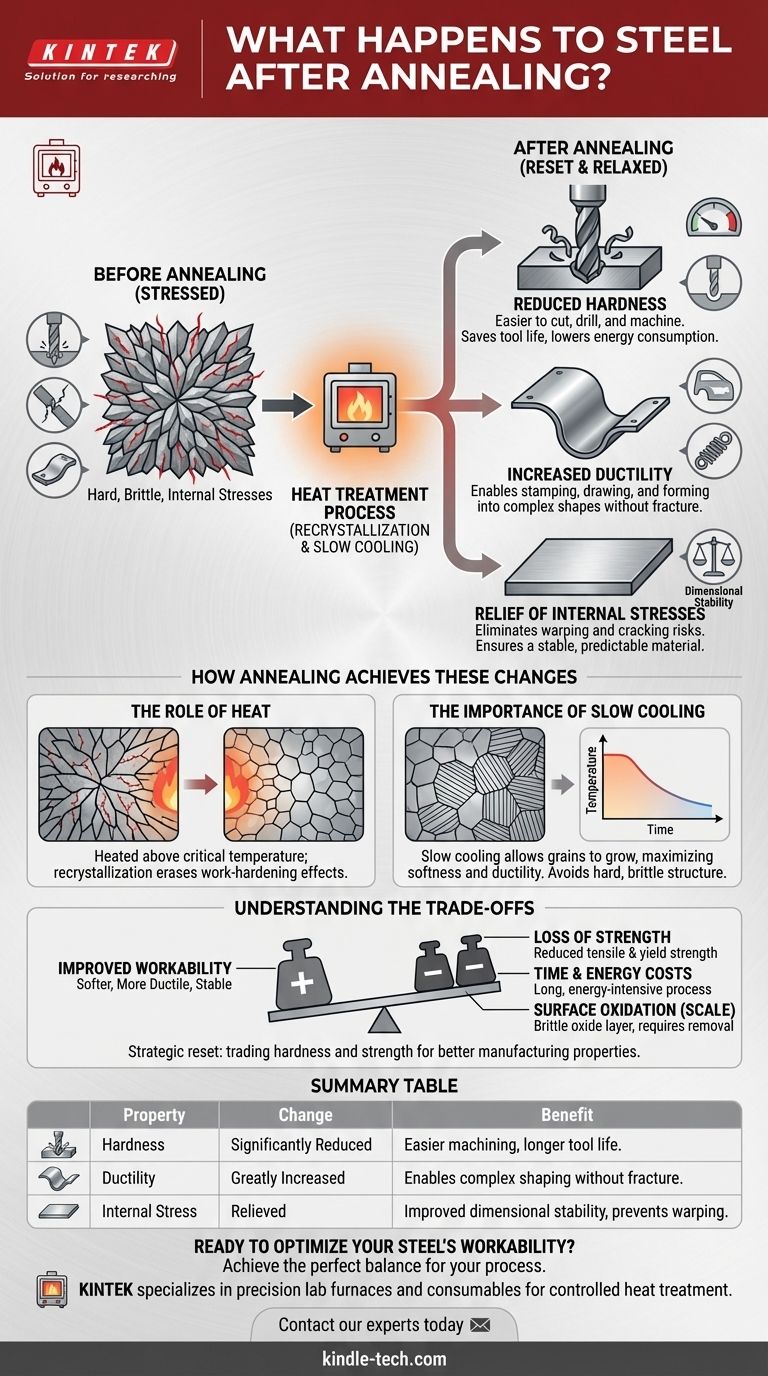
In short, annealing makes steel softer, more ductile, and free from internal stress. This fundamental change is achieved through a controlled heat treatment process that alters the steel's internal microstructure, making it significantly easier to shape, machine, or weld in subsequent manufacturing steps.
Annealing is best understood not as a final treatment, but as a strategic reset. It deliberately trades hardness and strength for improved workability and stability, preparing the steel for its next transformation.

The Core Changes in Annealed Steel
Annealing induces three primary changes in steel's mechanical properties, each serving a distinct purpose in manufacturing and engineering.
Reduced Hardness
Hardness is a measure of a material's resistance to localized deformation, such as scratching or indentation.
