several thousand degrees Celsius—and provides the concentrated energy needed for melting.
The Role of the Electrode
The electrode is the tool that initiates and sustains the arc. In most laboratory and high-purity applications, a non-consumable tungsten electrode is used.
The system strikes an arc between this electrode and the source material (the "charge"). The intense heat from the arc transfers directly to the material, causing it to liquefy rapidly.
Creating a Controlled Environment
Arc melting is almost always performed inside a sealed chamber. This chamber is first evacuated to a high vacuum and then typically backfilled with an inert gas, such as argon.
This step is crucial. The inert atmosphere prevents the molten metal from reacting with oxygen or nitrogen from the air, which would otherwise form undesirable oxides and nitrides, compromising the final material's purity and properties.
Key Applications and Advantages
The unique characteristics of arc melting make it the preferred method for several demanding metallurgical tasks, particularly in research and specialized manufacturing.
High-Purity Alloy Development
Because the inert environment prevents contamination, arc melting is ideal for creating custom alloys with very precise compositions. Researchers can mix precise amounts of different elements and melt them into a homogeneous "button" or ingot for analysis and testing.
Melting Refractory and Reactive Metals
Many advanced materials, like titanium, tungsten, zirconium, and niobium, have extremely high melting points, making them "refractory." The intense, localized heat of an electric arc is one of the few practical ways to melt them effectively. It's also ideal for reactive metals like titanium that readily absorb atmospheric gases when molten.
Reshaping and Material Purification
The process is also used for re-melting and casting materials into new shapes. The repeated melting can sometimes help purify a material by "boiling off" volatile impurities that have a lower boiling point than the base metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single method is perfect for every application. Understanding where arc melting fits in comparison to other techniques is key to making an informed decision.
Comparison with Induction Melting
Induction melting works on a different principle. It uses electromagnetic fields to induce electrical currents within the metal itself, causing it to heat up and melt from the inside out.
Induction furnaces are excellent for melting larger volumes and can offer very uniform heating. However, they may not reach the extreme temperatures of an arc melter and can be less suitable for the small, high-purity batches where arc melting excels.
Common Limitations
Arc melting is primarily a batch process, often on a small scale (grams to a few kilograms). It is not designed for the continuous, large-tonnage production seen in steel mills.
Additionally, the intense heat is concentrated at the point of the arc, which can sometimes lead to less uniform temperature distribution throughout the melt compared to other methods. This requires skill from the operator, who often has to move the arc around to ensure a homogeneous liquid.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct melting process depends entirely on your material, your desired purity, and the scale of your operation.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity, custom alloys or melting refractory metals: Arc melting is the superior choice due to its controlled atmosphere and extreme temperatures.
- If your primary focus is melting larger volumes of standard metals where purity is less critical: An induction furnace or other bulk melting methods will almost certainly be more efficient and cost-effective.
Ultimately, choosing arc melting is a decision to prioritize material purity and temperature capability above all else.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Electrothermal melting using a high-temperature electric arc. |
| Key Advantage | Extreme temperatures and high-purity results in a controlled, inert atmosphere. |
| Ideal For | Refractory metals (tungsten, titanium), reactive metals, and custom alloy development. |
| Scale | Typically small-scale, batch processing (grams to kilograms). |
Ready to achieve unparalleled purity in your metal processing?
Arc melting is the definitive solution for researchers and engineers working with refractory metals and developing high-purity alloys. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment you need to excel in these demanding applications.
Our expertise ensures you get the right tools for controlled, contamination-free melting. Let us help you push the boundaries of material science.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover the perfect arc melting solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the remelting process? Achieve Ultimate Purity and Performance for High-Strength Alloys
- What is VAR in metallurgy? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Performance
- What is the process of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Ultimate Purity for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the benefit of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Structural Integrity
- What is a remelting process? A Guide to High-Purity Metal Refinement



















