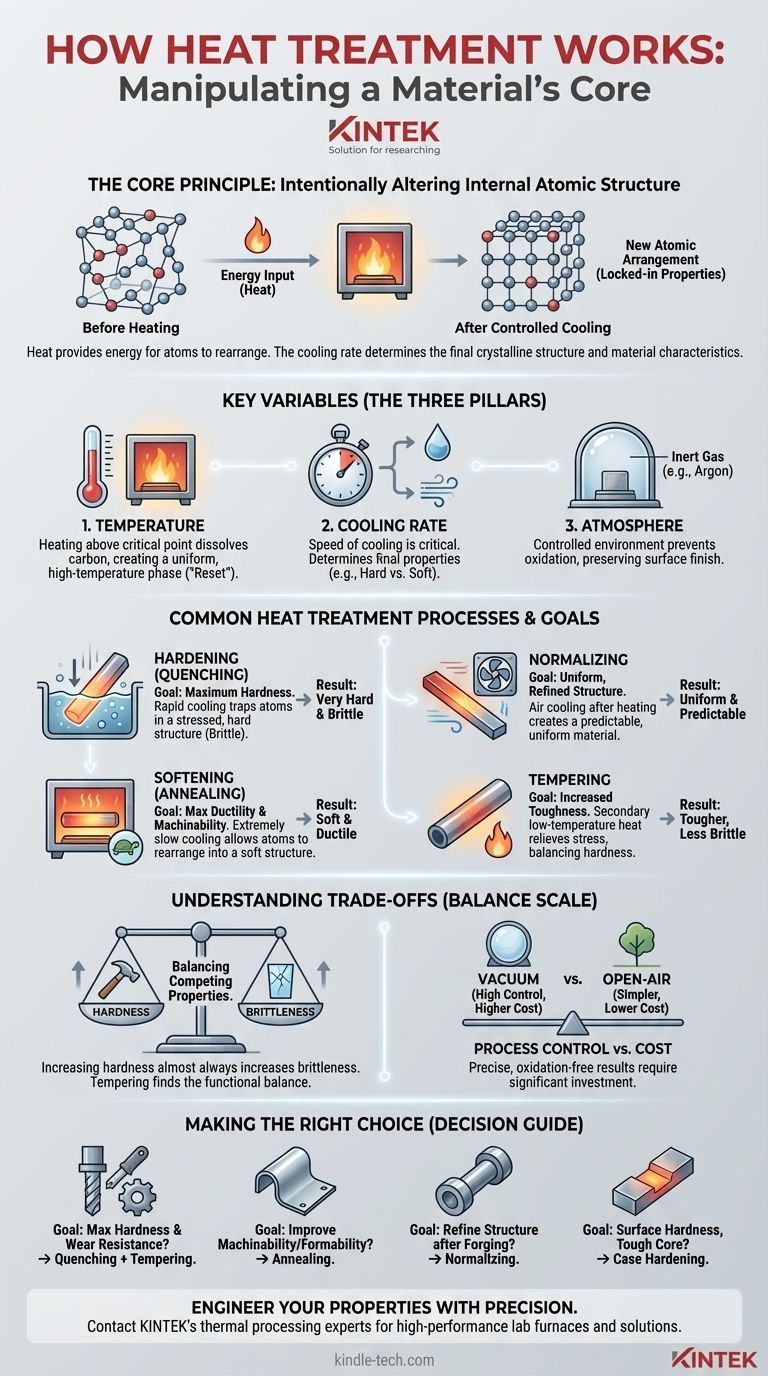
At its core, heat treatment works by using controlled heating and cooling cycles to intentionally alter a material's internal atomic structure. This process is not simply about making a metal hot; it's a precise metallurgical tool used to manipulate the crystalline arrangement of atoms, thereby changing the material's physical and mechanical properties, such as its hardness, toughness, or ductility.
The fundamental principle is that heat provides the energy for atoms within a metal's crystal lattice to move and rearrange, while the rate of cooling determines which new atomic structure gets locked into place, defining the material's final characteristics.

The Core Principle: Manipulating Atomic Structure
Heat treatment is a deliberate modification of a material at the microscopic level. Understanding the "how" requires looking at three key variables: temperature, cooling rate, and atmospheric control.
The Role of Temperature
Heating a material, typically steel, above a critical temperature provides the energy needed to break down its existing crystalline structure. This allows atoms, particularly carbon atoms in steel, to dissolve and distribute more evenly throughout the material.