Annealing significantly reduces the hardness of steel, making it much easier to cut, drill, and machine. This saves tool life, reduces manufacturing time, and lowers energy consumption.
Increased Ductility
Ductility is the ability of a material to deform under tensile stress—essentially, its capacity to be stretched or bent without breaking.
By increasing ductility, annealing allows steel to be stamped, drawn, or formed into complex shapes without fracturing. This property is critical for producing everything from car body panels to kitchen sinks.
Relief of Internal Stresses
Processes like casting, forging, or cold working can introduce significant internal stresses into steel. These hidden stresses can cause the material to warp or crack unexpectedly during machining or over its service life.
Annealing relieves these internal stresses, resulting in a more dimensionally stable and predictable material.
How Annealing Achieves These Changes
The changes in properties are a direct result of modifying the steel's internal grain structure, a process known as recrystallization.
The Role of Heat
When steel is heated above a specific critical temperature, its rigid, stressed crystalline structure begins to break down. New, stress-free grains begin to form and grow, consuming the old, deformed ones.
This process, called recrystallization, effectively erases the effects of prior work-hardening and realigns the microstructure into a more uniform state.
The Importance of Slow Cooling
The cooling phase is just as critical as the heating. In annealing, the steel is cooled very slowly, often by letting it cool down inside the turned-off furnace.
This slow cooling process allows the newly formed grains to grow into a coarse, well-ordered structure (like pearlite) that corresponds to maximum softness and ductility. Rapid cooling, by contrast, would trap the grains in a hard, brittle structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly beneficial, annealing involves a clear exchange of one set of properties for another.
Loss of Strength
The most significant trade-off is a reduction in tensile strength and yield strength. By making the steel softer and more ductile, you inherently make it less strong and less resistant to wear. For many applications, a subsequent heat treatment like hardening and tempering is required to restore strength after manufacturing is complete.
Time and Energy Costs
Annealing is not a quick process. It requires heating material to high temperatures, holding it there for a period, and then allowing it to cool over many hours. This cycle is energy-intensive and can be a bottleneck in high-volume production environments.
Surface Oxidation (Scale)
Heating steel in the presence of air will cause an oxide layer, or "mill scale," to form on the surface. This scale is brittle and typically must be removed through processes like sandblasting or acid pickling before further processing, adding an extra step and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Annealing is a tool used to solve specific manufacturing challenges. You should consider it based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is machinability: Anneal the steel to soften it, which will drastically reduce tool wear and allow for faster cutting speeds.
- If your primary focus is formability: Use annealing to maximize ductility, enabling you to bend, stamp, or draw the material into a desired shape without failure.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability: Anneal the material after heavy forging or cold working to eliminate internal stresses that could cause warping later on.
Ultimately, annealing is a preparatory step that resets steel's properties, making it an ideal canvas for the next stage of manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Property Change | Effect of Annealing | Benefit for Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Significantly Reduced | Easier machining, longer tool life |
| Ductility | Greatly Increased | Enables complex shaping without fracture |
| Internal Stress | Relieved | Improved dimensional stability, prevents warping |
Ready to Optimize Your Steel's Workability?
Achieve the perfect balance of softness, ductility, and stability for your manufacturing process. KINTEK specializes in precision lab furnaces and consumables for controlled heat treatment processes like annealing.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our reliable equipment can help you reset your steel's properties and enhance your production efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of using a laboratory drying oven for Mo-Ti-N catalysts? Protect Your Porous Architecture
- What are the advantages of sintered metal? Achieve Strong, Complex Parts Cost-Effectively
- What is the importance of a laboratory electric constant temperature drying oven? Ensure Accurate Biomass Analysis
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of SLS process? Unlock Complex, Functional Parts
- Why does graphite not melt? Unlocking the Secrets of Its Extreme Heat Resistance
- Why is a high-purity hydrogen environment used during the RMA of zirconium alloy? Achieve Precision Powder Processing
- Is pyrolysis oil same as diesel? Uncover the Critical Differences in Fuel Properties
- Which heat treatment gives highest hardness? Quenching to Form Martensite for Maximum Hardness



















