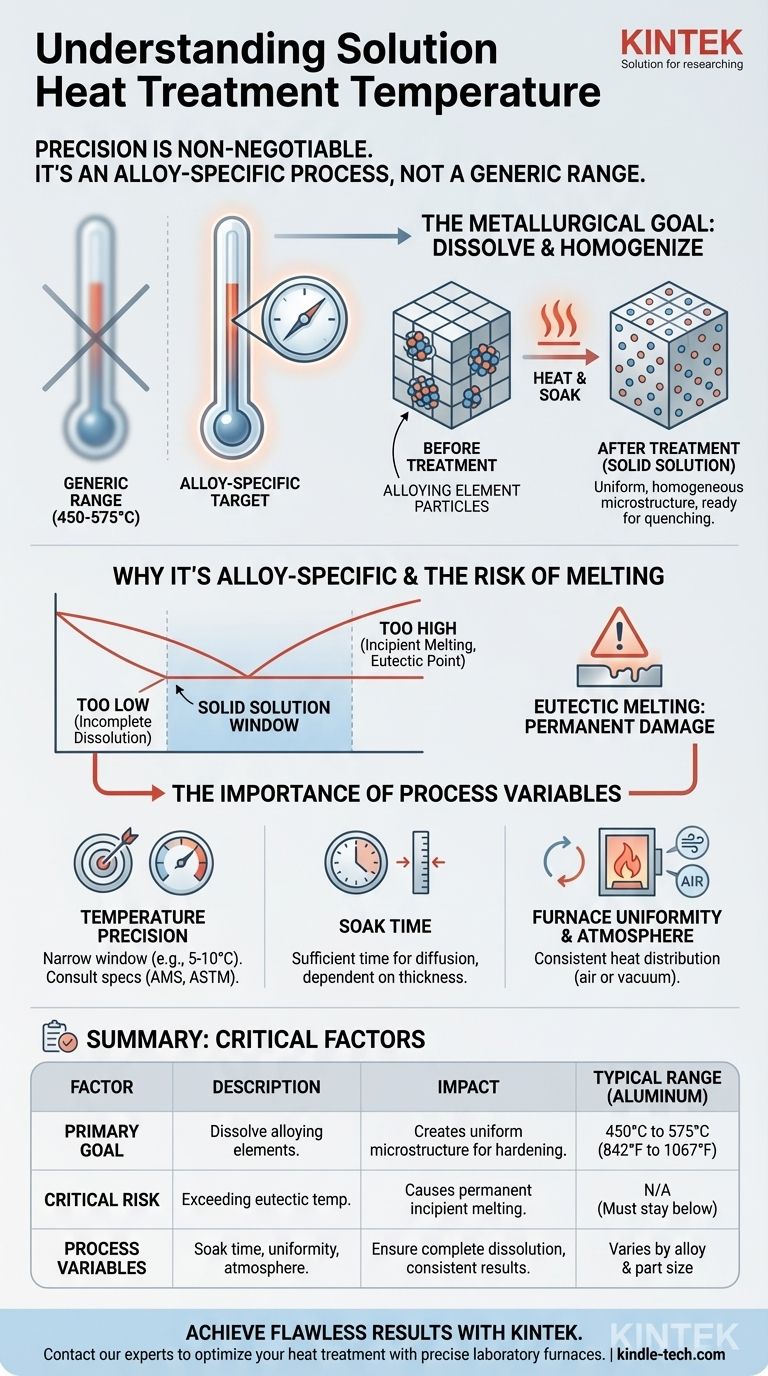
The typical temperature range for solution heat treatment of aluminum alloys is between 450 and 575°C (842 to 1067°F). However, this is not a universal range. The precise temperature is a critical specification that depends entirely on the exact composition of the alloy being treated.
Solution heat treatment isn't about hitting a generic temperature range; it's about reaching a precise temperature, specific to an alloy's composition, that allows alloying elements to dissolve fully into the base metal without melting the material.

The Metallurgical Goal of Solution Treatment
To understand the temperature requirement, you must first understand the purpose of the process. It's the critical first step in a multi-stage process (like age hardening) designed to dramatically increase a metal's strength and hardness.
Dissolving Alloying Elements
At room temperature, the alloying elements within a metal (like copper in aluminum) are often locked in place as separate microscopic particles. The primary goal of solution heat treatment is to heat the metal to a point where these elements dissolve and disperse uniformly into the crystal structure of the base metal, forming a solid solution.
