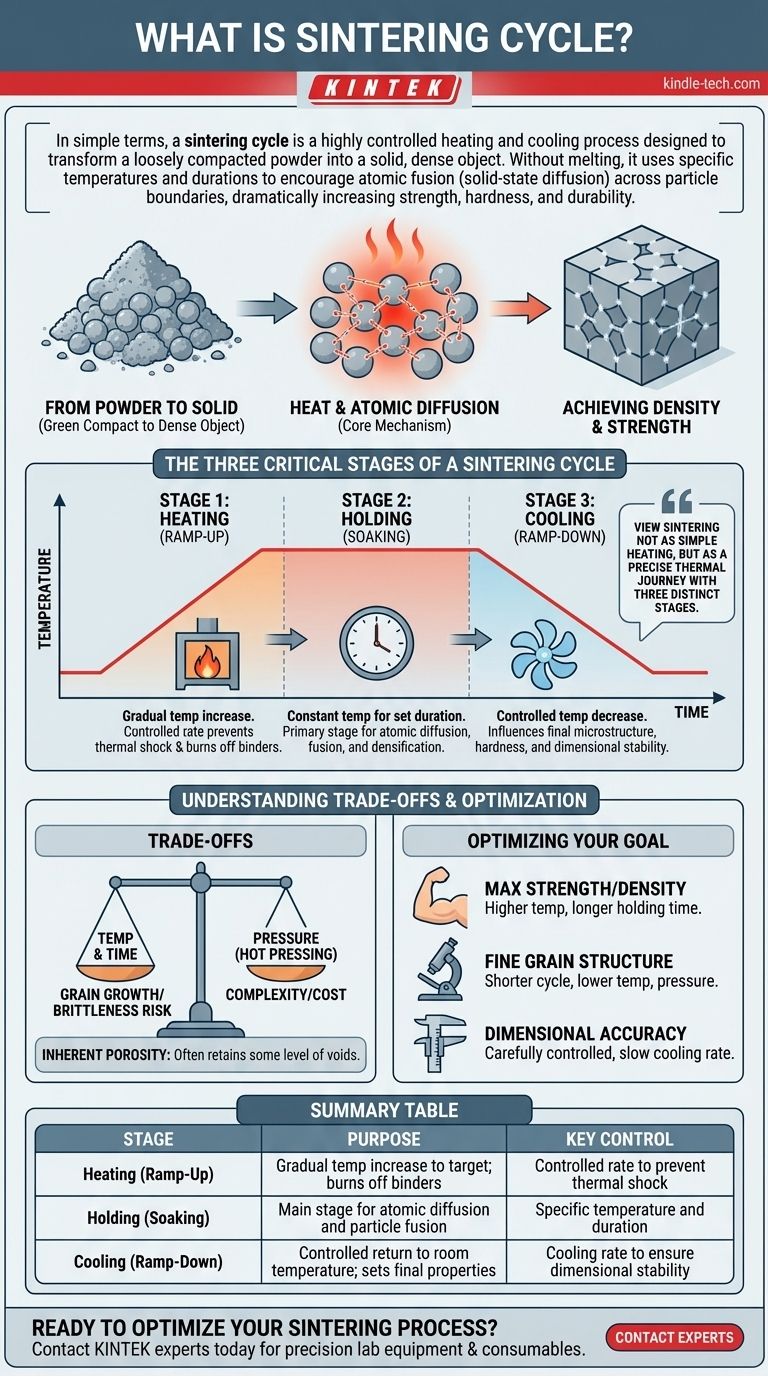
In simple terms, a sintering cycle is a highly controlled heating and cooling process designed to transform a loosely compacted powder into a solid, dense object. Without melting the core material, the cycle uses specific temperatures and durations to encourage atoms to fuse across particle boundaries. This solid-state diffusion welds the particles together, dramatically increasing the material's strength, hardness, and durability.
