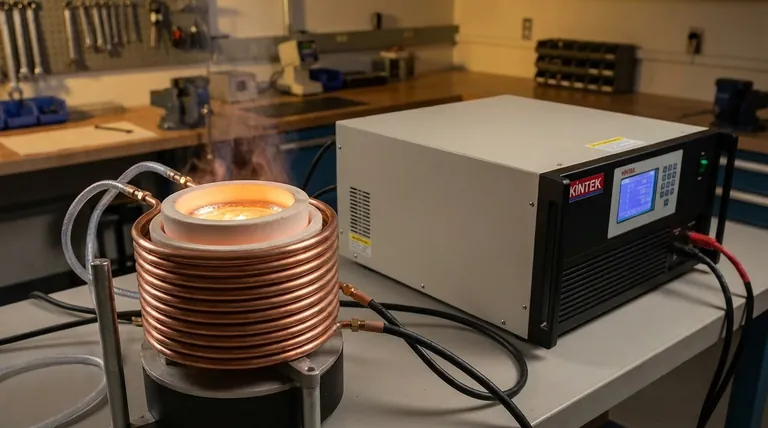
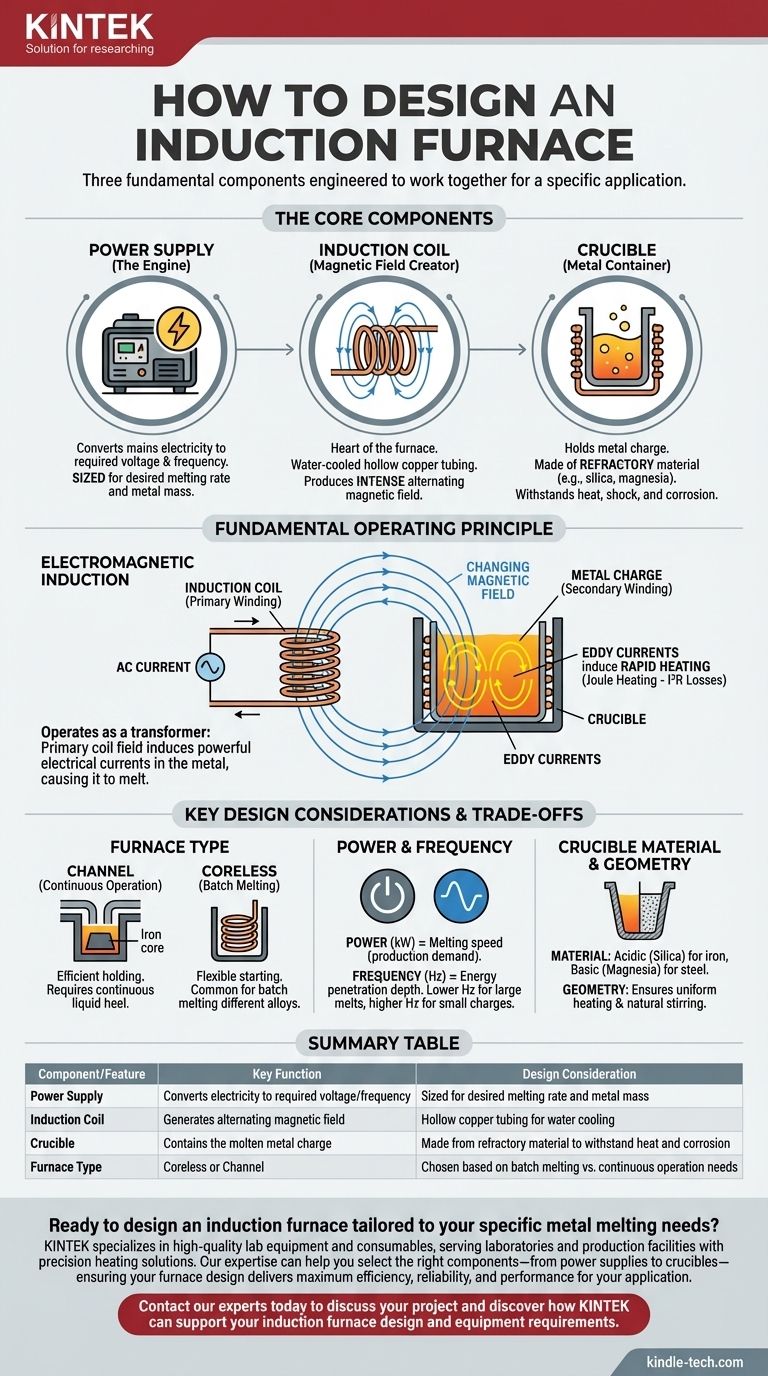
Designing an induction furnace is a process centered on three fundamental components: a power supply to provide the necessary electrical energy, an induction coil to generate a powerful alternating magnetic field, and a refractory crucible to safely contain the metal being melted. The effectiveness of the final design hinges on how these elements are engineered to work together for a specific application.
The key to designing an effective induction furnace is to view it not as a simple container for heat, but as a carefully engineered transformer. The design choices for the coil, power supply, and crucible all serve one goal: to efficiently transfer electromagnetic energy into the metal charge, which acts as the transformer's secondary coil.

