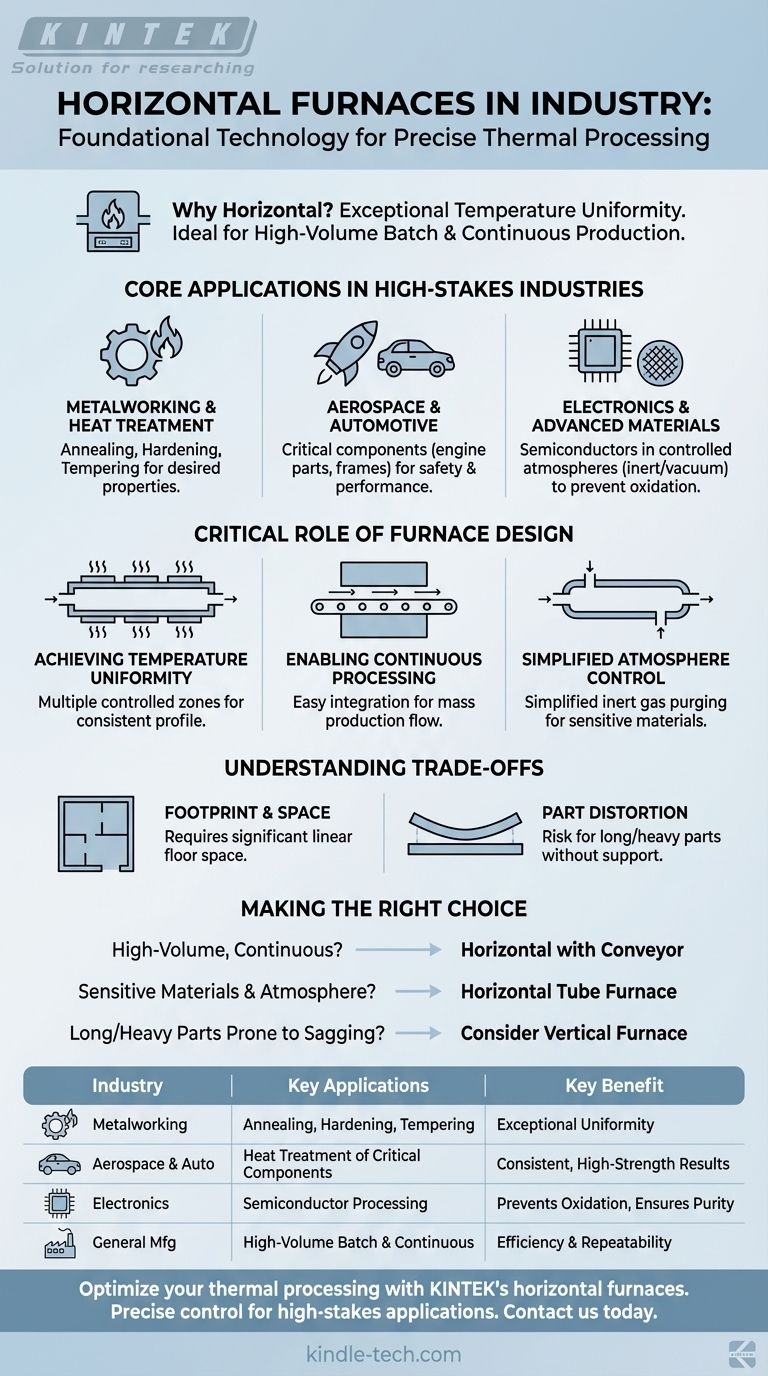
Horizontal furnaces are a foundational technology used extensively in industries where precise thermal processing is non-negotiable. They are primarily found in metalworking, aerospace, automotive, and electronics manufacturing for critical applications like annealing, forging, hardening, and tempering materials under highly controlled conditions.
The core reason horizontal furnaces are so widely adopted is their design, which excels at providing exceptional temperature uniformity over a long, accessible heating zone. This makes them the default choice for high-volume batch processing and continuous production lines where consistency is paramount.
