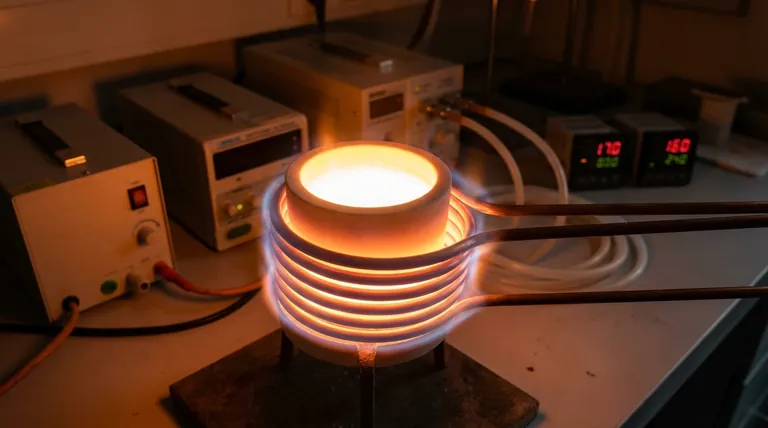
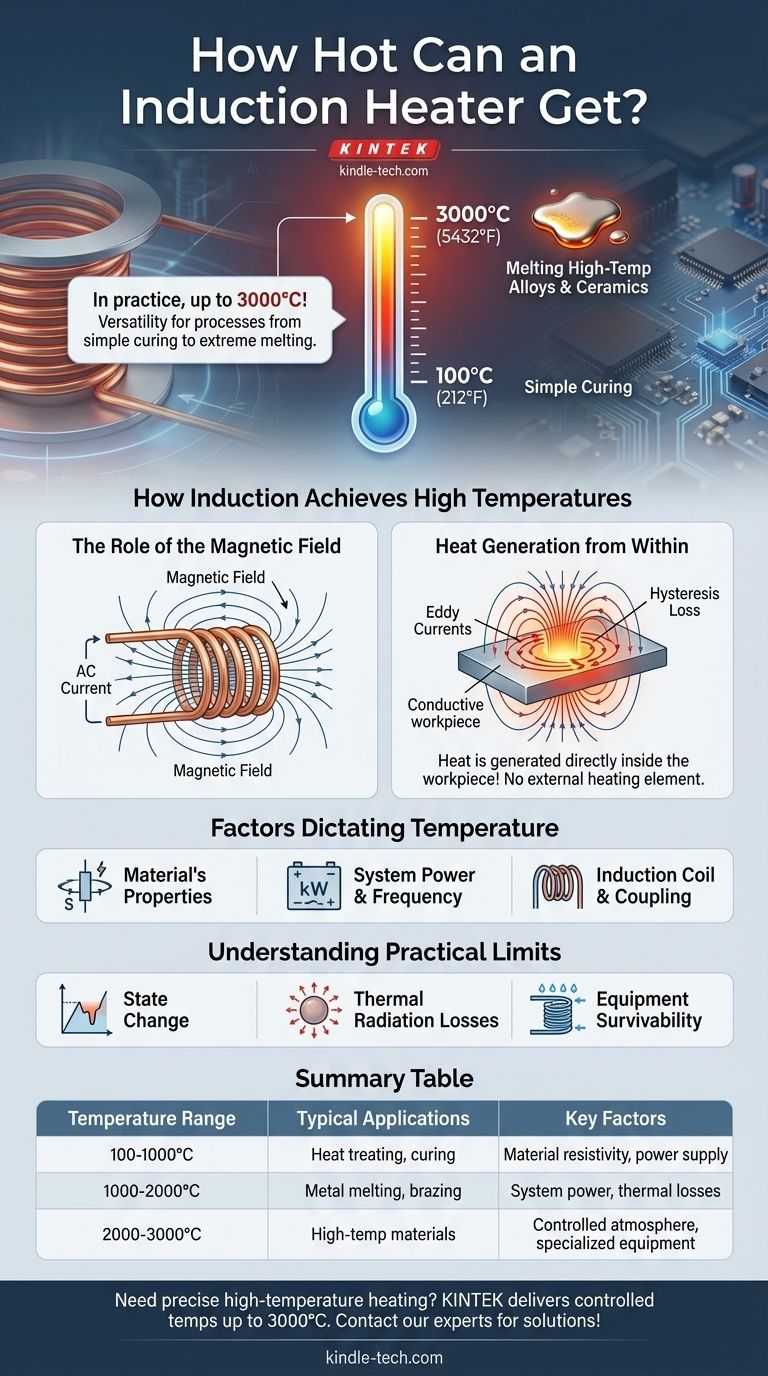
In practice, an induction heater can achieve temperatures as high as 3000°C (5432°F). This wide operational range, from as low as 100°C (212°F), allows it to handle processes from simple curing to the melting of high-temperature alloys and ceramics. The technology's versatility also extends to time, enabling processes that last for months or for less than half a second.