The Core Components of an Induction Furnace
Every induction furnace design begins with an understanding of its three primary systems. Each must be specified according to the intended use.
The Power Supply: The Engine of the Furnace
The power supply converts mains electricity into the voltage and frequency required to drive the induction coil. Its capacity is a primary design consideration.
Sizing the power supply directly relates to the desired melting rate and the mass of the metal. As noted in the references, some applications require very high power for rapid melting, while others may only need moderate power for holding metal at temperature.
The Induction Coil: Creating the Magnetic Field
The induction coil is the heart of the furnace. It is typically a helix of hollow copper tubing through which cooling water flows.
When energized by the power supply, this coil produces an intense and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space enclosed by the crucible.
The Crucible: Containing the Molten Metal
The crucible is the vessel that holds the metal charge. It sits inside the induction coil but does not touch it.
This component must be constructed from a refractory material. This means it must be a poor electrical conductor to avoid heating up itself and must be able to withstand extreme thermal shock and the corrosive action of molten metal.
The Fundamental Operating Principle: Electromagnetic Induction
The genius of an induction furnace is its ability to heat the metal directly without any external flame or heating element. This is achieved by applying the principles of a transformer.
Functioning as a Transformer
The system is designed as a simple air-core transformer. The furnace's induction coil acts as the primary winding.
The metal charge placed inside the crucible acts as a single-turn secondary winding. The magnetic field created by the primary coil passes through the metal, completing the transformer circuit.
Generating Heat via Eddy Currents
Because the power supply delivers an alternating current (AC) to the coil, the magnetic field it produces is constantly changing.
This changing magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, to flow within the metal charge itself. The metal's natural electrical resistance causes it to heat up rapidly and melt as these intense currents circulate within it—a principle known as Joule heating (I²R losses).
Key Design Considerations and Trade-offs
Beyond the basic components, a robust design requires making critical choices about the furnace's architecture and operating parameters.
Furnace Type: Channel vs. Coreless
The references describe a channel induction furnace, which includes an iron core to concentrate the magnetic field into a specific "channel" of molten metal. This design is highly efficient for holding large amounts of metal at temperature but requires a continuous liquid heel to operate.
The alternative is a coreless induction furnace, which consists only of the coil and crucible. This design is more flexible for starting from a cold solid charge and is common for batch melting of different alloys.
Power and Frequency Selection
The power rating (in kilowatts) determines how quickly you can melt a given amount of metal. This must be matched to production demand.
The operating frequency (in hertz) is just as critical. Lower frequencies penetrate deeper into the metal charge, making them ideal for large-diameter melts. Higher frequencies generate heat closer to the surface and are better for smaller charges.
Crucible Material and Geometry
The choice of refractory material for the crucible is dictated by the type of metal being melted. An acidic refractory like silica is used for iron, while a basic refractory like magnesia is needed for steel to prevent unwanted chemical reactions.
The crucible's shape and size must be designed to couple efficiently with the magnetic field produced by the coil, ensuring uniform heating and promoting a natural stirring action in the molten bath.
Matching the Design to the Application
The optimal design is always the one that best serves a specific operational goal. Consider your primary objective when making key decisions.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, continuous operation or holding: A channel-type furnace is often the most energy-efficient choice due to its excellent thermal and electrical efficiency.
- If your primary focus is batch melting of various alloys: A coreless induction furnace provides greater operational flexibility and is easier to completely empty and clean between different metal types.
- If your primary focus is maximizing efficiency: Carefully match the power supply's frequency to the size of the material being melted to control the depth of energy penetration and minimize heat loss.
Ultimately, a successful induction furnace design is a precise balance between electrical principles, material science, and the specific production demands of the application.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Design Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Power Supply | Converts electricity to required voltage/frequency | Sized for desired melting rate and metal mass |
| Induction Coil | Generates alternating magnetic field | Hollow copper tubing for water cooling |
| Crucible | Contains the molten metal charge | Made from refractory material to withstand heat and corrosion |
| Furnace Type | Coreless or Channel | Chosen based on batch melting vs. continuous operation needs |
Ready to design an induction furnace tailored to your specific metal melting needs?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories and production facilities with precision heating solutions. Our expertise can help you select the right components—from power supplies to crucibles—ensuring your furnace design delivers maximum efficiency, reliability, and performance for your application.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can support your induction furnace design and equipment requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the working frequency of an induction furnace? Choosing the Right Frequency for Your Application
- What is the power consumption for melting light aluminum scrap? Optimize Your Energy Efficiency and Costs
- What metals can be melted in an induction furnace? Unlock the Power to Melt Virtually Any Metal
- What is high frequency induction heating? Master Precision Surface Hardening & Brazing
- What metal is best for induction heating? Unlock Rapid, Efficient Heat with Ferromagnetic Metals
- What technical advantages does a vacuum induction melting furnace offer? Achieve High-Purity Steel Composites
- What is the function of the electric arc vacuum chamber in the ITT process? Single-Step Titanium Powder Production
- What is frequency in induction hardening? Mastering Case Depth Control for Precision Parts



















