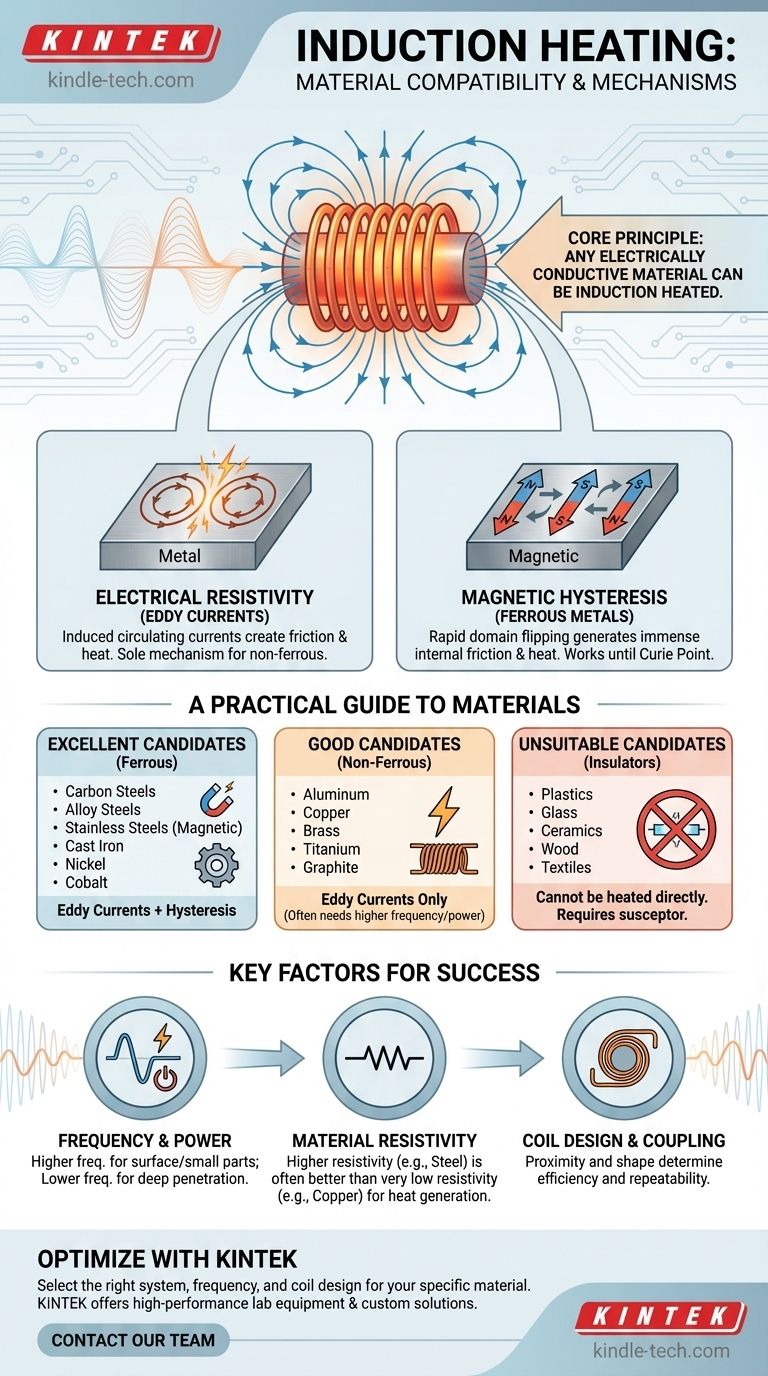
In short, any electrically conductive material can be induction heated. However, the efficiency of the heating process depends dramatically on two key properties: electrical resistivity and, most importantly, magnetic permeability. This is why ferrous metals like iron and steel heat exceptionally well, while non-ferrous metals like copper and aluminum require different parameters.
The core principle to understand is that induction heating is not about the material being "magnetic" in the common sense, but about its ability to conduct electricity and interact with a magnetic field. Ferrous metals are simply far more efficient because they generate heat through two separate mechanisms, while other conductors only use one.

The Physics Behind Induction Heating
To select the right material, you must first understand the two phenomena that generate heat: eddy currents and magnetic hysteresis. The effectiveness of each depends entirely on the material's properties.
The Role of Electrical Resistivity (Eddy Currents)
An induction coil generates a powerful, alternating magnetic field.
When a conductive material is placed within this field, it induces circulating electrical currents within the material. These are known as eddy currents.
Every material has some resistance to the flow of electricity. This electrical resistivity causes friction as the eddy currents flow, which generates precise, localized heat. This is the sole mechanism for heating non-magnetic materials like aluminum, copper, and brass.