The maximum temperature an induction heater can achieve is not a fixed limit of the heater itself. Instead, it is determined by the properties of the material being heated, the efficiency of the system, and the point at which the material melts, vaporizes, or loses heat to the environment as fast as it gains it.

How Induction Achieves High Temperatures
To understand the temperature limits, you must first understand that induction is not a conventional heat source. Unlike a furnace or flame, an induction heater does not get hot and then transfer that heat to the part.
The Role of the Magnetic Field
An induction heating system uses an alternating electric current flowing through a copper coil. This generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil.
Heat Generation from Within
When a conductive material (like a metal workpiece) is placed within this field, two phenomena occur. Eddy currents, which are internal electrical currents, are induced within the part. The material's natural resistance to these currents generates precise, internal friction and thus, intense heat. In magnetic materials, a secondary effect called hysteresis loss also contributes to the heating.
A Fundamentally Different Approach
This method generates heat directly inside the workpiece. There is no external heating element, which means the theoretical temperature is not limited by the melting point of a furnace component. The part itself becomes the source of the heat.
The Factors That Dictate Temperature
The final temperature of a workpiece is a dynamic balance between the energy being delivered by the induction system and the energy being lost to the surrounding environment.
The Material's Properties
The composition of the workpiece is the single most important factor. Materials with high electrical resistivity heat up more quickly. The magnetic properties of a metal (its permeability) also dramatically increase the efficiency of the heating process below a certain temperature, known as the Curie point.
The System's Power and Frequency
A power supply with a higher kilowatt (kW) rating can deliver more energy per second, resulting in a faster rate of temperature increase. The operating frequency of the system is also tuned to the material's properties and the desired heating depth to maximize energy transfer.
The Induction Coil and Coupling
The design of the induction coil and its proximity to the workpiece (known as coupling) are critical. A coil that is closely coupled to the part transfers energy far more efficiently, enabling higher temperatures to be reached more quickly.
Understanding the Practical Limits
While the theory allows for extremely high temperatures, real-world applications are governed by several practical constraints.
The Material's State Change
The most obvious limit is the melting or vaporization point of the material being heated. You cannot heat a piece of aluminum in open air much beyond its melting point of 660°C (1220°F) and expect it to remain a solid object. The 3000°C figure applies to materials with extremely high melting points, such as graphite or tungsten, often within a vacuum or controlled atmosphere.
Thermal Radiation Losses
As an object gets hotter, it radiates heat away into the environment at an exponentially increasing rate. At a certain point, the object will lose heat as fast as the induction system can deliver it. Overcoming this thermal equilibrium to reach higher temperatures requires a significant increase in power.
Equipment Survivability
While the workpiece gets hot, the induction coil must remain cool. High-power induction systems use water-cooled copper coils to prevent them from overheating and melting themselves. The power supply components also have thermal limits that dictate their maximum continuous output.
Matching the Technology to Your Goal
The right question is not "how hot can it get," but "can induction deliver the right amount of energy to the right place for my specific application?"
- If your primary focus is precision heat treating: Induction is ideal, as the final temperature is a highly repeatable function of power, frequency, and time.
- If your primary focus is melting metals: Success depends on having a power supply with enough kilowatts to overcome the material's melting point and subsequent thermal losses.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature material science: Induction is one of the few methods capable of reaching 2000-3000°C in controlled atmospheres, but this requires specialized equipment.
Ultimately, the power of induction heating lies in its precise, rapid, and controlled delivery of energy directly into a material.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Typical Applications | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| 100-1000°C | Heat treating, curing | Material resistivity, power supply |
| 1000-2000°C | Metal melting, brazing | System power, thermal losses |
| 2000-3000°C | High-temperature materials | Controlled atmosphere, specialized equipment |
Need precise high-temperature heating solutions for your laboratory or production process? KINTEK specializes in advanced induction heating systems that deliver controlled temperatures up to 3000°C for materials research, metal processing, and specialized industrial applications. Our experts will help you select the right equipment based on your material properties, temperature requirements, and process goals. Contact our heating specialists today to discuss how our induction technology can enhance your thermal processing capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis



















