In short, induction heating is most accurately also known as eddy current heating. This name points directly to the primary physical mechanism responsible for generating the heat. The process also relies on the principle of Joule heating, which describes how electrical currents produce heat as they overcome a material's resistance.
The various names for induction heating all describe the same core process: using a changing magnetic field to generate heat directly within an electrically conductive object, offering a method that is precise, fast, and requires no physical contact.

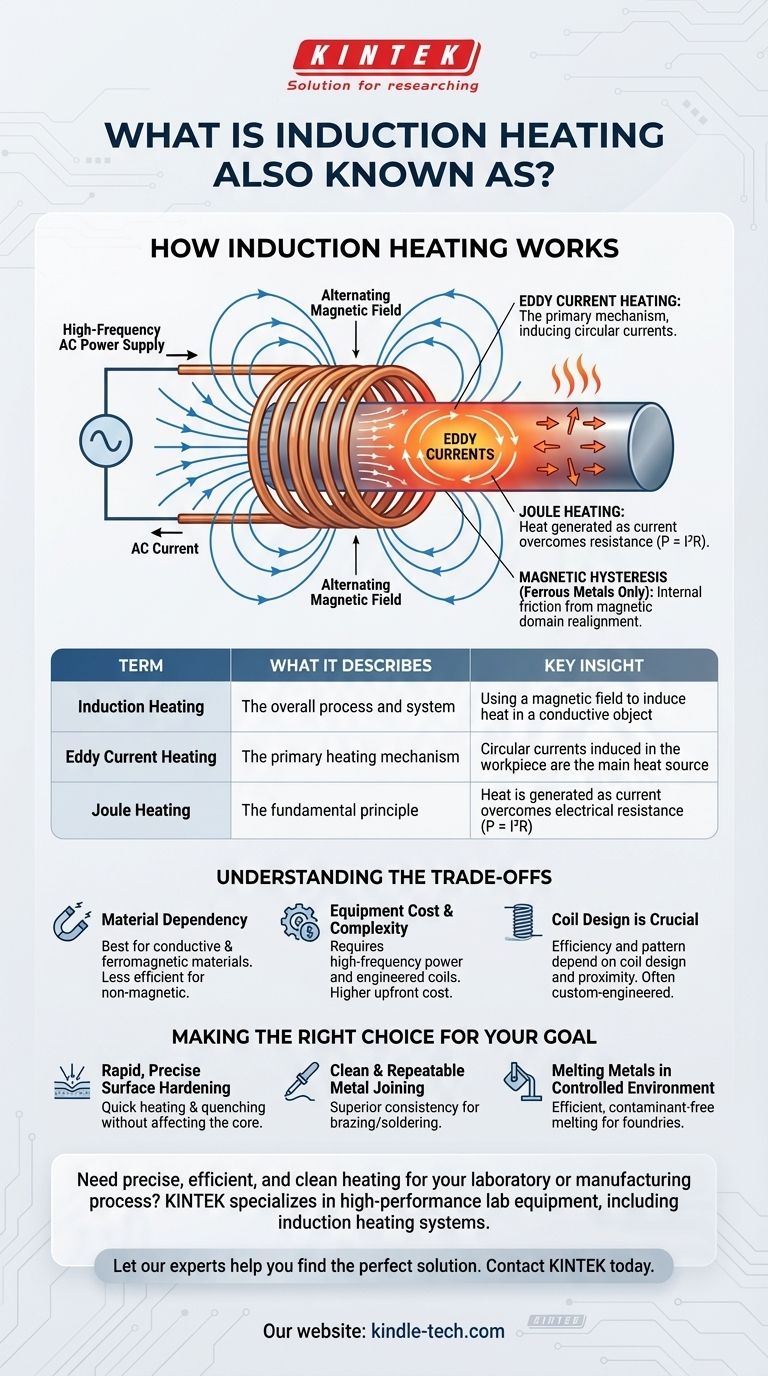
How Induction Heating Actually Works
Understanding the mechanism reveals why the different names are used. The entire process is a direct application of Faraday's Law of Induction and the principles of electrical resistance.