Think of it like dissolving sugar in water. As you heat the water, you can dissolve much more sugar until it's completely uniform.
Creating a Homogeneous Structure
This process creates a consistent, homogeneous microstructure. This uniform state is essential for achieving the desired mechanical properties in subsequent steps. Without a fully dissolved solution, the final strength of the material will be compromised.
Preparing for the Quench
Solution treatment is immediately followed by a rapid cooling process called quenching. This quench freezes the atoms in place, trapping the dissolved alloying elements in the solid solution. This supersaturated state is unstable and is the key to subsequent age hardening.
Why Temperature Is Alloy-Specific
The statement that "the exact temperature required is dependent on the alloy composition" is the most important principle to understand. Using the wrong temperature, even by a small margin, can ruin the component.
The Role of the Phase Diagram
Metallurgists use a phase diagram as a map for each specific alloy. This diagram shows which microstructures (phases) exist at different temperatures. The correct solution treatment temperature is located in a narrow window within a single-phase region, just below the point where melting begins.
The Risk of Eutectic Melting
Every alloy has a eutectic temperature—the lowest temperature at which any part of it will begin to melt. Exceeding this temperature, even for a moment, causes permanent and irreversible damage called incipient melting along the grain boundaries, which severely weakens the material.
The solution treatment temperature must be high enough to dissolve the elements but safely below this critical melting point.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Process Variables
Achieving the desired outcome requires precise control over not just the temperature but the entire process.
Temperature Precision is Non-Negotiable
A temperature that is too low will result in incomplete dissolution of the alloying elements. This means the material will not achieve its full potential strength after subsequent aging.
A temperature that is too high leads to incipient melting, rendering the part useless. For many alloys, the acceptable window between these two points can be as narrow as 5-10°C.
The Importance of Soak Time
The component must be held at the specified temperature for a sufficient duration, known as the soak time. This gives the alloying elements enough time to fully dissolve and diffuse throughout the material. Thicker sections require longer soak times.
Furnace Atmosphere and Uniformity
For aluminum, solution treatment is often done in an air atmosphere furnace. For reactive metals like titanium or certain specialty steels, a vacuum furnace is used to prevent oxidation. Regardless of the type, the furnace must provide excellent temperature uniformity to ensure every part of the component reaches the target temperature.
Determining the Correct Temperature for Your Application
There is no room for guesswork in solution heat treatment. Precision is the primary requirement for success and material safety.
- If your primary focus is processing a known alloy: Always consult the material's governing specification (e.g., AMS, ASTM, or the manufacturer's data sheet). This document will define the precise temperature and time required.
- If your primary focus is material design or process development: You must use the alloy's phase diagram to identify the solid-solution window and engineer a process that stays safely below the eutectic temperature.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting poor mechanical properties: Your first step should be to verify the furnace's calibration, temperature uniformity records, and the actual part temperature logs from the treatment cycle.
Ultimately, successful heat treatment depends on treating the specified temperature not as a guideline, but as a critical engineering requirement.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Range (Aluminum) | 450°C to 575°C (842°F to 1067°F) | Baseline for common alloys |
| Primary Goal | Dissolve alloying elements into a solid solution | Creates a uniform microstructure for subsequent hardening |
| Critical Risk | Exceeding the alloy's eutectic temperature | Causes incipient melting and permanent part failure |
| Process Variables | Soak time, furnace atmosphere, temperature uniformity | Ensure complete dissolution and consistent results |
Achieve flawless material properties with precision heat treatment.
At KINTEK, we understand that the success of your solution heat treatment process hinges on precise temperature control and uniformity. Our specialized lab furnaces are engineered to deliver the exact conditions your specific alloy requires, ensuring complete dissolution of alloying elements without the risk of incipient melting.
Whether you are processing aluminum, titanium, or specialty steels, KINTEK's equipment provides the reliability and accuracy needed for consistent, high-strength results. Don't leave your material's performance to chance.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's laboratory equipment can optimize your heat treatment process and enhance your material outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- Why do you vacuum for heat treatment? Achieve Flawless, High-Performance Metal Components
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- Can I vacuum the inside of my furnace? A Guide to Safe DIY Cleaning vs. Professional Service



