The Power of Magnetic Hysteresis
Ferrous metals (like iron, nickel, and cobalt) have an additional, more powerful source of heat.
These materials are composed of small magnetic regions called domains. The alternating magnetic field from the induction coil causes these domains to rapidly flip their polarity, billions of times per second.
This rapid flipping creates immense internal friction, which generates significant heat. This hysteresis effect is what makes ferrous metals heat so much more quickly and efficiently than their non-ferrous counterparts.
The Curie Point: A Critical Threshold
Hysteresis only works as long as the material is magnetic.
Every magnetic material has a specific temperature, called the Curie point (or Curie temperature), at which it loses its magnetic properties. For steel, this is around 770°C (1420°F).
Once a material is heated past its Curie point, hysteresis heating stops completely. From that point on, any further heating is accomplished only through the less efficient eddy current mechanism.
A Practical Guide to Materials
Materials can be grouped into three categories based on their suitability for induction heating.
Excellent Candidates (Ferrous Metals)
These materials benefit from both eddy currents and hysteresis, making them ideal for induction.
- Carbon Steels
- Alloy Steels
- Stainless Steels (Magnetic Grades, e.g., 400 series)
- Cast Iron
- Nickel
- Cobalt
Good Candidates (Non-Ferrous Conductors)
These materials can be heated but rely solely on eddy currents. The process often requires higher frequencies and more power.
- Aluminum
- Copper
- Brass
- Titanium
- Graphite
Unsuitable Candidates (Insulators)
These materials are electrical insulators and cannot have currents induced within them. Therefore, they cannot be heated directly by induction.
- Plastics
- Glass
- Ceramics
- Wood
- Textiles
It is possible to heat these materials indirectly by using a conductive susceptor (like a graphite or metal crucible) that is heated by induction and transfers its heat to the non-conductive material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Factors
Simply choosing a conductive material is not enough. The success of an induction process is determined by a combination of factors.
Frequency and Power
The frequency of the alternating current is critical. Higher frequencies are used for surface heating or small parts, while lower frequencies penetrate deeper into the material, which is better for large parts or through-hardening. Heating non-ferrous metals often requires significantly higher frequencies to generate sufficient eddy currents.
Material Resistivity
A common misconception is that higher conductivity is always better. In reality, a material like copper has very low electrical resistance, which can make it harder to heat because the eddy currents flow with little friction. Steel's higher resistivity is actually an advantage, as it creates more heat from the same amount of current (I²R losses).
Coil Design and Coupling
The induction coil's shape and its proximity to the workpiece are paramount. The "coupling distance" determines how efficiently the magnetic field is transferred to the part. A well-designed coil is crucial for an effective and repeatable heating process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your material choice and process parameters are dictated entirely by your end goal.
- If your primary focus is rapid, efficient bulk heating for forging or hardening: Ferrous metals like carbon steel are the superior choice due to the powerful dual-heating effect of hysteresis and eddy currents.
- If your primary focus is brazing or melting non-magnetic metals like copper or aluminum: Plan for a system that uses higher frequencies and has sufficient power to compensate for the absence of hysteresis heating.
- If your primary focus is curing an adhesive on a non-conductive assembly: Direct induction is impossible; you must design the process around indirectly heating a conductive element that transfers thermal energy to your target material.
By understanding these principles of conductivity and magnetism, you can confidently select the ideal material and process for any induction heating challenge.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Key Properties | Heating Mechanism | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Excellent Candidates | High magnetic permeability, good electrical resistivity | Eddy currents & magnetic hysteresis | Carbon steel, stainless steel, cast iron, nickel |
| Good Candidates | High electrical conductivity, non-magnetic | Eddy currents only | Aluminum, copper, brass, titanium, graphite |
| Unsuitable Materials | Electrical insulators | Cannot be heated directly | Plastics, glass, ceramics, wood |
Optimize Your Induction Heating Process with KINTEK
Whether you're working with ferrous metals for rapid hardening or need to braze non-ferrous materials like aluminum, selecting the right equipment is crucial for efficiency and results. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, offering induction heating solutions tailored to your specific material and application needs.
Our experts can help you:
- Choose the right system based on your material's conductivity and magnetic properties.
- Optimize frequency and power settings for maximum efficiency, whether for surface treatments or deep heating.
- Design custom coil configurations to ensure precise, repeatable results for your laboratory or production environment.
Don't let material limitations hinder your process—contact our team today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your induction heating capabilities and drive your projects forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What material is used for making heating element? Choose the Right Alloy for Your Application
- What are the uses of silicon carbide rod? The Ultimate Heating Solution for Extreme Temperatures
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes



















