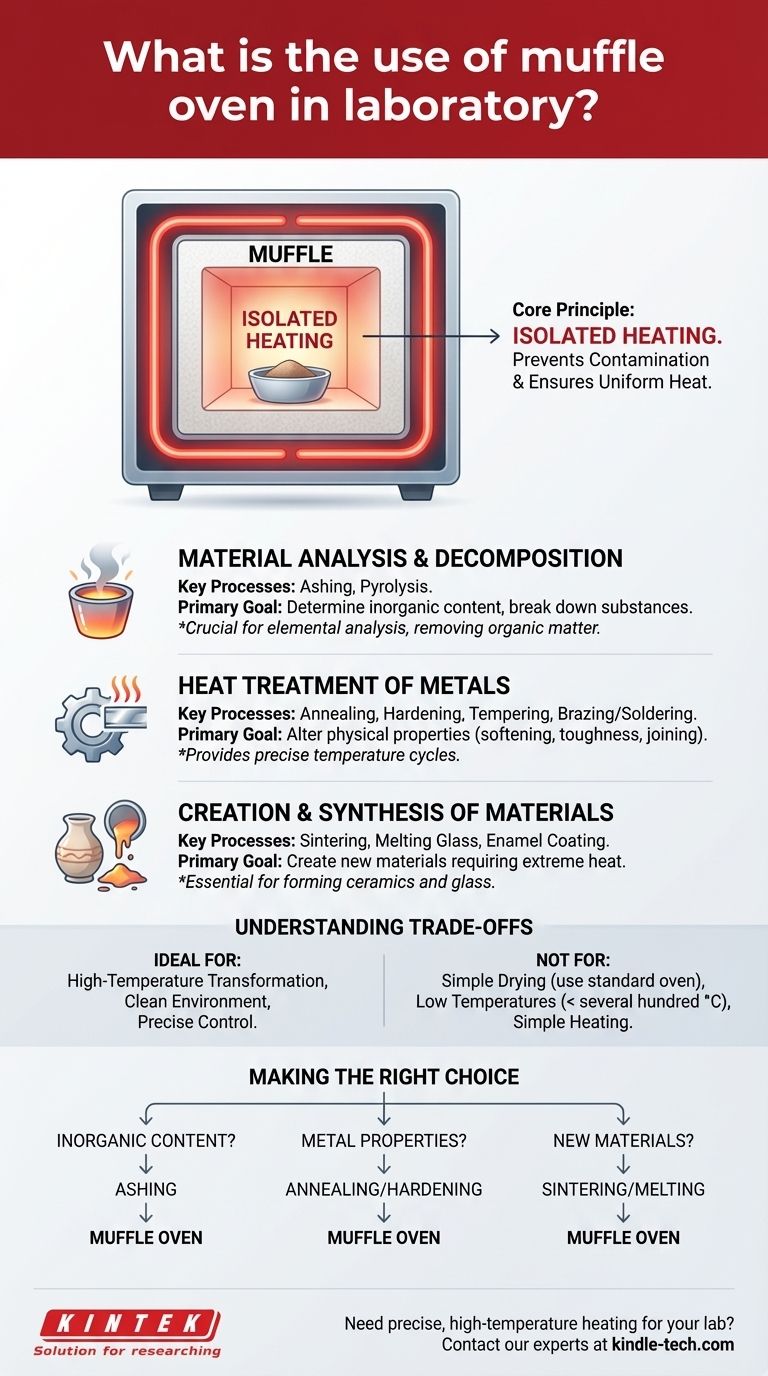
At its core, a muffle oven is used in a laboratory to heat materials to extremely high temperatures in a clean, controlled environment. Unlike a simple oven, its defining feature is a "muffle," an insulating chamber that isolates the sample from the direct heat source and any contaminating byproducts of combustion. This allows for processes like ashing, heat-treating metals, and creating ceramics without altering the sample's chemical composition.
The essential purpose of a muffle oven, also known as a muffle furnace, is not just to get things hot, but to do so without contamination. It's the go-to instrument when a sample must be heated to extreme temperatures while being completely isolated from the flame or heating elements generating that heat.

The Core Principle: Isolated Heating
The name "muffle furnace" reveals its primary function. The internal chamber, or muffle, acts as a barrier.
Preventing Contamination
The muffle physically separates the material being heated from the fuel and combustion gases. This is critical for applications like elemental analysis, where any external residue would invalidate the results.
Ensuring Uniform Heat
This isolated chamber design allows for highly uniform and stable temperatures, which is essential for processes like annealing metals or firing ceramics where precise thermal control dictates the final product's quality.
Key Laboratory Applications
The ability to provide clean, high heat makes the muffle furnace indispensable across numerous scientific and industrial fields. Its applications can be grouped into three main categories.
Material Analysis and Decomposition
This involves breaking down a substance to understand its composition.
Ashing is one of the most common uses. The furnace heats a sample to a temperature high enough to completely burn away all organic material, leaving only the inorganic ash for analysis.
Pyrolysis is another key use, involving the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an inert atmosphere.
Heat Treatment of Metals
Muffle furnaces are central to metallurgy for altering the physical properties of metals.
Processes like hardening, annealing (softening), and tempering (increasing toughness) all require precise temperature cycles that a muffle furnace can provide.
It is also used for joining metals through brazing and soldering, which require high heat in a controlled environment.
Creation and Synthesis of Materials
The furnace is used to create entirely new materials that require extreme temperatures to form.
This includes sintering ceramics, melting glass, and applying enamel coatings. These processes rely on the furnace's ability to reach and hold temperatures that can fundamentally change a material's state.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a specialized tool, not a general-purpose oven. Its design for extreme, isolated heat comes with specific considerations.
Not for Simple Drying
For low-temperature applications like drying glassware or removing moisture from samples, a standard laboratory oven is far more efficient and appropriate. Muffle furnaces are overkill for tasks below several hundred degrees Celsius.
Atmosphere is a Factor
A basic muffle furnace operates with an air atmosphere. If a process requires an inert or controlled atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation, a more specialized furnace with gas-purging capabilities is necessary.
Safety and Energy Use
These devices reach extreme temperatures and consume significant energy. They require proper ventilation, operator training, and an understanding of the thermal properties of the materials being heated to prevent accidents.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating process depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is determining the inorganic or mineral content of a sample: You need a muffle furnace for ashing to completely and cleanly combust all organic matter.
- If your primary focus is altering the physical properties of metals: A muffle furnace provides the controlled, high-heat environment necessary for processes like annealing or hardening.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials like technical ceramics or glass: The furnace offers the extreme, isolated heat required for melting, sintering, and forming these materials.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace is the essential laboratory tool for any process that demands pure, high-temperature transformation.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Material Analysis | Ashing, Pyrolysis | Determine inorganic content, decompose materials |
| Metal Treatment | Annealing, Hardening, Tempering | Alter physical properties of metals |
| Material Synthesis | Sintering, Melting Glass, Enameling | Create new materials like ceramics and glass |
Need precise, high-temperature heating for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance muffle furnaces and lab equipment designed for applications like ashing, heat treatment, and material synthesis. Our solutions ensure the clean, controlled environment your research demands.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your specific application and enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the use of muffle furnace in pharmaceuticals? Essential for Purity & Quality Control
- What are the advantages of a muffle furnace? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Precision in Your Lab
- What is the temperature of a muffle furnace? It's Not a Single Number—Find Your Perfect Range
- Can a muffle furnace be used for pyrolysis? How to adapt it for oxygen-free thermal decomposition
- What is the muffle furnace used for in metallurgy? Achieve Precise, Contaminant-Free Heat Treatment



















