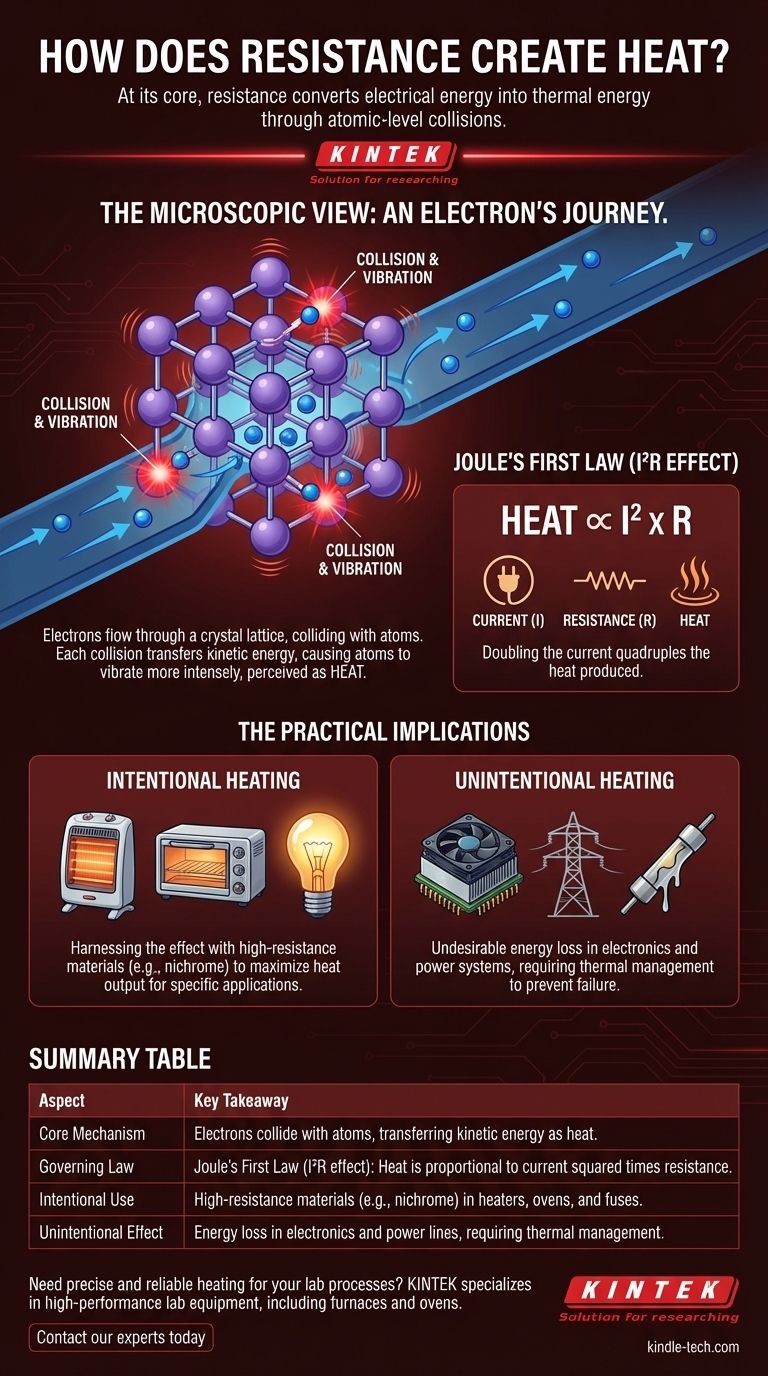
At its core, resistance creates heat by converting electrical energy into thermal energy through atomic-level collisions. As electrons are forced through a material, they collide with the atoms that make up its structure. Each collision transfers kinetic energy from the electron to the atom, causing the atom to vibrate more intensely. This widespread increase in atomic vibration is what we perceive and measure as heat.
The generation of heat from electrical resistance is not a side effect; it is a fundamental energy conversion. Think of it as a form of friction for flowing electrons—the more "friction" (resistance) they encounter, the more of their electrical energy is transformed directly into heat.