The Alternating Magnetic Field
It all begins with an induction coil, typically made of copper tubing. A high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil. This flow of electricity generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space around and within the coil.
Generating Eddy Currents
When an electrically conductive workpiece (like a piece of steel) is placed within this magnetic field, the field induces circular electric currents inside the metal. These looping currents are known as eddy currents. This is the "induction" part of the name.
The Role of Electrical Resistance (Joule Heating)
Every conductive material has some electrical resistance. As the induced eddy currents flow through the workpiece, they encounter this resistance. This opposition causes friction on an atomic level, which dissipates energy in the form of intense, localized heat. This phenomenon is called Joule heating, described by the formula P = I²R (Power = Current² x Resistance).
Magnetic Hysteresis (For Ferrous Metals)
For magnetic materials like iron and steel, a secondary heating effect occurs. The rapidly alternating magnetic field causes the magnetic domains within the material to rapidly flip their orientation. This constant realignment creates internal friction, which also generates heat. However, this effect, known as hysteresis loss, only occurs below the material's Curie temperature and is a smaller contributor than eddy currents.
Why the Different Names Matter
Each term highlights a different aspect of the same unified process, which can be useful for understanding the physics from different angles.
Induction Heating: The Overall Process
This is the most common and comprehensive term. It describes the entire system and method—using electromagnetic induction to create heat.
Eddy Current Heating: The Primary Mechanism
This name is more specific. It focuses on the fact that the eddy currents induced within the workpiece are the primary source of the thermal energy. For non-magnetic but conductive materials like aluminum or copper, this is virtually the only heating mechanism.
Joule Heating: The Fundamental Principle
This term refers to the universal law of physics that governs why the eddy currents create heat. It's the most fundamental description of the energy conversion taking place, applicable to any situation where current flows through a resistor, not just induction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is governed by specific physical constraints.
Material Dependency
The process is most effective on materials that are both electrically conductive and magnetic (ferromagnetic), like steel and iron. It can work on non-magnetic conductors like aluminum and copper, but it is generally less efficient. It does not work on non-conductive materials like plastics, ceramics, or wood.
Equipment Cost and Complexity
Induction heating systems require a high-frequency power supply and a precisely engineered copper coil. This equipment is more complex and typically has a higher upfront cost than a simple gas forge or resistance furnace.
Coil Design is Crucial
The efficiency and pattern of the heating are entirely dependent on the design of the induction coil and its proximity to the workpiece. Proper coil engineering is essential for achieving the desired result and is often custom-designed for a specific application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the principle behind the name helps you recognize where this technology excels.
- If your primary focus is rapid, precise surface hardening: Induction is the ideal choice because it generates heat on the surface of the part, allowing for quick heating and quenching without affecting the core.
- If your primary focus is clean and repeatable metal joining: For applications like brazing or soldering in manufacturing, the localized and contaminant-free nature of induction heat provides superior consistency over torch methods.
- If your primary focus is melting metals in a controlled environment: Induction furnaces are central to modern foundries for their efficiency and ability to prevent contamination of the melt.
By understanding that induction relies on generating internal eddy currents, you can better identify applications where this precise and efficient heating method offers a decisive advantage.
Summary Table:
| Term | What It Describes | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Induction Heating | The overall process and system | Using a magnetic field to induce heat in a conductive object |
| Eddy Current Heating | The primary heating mechanism | Circular currents induced in the workpiece are the main heat source |
| Joule Heating | The fundamental principle | Heat is generated as current overcomes electrical resistance (P = I²R) |
Need precise, efficient, and clean heating for your laboratory or manufacturing process?
Induction heating, powered by eddy currents, offers unmatched control for applications like surface hardening, brazing, and metal melting. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction heating systems, designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern laboratories and production facilities.
Let our experts help you find the perfect solution. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our technology can enhance your efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is the temperature of PECVD deposition? Achieve High-Quality Films at Low Temperatures
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