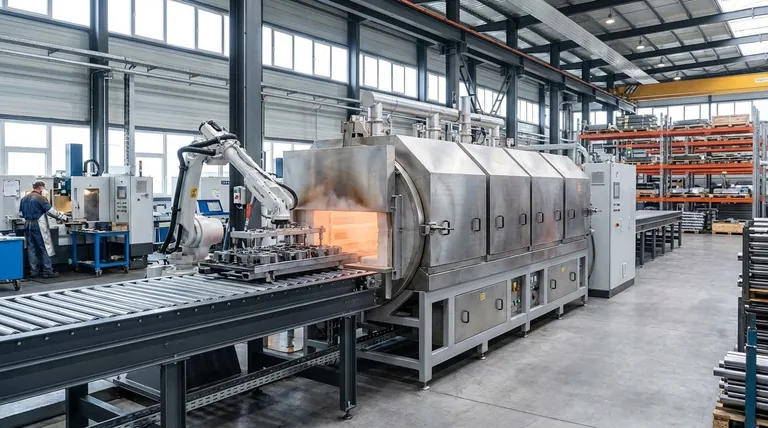

Core Applications in High-Stakes Industries
The reliability of horizontal furnaces makes them indispensable in sectors where material failure is not an option. Their ability to deliver consistent results across large batches is key to their value.
Metalworking and Heat Treatment
Nearly all advanced metal components undergo some form of heat treatment to achieve desired properties like hardness, strength, or ductility.
Horizontal furnaces are used for processes like annealing (softening metal), hardening (increasing strength), and tempering (reducing brittleness). The uniform heating ensures the entire part or batch achieves the exact same metallurgical structure.
Aerospace and Automotive
In these industries, component reliability is a matter of safety and performance. Engine parts, landing gear, and structural frames must withstand extreme stress.
Horizontal furnaces provide the precise thermal cycling required to create these high-strength, fatigue-resistant metal alloys, ensuring every component meets stringent quality standards.
Electronics and Advanced Materials
The manufacturing of semiconductors and other electronic components often requires processing in a highly controlled environment.
Specialized horizontal tube furnaces are used for these applications. They can process small samples or wafers in an inert atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen) or in a vacuum to prevent oxidation and ensure the purity of the final product.
The Critical Role of Furnace Design
The physical layout of a horizontal furnace is not an arbitrary choice. It directly enables the key processes for which it is known.
Achieving Temperature Uniformity
The elongated chamber of a horizontal furnace allows for multiple, independently controlled heating zones.
This design ensures that as a part or a batch of parts sits in or moves through the furnace, it experiences a perfectly consistent and predictable temperature profile from end to end.
Enabling Continuous Processing
The horizontal orientation is naturally suited for integration with conveyor systems.
This allows for a continuous flow of parts through the furnace, making it an ideal solution for mass production environments where efficiency and throughput are critical economic drivers.
Simplified Atmosphere Control
Maintaining a specific atmosphere is often easier in a sealed horizontal tube than in other furnace configurations.
This design makes it simple to purge oxygen and fill the chamber with an inert gas, which is essential for processing sensitive materials that would be damaged by oxidation at high temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, horizontal furnaces are not the universal solution for every thermal process. Understanding their limitations is key to proper application.
Footprint and Space Requirements
By their nature, horizontal furnaces require a significant amount of linear floor space. In facilities where space is at a premium, this can be a major constraint compared to more compact vertical furnace designs.
Potential for Part Distortion
For very long, thin, or heavy parts, gravity can become a factor at high temperatures. Without adequate support along their length, parts can sag or warp inside a horizontal furnace, compromising their final geometry.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use a horizontal furnace should be driven by the specific demands of your material and production goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production: A horizontal furnace integrated with a conveyor system is the industry standard for efficiency and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is processing sensitive materials in a controlled atmosphere: A horizontal tube furnace offers an excellent combination of thermal uniformity and atmospheric integrity.
- If your primary focus is treating very long or heavy parts prone to sagging: You should evaluate whether a vertical furnace, where the part can hang or be supported from the bottom, is a more appropriate choice.
Ultimately, understanding these core design principles allows you to select the right thermal processing tool to ensure process control and final product quality.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Metalworking | Annealing, Hardening, Tempering | Exceptional temperature uniformity |
| Aerospace & Automotive | Heat treatment of critical components | Consistent, high-strength results |
| Electronics | Semiconductor processing in controlled atmospheres | Prevents oxidation, ensures purity |
| General Manufacturing | High-volume batch & continuous processing | Efficiency and repeatability |
Optimize your thermal processing with KINTEK's horizontal furnaces. Whether you're in metalworking, aerospace, or electronics manufacturing, our lab equipment delivers the precise temperature control and uniformity your high-stakes applications demand. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your process efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab



