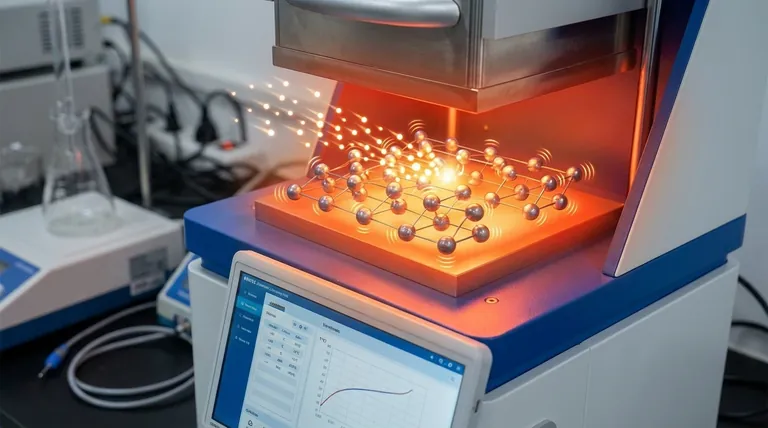

The Microscopic View: An Electron's Journey
To truly understand resistive heating, we must look at what happens inside the conductor as current flows. It's a process governed by interactions at the atomic level.
What is Electric Current?
An electric current is simply the directed flow of charged particles, typically electrons, through a material. A voltage source, like a battery, provides the "push" or electrical pressure to get these electrons moving.
The Nature of Resistance
Electrical resistance is a measure of how much a material opposes the flow of electric current. It's not a "blockage," but rather an inherent property determined by the material's atomic structure.
In a conductor, the atoms are arranged in a crystal lattice. As electrons try to flow through this lattice, they inevitably collide with these atoms and with each other.
The Collision Model: From Motion to Heat
Each collision transfers a small amount of the electron's kinetic energy to the atom it strikes. This energy transfer forces the atom to vibrate more rapidly in its fixed position within the lattice.
When billions of electrons are flowing and colliding, this effect is multiplied across the entire material. The collective increase in atomic vibration raises the material's internal energy, which manifests as a rise in temperature.
Quantifying the Heat: The I²R Effect
This phenomenon is formally described by Joule's First Law. The heat generated (power dissipated as heat) is directly proportional to the square of the current (I) multiplied by the resistance (R) of the material.
This is often called the I²R effect. It shows that current has a much greater impact on heat generation than resistance does. Doubling the current through a fixed resistor quadruples the amount of heat produced.
The Practical Implications of Resistive Heating
This energy conversion is a double-edged sword in engineering. It can be a highly useful tool or a significant source of waste and failure, depending entirely on the application.
Intentional Heating: Harnessing the Effect
Many technologies are designed specifically to use this principle. Materials with high electrical resistance, like nichrome wire, are chosen to maximize heat output for a given current.
Applications include electric space heaters, toaster ovens, incandescent light bulbs (where the filament gets so hot it glows), and electronic fuses that melt to break a circuit when current is too high.
Unintentional Heating: A Source of Inefficiency
In most electronic circuits and power transmission systems, resistive heating is an undesirable energy loss. The goal is to move electrical energy from one point to another with minimal waste.
The heat generated in power lines or inside a computer's CPU represents energy that is not being used for its intended purpose. This waste heat must be managed with fans or heat sinks to prevent components from overheating and failing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this principle allows you to select materials and design systems based on your specific objective, whether it's to generate heat or to avoid it.
- If your primary focus is generating heat: Choose materials with high intrinsic resistance and design the circuit to handle the required current safely.
- If your primary focus is minimizing energy loss: Use conductors with the lowest possible resistance (like copper or gold) and keep conductor lengths as short as possible.
Ultimately, mastering the flow of electricity means mastering the management of its conversion into heat.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Electrons collide with atoms, transferring kinetic energy as heat. |
| Governing Law | Joule's First Law (I²R effect): Heat is proportional to current squared times resistance. |
| Intentional Use | High-resistance materials (e.g., nichrome) in heaters, ovens, and fuses. |
| Unintentional Effect | Energy loss in electronics and power lines, requiring thermal management. |
Need precise and reliable heating for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including furnaces and ovens that expertly utilize resistive heating for consistent, controlled results. Let our solutions enhance your research efficiency and accuracy. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory hot press necessary for the production of plastic crystal polymer electrolyte reinforced membranes?
- How is pressure generated and applied in a hot press? Master High-Intensity Hydraulic & Pneumatic Systems
- Why is a laboratory precision hot press necessary for processing high-performance composite solid-state electrolyte membranes?
- What are the advantages of hot pressing for PEO electrolytes? Achieve superior density and solvent-free performance.
- How does a laboratory hot press improve the microscopic structure of polymer-ceramic composite cathodes? | KINTEK



