The material enters a new phase with a different crystal pattern. This high-temperature state acts as a "reset," erasing the effects of previous manufacturing processes and creating a uniform internal structure.
The Importance of Cooling Rate
The speed at which the material is cooled from this high-temperature state is the most critical factor in determining the final properties.
A very fast cooling process, known as quenching, traps the atoms in a stressed, distorted structure. This results in a very hard but also very brittle material.
Conversely, a slow cooling process, such as letting the material cool in still air (normalizing) or inside an insulated furnace (annealing), gives the atoms time to rearrange into a more stable, less stressed structure. This produces a softer, more ductile material.
The Controlled Environment
Modern heat treatment is a highly controlled process. Many procedures are performed in a vacuum furnace where the oxygen is removed and replaced with an inert gas like argon.
This prevents oxidation and scaling on the part's surface, preserving its finish and integrity. Furthermore, the entire cycle is often computer-controlled to ensure the heating and cooling rates are precise, uniform, and repeatable for every part in a batch.
Common Heat Treatment Processes and Their Goals
Different combinations of heating, holding, and cooling achieve different outcomes. The name of the process is shorthand for the goal it is designed to achieve.
Hardening (Quenching)
The goal here is to make the material as hard as possible. This involves heating the steel to a high temperature and then cooling it with extreme speed, often by submerging it in water, oil, or brine.
Softening (Annealing)
Annealing is the opposite of hardening. The material is heated and then cooled extremely slowly, often by leaving it in the furnace to cool over many hours. This relieves internal stresses and makes the material soft, ductile, and easy to machine or form.
Normalizing
Normalizing is often used after a part has been forged or shaped. The material is heated to a higher temperature than in annealing and then cooled in open air. This refines the grain structure, evens out the carbon content, and creates a more uniform and predictable material than one that was simply allowed to cool after being formed.
Tempering
A part that has been hardened by quenching is often too brittle for practical use. Tempering is a secondary, low-temperature heat treatment that slightly reduces the hardness but significantly increases the material's toughness, making it less likely to fracture.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a heat treatment process involves balancing competing properties. It is impossible to maximize all desirable characteristics simultaneously.
Hardness vs. Brittleness
This is the most fundamental trade-off in heat treatment. Increasing a material's hardness almost always increases its brittleness. A file, for instance, is extremely hard to hold an edge but will shatter if dropped. Tempering is the primary method used to find a functional balance between these two properties.
Process Control vs. Cost
A highly controlled process like vacuum heat treatment produces superior, consistent results with no surface oxidation. However, the equipment and operational costs are significant. For less critical applications, a simpler, open-air furnace may be sufficient and more cost-effective.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency
Heat treatment is an energy-intensive process, requiring furnaces to reach temperatures up to 2400°F (1315°C). Modern facilities focus on efficiency by using new insulation materials, optimizing process cycles, and even utilizing the waste heat from one process to pre-heat another, reducing overall energy consumption and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal heat treatment is entirely dependent on the final application of the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: A quenching process, followed by a specific tempering cycle, is the correct path.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability or formability: Annealing is the best choice to make the material as soft and stress-free as possible.
- If your primary focus is refining the structure after forging: Normalizing will create a uniform and reliable material with good strength and toughness.
- If your primary focus is adding surface hardness while keeping the core tough: Case hardening techniques like carburizing are specifically designed for this purpose.
By understanding these core principles, you can move beyond simply following a specification and begin to engineer material properties with purpose and precision.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening (Quenching) | Maximum Hardness | Rapid cooling in water, oil, or brine |
| Softening (Annealing) | Maximum Ductility & Machinability | Extremely slow, controlled cooling |
| Normalizing | Uniform, Refined Structure | Air cooling after heating |
| Tempering | Increased Toughness | Secondary, low-temperature treatment |
Ready to Engineer Your Material's Properties with Precision?
Heat treatment is a precise science, and achieving the perfect balance of hardness, toughness, and durability for your components requires the right equipment and expertise.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and thermal processing solutions for laboratories and manufacturers. Whether you need the controlled environment of a vacuum furnace for oxidation-free results or a robust system for quenching and tempering, we have the technology to meet your specific material goals.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK's equipment can help you achieve superior, repeatable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
People Also Ask
- How does argon and nitrogen cooling compare in vacuum furnaces? A Guide to Faster, Cheaper Quenching
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Hot Zone Materials and Processed Metals
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions
- What is vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Control, Cleanliness, and Quality



















