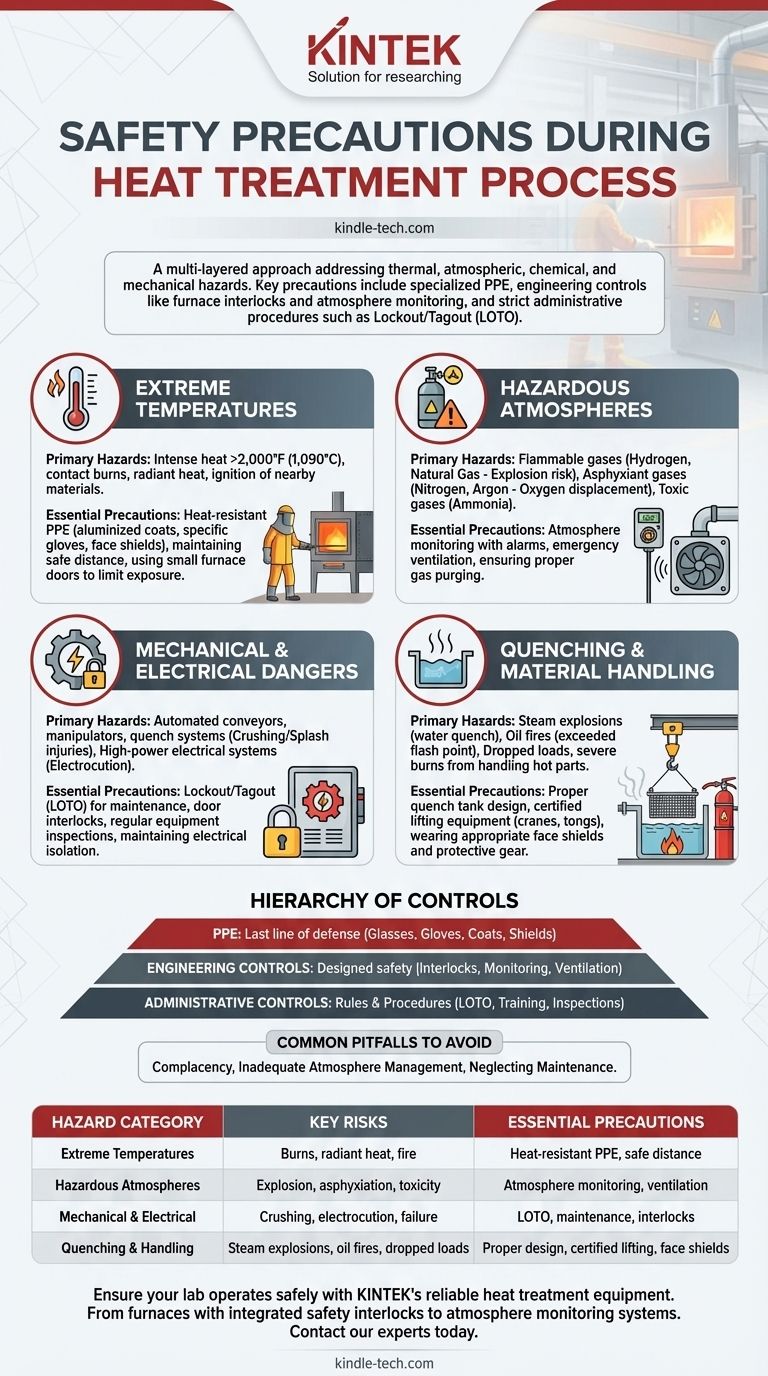
In short, safety during heat treatment requires a multi-layered approach that addresses thermal, atmospheric, chemical, and mechanical hazards. Key precautions include using specialized Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), implementing engineering controls like furnace interlocks and atmosphere monitoring, and adhering to strict administrative procedures such as Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) for maintenance.
Heat treatment safety is not merely about avoiding burns. It is a comprehensive discipline focused on controlling extreme temperatures, managing potentially explosive or toxic atmospheres, and ensuring the mechanical and electrical integrity of all equipment.
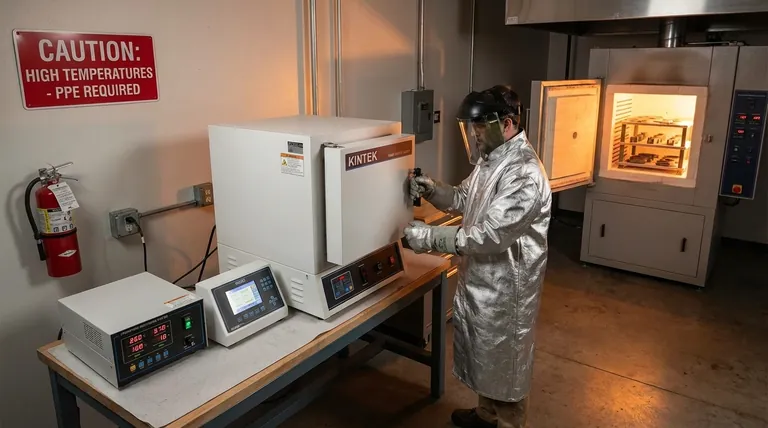

The Primary Hazards: A Multi-Faceted Risk Profile
Understanding the full spectrum of risks is the first step toward creating a safe environment. Heat treatment operations present dangers that go far beyond the obvious high temperatures.
