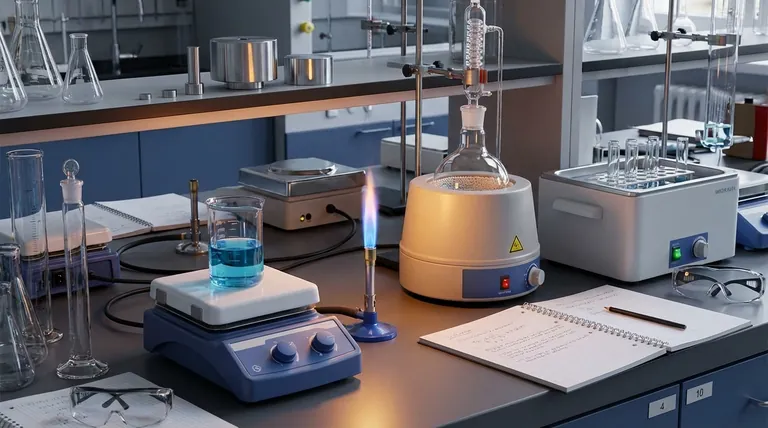
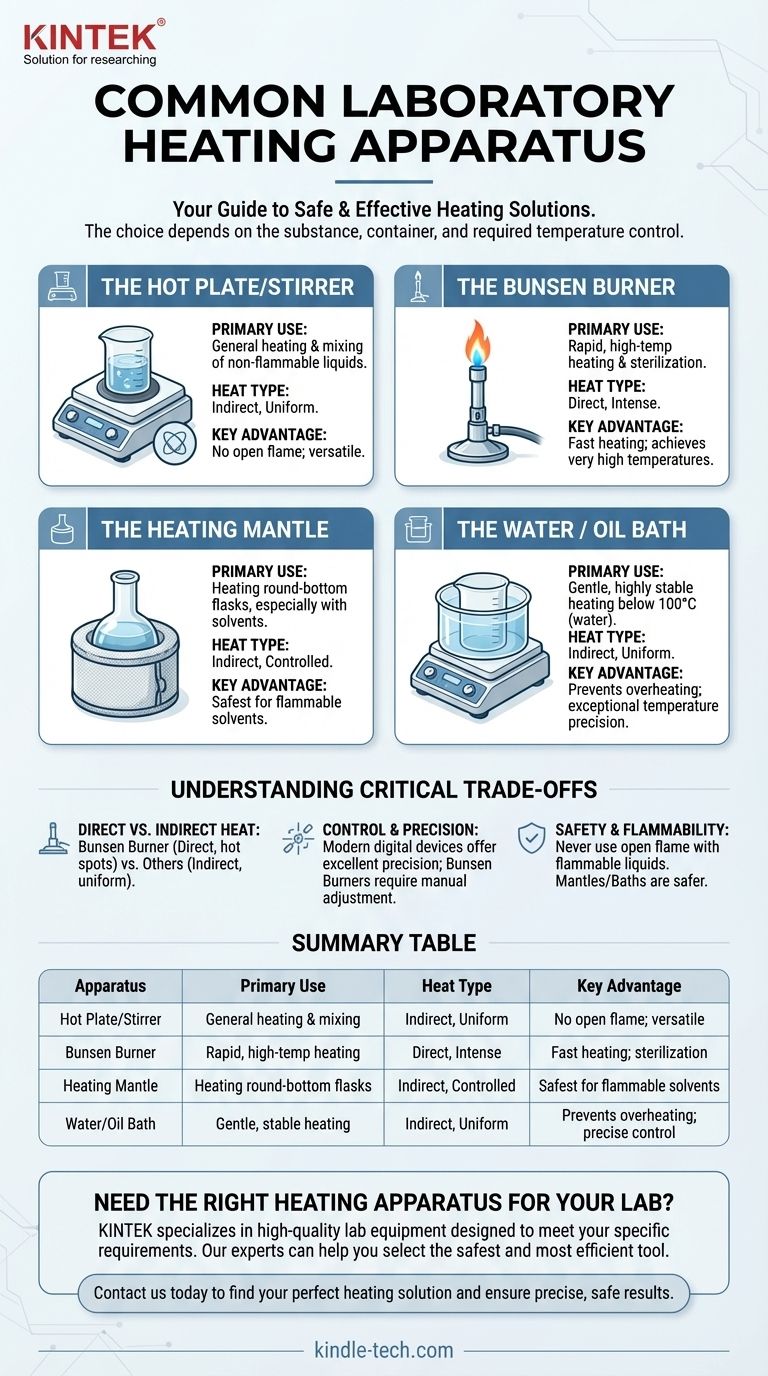
In a typical laboratory setting, the most common heating apparatus includes hot plates, Bunsen burners, heating mantles, and water baths. Each is designed for a specific purpose, trading off between heat intensity, temperature control, and safety. A hot plate, for instance, is frequently used for uniformly heating samples without an open flame, making it a versatile and relatively safe option.