The critical insight is to view sintering not as simple heating, but as a precise thermal journey with three distinct stages: a controlled ramp-up, a specific hold at temperature, and a carefully managed cool-down. Each stage plays a vital role in fusing the particles and achieving the final, desired material properties.

The Core Mechanism: How Sintering Works
From Powder to Solid
The process begins with a mass of fine particles—typically metal, ceramic, or plastic—that has often been pressed into a desired shape. This initial object is known as a "green compact" and is fragile, with significant empty space, or porosity, between the particles.
The Role of Heat
The sintering cycle introduces thermal energy. This energy doesn't melt the material but excites the atoms, giving them the mobility to move.
Atomic Diffusion
At the high temperatures of the sintering cycle, atoms migrate across the boundaries where individual particles touch. This process, called solid-state diffusion, builds "necks" or bridges between adjacent particles.
Achieving Density and Strength
As these necks grow, they pull the particles closer together, shrinking the voids between them. The entire mass densifies and fuses into a single, coherent piece with mechanical properties vastly superior to the original powder.
The Three Critical Stages of a Sintering Cycle
A successful outcome depends on meticulously controlling each phase of the thermal cycle.
Stage 1: Heating (Ramp-Up)
The furnace temperature is gradually increased to the target sintering temperature. This must be done at a controlled rate to prevent thermal shock, which could crack the part. This stage also serves to cleanly burn off any lubricants or binders used during the initial compaction phase.
Stage 2: Holding (Soaking)
The material is held at a constant, specific sintering temperature for a set duration. During this "soaking" period, the majority of atomic diffusion occurs. This is the primary stage where the particles fuse, porosity decreases, and the part gains its strength and density.
Stage 3: Cooling (Ramp-Down)
Finally, the temperature is slowly and deliberately lowered back to room temperature. The cooling rate is just as critical as the heating rate, as it influences the final microstructure, hardness, and dimensional stability of the finished component.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The effectiveness of a sintering cycle is determined by a balance of competing factors.
Temperature vs. Time
A higher sintering temperature can accelerate diffusion and shorten the required holding time. However, it also increases energy costs and the risk of undesirable grain growth, which can sometimes make a material more brittle.
The Impact of Pressure
Some sintering cycles apply external pressure during heating (a process known as hot pressing). This can achieve higher final densities at lower temperatures but adds significant complexity and cost to the equipment and process.
Inherent Porosity
While sintering dramatically increases density, it rarely eliminates all voids. Most sintered parts retain some level of residual porosity, which must be accounted for in engineering applications. The process is ideal for materials with extremely high melting points, like tungsten and molybdenum, where traditional casting is impractical.
Optimizing the Cycle for Your Goal
The ideal sintering cycle is always tailored to the material and the desired outcome for the final part.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: You will need a cycle with a higher sintering temperature and a longer holding time to maximize atomic diffusion.
- If your primary focus is preserving a fine grain structure: A shorter cycle at a lower temperature, sometimes with applied pressure, is the preferred approach.
- If your primary focus is dimensional accuracy: A carefully controlled, slower cooling rate is paramount to prevent warping and minimize internal stresses.
Mastering the sintering cycle is about precisely balancing time, temperature, and pressure to engineer a material's final properties from the particle level up.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Purpose | Key Control |
|---|---|---|
| Heating (Ramp-Up) | Gradual temperature increase to target; burns off binders | Controlled rate to prevent thermal shock |
| Holding (Soaking) | Main stage for atomic diffusion and particle fusion | Specific temperature and duration |
| Cooling (Ramp-Down) | Controlled return to room temperature; sets final properties | Cooling rate to ensure dimensional stability |
Ready to optimize your sintering process for stronger, more durable parts?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment for sintering applications. Our furnaces and consumables are designed to deliver the exact temperature control and uniformity your materials require. Whether you are working with metals, ceramics, or other powders, we can help you achieve maximum density, strength, and dimensional accuracy.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How is the temperature in a tube furnace measured and controlled? Master Precise Thermal Processing
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance



