Extreme Temperatures
The most apparent hazard is the intense heat generated by furnaces, which can exceed 2,000°F (1,090°C). This creates risks of severe contact burns, radiant heat exposure, and potential ignition of nearby combustible materials.
Hazardous Atmospheres
Many heat treatment processes require specific atmospheres to achieve the desired metallurgical properties. These atmospheres introduce significant, often invisible, dangers.
Gases like hydrogen and natural gas are highly flammable and can create explosive mixtures. Inert gases like nitrogen and argon, while not flammable, displace oxygen and pose a severe asphyxiation risk in confined or poorly ventilated spaces. Processes like nitriding use ammonia, which is both toxic and flammable.
Mechanical and Electrical Dangers
Furnaces are complex industrial machines. Dangers include automated conveyors, manipulators, and quench systems that can cause crushing or splash injuries. Furthermore, the high-power electrical systems for heating elements or induction coils present a constant risk of electrocution if not properly maintained and isolated.
Quenching and Material Handling
The quenching stage, where a hot part is rapidly cooled in a liquid like oil or water, can be violent. Water quenching can cause steam explosions, while oil quenching carries a significant fire risk if the oil's flash point is exceeded. Handling hot, heavy parts with cranes or tongs also presents a risk of dropped loads and severe burns.
Essential Safety Protocols and Controls
A robust safety program relies on a hierarchy of controls, from equipment design down to individual actions.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is Non-Negotiable
PPE is the last line of defense for an operator. Standard issue includes safety glasses with side shields, but task-specific gear is critical. This often includes aluminized coats to reflect radiant heat, heat-resistant gloves rated for the specific temperatures, and face shields to protect against splashes and heat.
Engineering Controls: Designing Safety In
The safest systems are designed to minimize hazard exposure. Furnace doors are kept small not only for thermal efficiency but also to limit operator exposure to radiant heat and hazardous atmospheres.
Crucial engineering controls include door interlocks that shut down heating elements when opened, emergency ventilation systems, and calibrated atmosphere monitoring systems with alarms for flammable gases, toxic gases, or low oxygen levels.
Administrative Controls: Safe Work Practices
These are the rules and procedures that govern how work is performed. The most critical is the Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) procedure, which ensures equipment is de-energized and cannot be started during maintenance. Other vital practices include regular equipment inspections, formal training on all procedures, and clear protocols for emergency response.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Even with the right equipment, human error and complacency can lead to disaster. Recognizing these common failure points is critical for maintaining a safe operation.
The Complacency of Experience
Long-time operators may develop a false sense of security, leading them to bypass safety interlocks or neglect wearing proper PPE for "quick" tasks. This is a leading cause of industrial accidents.
Inadequate Atmosphere Management
Assuming an inert gas is "safe" is a fatal mistake. Without proper ventilation and oxygen monitoring, a nitrogen or argon leak can silently create a deadly, oxygen-deficient environment. Similarly, failure to properly purge flammable atmospheres before opening a furnace can cause an explosion.
Neglecting Equipment Maintenance
A safety program is only as strong as the equipment it governs. Degraded door seals can leak hazardous gases, faulty temperature controllers can lead to overheating and fires, and uninspected hoist chains can fail, dropping hot components.
A Proactive Approach to Heat Treatment Safety
Implementing a successful safety strategy requires matching the right precautions to the specific role and task at hand.
- If you are an operator or technician: Your primary focus must be the diligent, consistent use of all required PPE and strict adherence to established operating procedures without deviation.
- If you are a safety manager or engineer: Prioritize the implementation and regular auditing of robust engineering controls, especially atmosphere monitoring and equipment interlocks, supported by comprehensive training.
- If you are performing maintenance: Never begin work without first applying a rigorous and verified Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) procedure to completely isolate the equipment from all energy sources.
Ultimately, safety in heat treatment is an active, continuous process of risk identification and mitigation, not a passive checklist.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Key Risks | Essential Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Temperatures | Contact burns, radiant heat, fire | Heat-resistant PPE (gloves, coats), safe distance from equipment |
| Hazardous Atmospheres | Explosion (hydrogen), asphyxiation (nitrogen), toxicity (ammonia) | Atmosphere monitoring, ventilation, gas detection alarms |
| Mechanical & Electrical | Crushing, electrocution, equipment failure | Lockout/Tagout (LOTO), regular maintenance, safety interlocks |
| Quenching & Handling | Steam explosions, oil fires, dropped loads | Proper quench tank design, certified lifting equipment, face shields |
Ensure your lab operates safely with KINTEK's reliable heat treatment equipment. From furnaces with integrated safety interlocks to atmosphere monitoring systems, we provide the robust tools and consumables your laboratory needs to mitigate risks and protect your team. Don't compromise on safety—contact our experts today to find the right solution for your specific heat treatment challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between combustion pyrolysis and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies
- What temperature is a ceramic furnace? Mastering the Ranges for Perfect Firing Results
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory vacuum drying oven? Preserve Catalyst Integrity and Nanostructure
- What critical experimental conditions do high-temperature furnaces provide for FeCrAl coatings? Expert Testing Guide
- What is the effect of temperature on sintering? Master the Thermal Profile for Superior Results
- What is the purpose of the specific loading arrangement in a high-temperature furnace during the Exo-Melt process?
- How does a high-temperature heat treatment furnace process zirconium and carbon steel? Optimize Composite Performance
- Why does copper-based porous foil as an interlayer in vacuum diffusion welding result in base-metal strength joints?



