The choice of heating apparatus is not about which is "best," but which is the most appropriate and safe for the specific substance, container, and temperature you require. Understanding the distinction between direct flame heat and indirect, controlled heat is the most critical factor in making the right decision.

A Survey of Common Heating Apparatus
Selecting the correct heating source is a foundational skill for ensuring both the success and safety of an experiment. The primary options each serve a distinct purpose.
The Hot Plate/Stirrer
The hot plate is one of the most ubiquitous pieces of lab equipment. It provides uniform, indirect heat from its flat surface, which can be made of ceramic, enamel, or aluminum.
Many models also include a magnetic stirring function, making them ideal for heating and mixing solutions in beakers or flasks simultaneously. Their key advantage is the absence of an open flame.
The Bunsen Burner
The Bunsen burner is the classic symbol of a chemistry lab. It provides an open flame, offering rapid and intense direct heat.
This makes it suitable for tasks like sterilizing equipment, performing specific chemical tests that require a flame, or achieving very high temperatures quickly. However, it offers less precise temperature control.
The Heating Mantle
A heating mantle is specifically designed to heat round-bottom flasks, which are common in organic chemistry. It's a "basket" that the flask sits inside.
The mantle provides extremely uniform, controlled heat across the bottom surface of the flask. It is a much safer alternative to a Bunsen burner when working with flammable organic solvents.
The Water or Oil Bath
For applications requiring gentle and highly stable temperatures, a water bath or oil bath is used. A container of water or oil is heated on a hot plate, and the experimental vessel is then placed into the heated liquid.
This method prevents overheating and provides exceptionally uniform temperature distribution, which is critical for many biological and chemical reactions that are sensitive to temperature fluctuations.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
The primary differences between these tools come down to safety, control, and the nature of the heat they provide. Making a mistake here can ruin an experiment or create a significant safety hazard.
Direct vs. Indirect Heat
A Bunsen burner provides direct heat, concentrating a flame on one spot. This can create "hot spots," causing bumping or uneven boiling and potentially cracking glassware.
Hot plates, mantles, and water baths provide indirect heat. The energy is distributed over a larger surface area, resulting in more uniform and gentle heating of the entire sample.
Temperature Control and Precision
Modern digital hot plates and heating mantles offer excellent temperature precision. You can often set a target temperature that the device will automatically maintain.
A Bunsen burner’s temperature is controlled only by adjusting the gas flow via the collar and valve. This is far less precise and requires constant monitoring.
Safety and Flammability
This is the most important trade-off. Never use an open flame like a Bunsen burner to heat a flammable liquid (e.g., ethanol, acetone). The vapors can easily ignite and cause a fire or explosion.
For flammable substances, a hot plate (used with care in a well-ventilated area) or, ideally, a heating mantle or steam bath is the only safe choice.
Selecting the Right Tool for Your Task
Your choice should always be dictated by the demands of your procedure. Base your decision on safety and the specific heating profile your experiment requires.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, uniform heating of non-flammable liquids in a beaker: A hot plate/stirrer is your best and most versatile tool.
- If your primary focus is safely heating flammable or sensitive liquids in a round-bottom flask: A heating mantle is the correct and safest choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving extremely stable, gentle heat below 100°C: A water bath is the ideal apparatus for maximum temperature stability.
- If your primary focus is rapid, high-temperature heating or sterilization where an open flame is permitted: A Bunsen burner is the most effective tool.
Matching the apparatus to the task is the hallmark of safe and effective scientific work.
Summary Table:
| Apparatus | Primary Use | Heat Type | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Plate/Stirrer | General heating & mixing | Indirect, Uniform | No open flame; versatile |
| Bunsen Burner | Rapid, high-temp heating | Direct, Intense | Fast heating; sterilization |
| Heating Mantle | Heating round-bottom flasks | Indirect, Controlled | Safest for flammable solvents |
| Water/Oil Bath | Gentle, stable heating | Indirect, Uniform | Prevents overheating; precise control |
Need the right heating apparatus for your lab?
Choosing the correct equipment is critical for safety and experimental success. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including hot plates, heating mantles, and water baths, designed to meet your specific heating requirements. Our experts can help you select the safest and most efficient tool for your application.
Contact us today to find your perfect heating solution and ensure precise, safe results in your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- How do constant temperature shakers enhance lignin removal? Optimize Alkaline Pretreatment with Mechanical Force
- What is preventive maintenance of laboratory equipment? A Proactive Strategy for Data Integrity and Safety
- What are the uses of pyrolysis oil? Unlock Its Potential as a Bio-Crude for Heat, Power, and Chemicals
- What is the principle behind the process of extraction? Mastering Selective Solubility for Efficient Separation
- How does a magnetic stirrer influence the efficiency of the sulfuric acid leaching process for zinc ash? Expert Insights
- What role do KOH and NaOH play in pyrolysis gas treatment? Neutralize Toxins and Protect Your Lab Equipment
- What is the difference between evaporation and sputtering in coating technology? Choose the Right Method for Your Lab
- How does temperature affect melting? Master Precise Control for Material Integrity



















