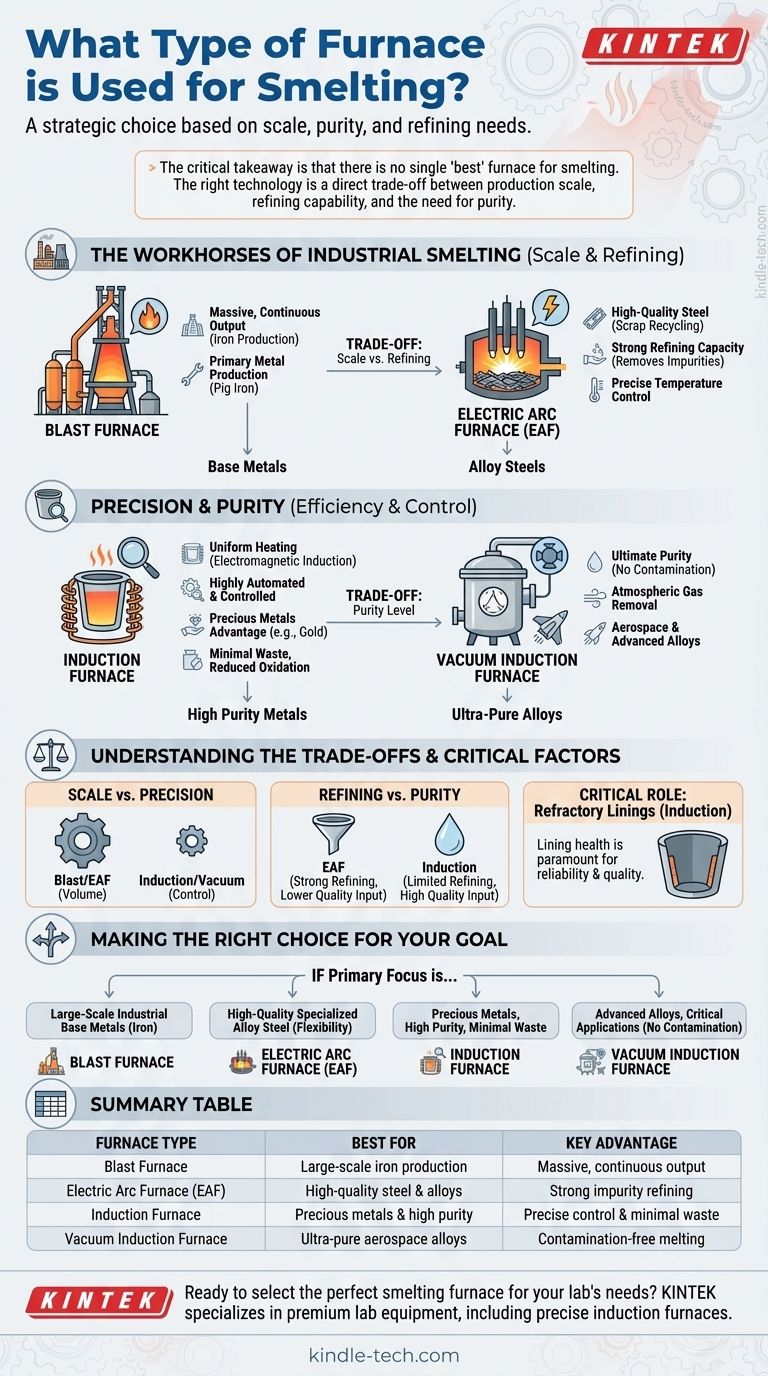
For smelting metals, several types of furnaces are used, with the choice depending entirely on the metal, the scale of production, and the required purity. The most common are blast furnaces for industrial pig iron, electric arc furnaces for high-quality steel, and induction furnaces, which are highly efficient for smelting precious metals and specialized alloys.
The critical takeaway is that there is no single "best" furnace for smelting. The right technology is a direct trade-off between production scale, refining capability, and the need for purity, forcing a choice between massive industrial furnaces and highly controlled, specialized systems.

The Workhorses of Industrial Smelting
Large-scale metal production relies on robust furnaces designed for massive throughput and the initial refining of raw ore. These are the foundation of heavy industry.
Blast Furnaces: For Primary Metal Production
A blast furnace is the classic technology used for smelting raw materials like iron ore to produce industrial metals, most commonly pig iron.
Its name comes from the "blast" of high-pressure, hot combustion air that is forced into the furnace to drive the chemical reactions needed to separate the metal from its ore.
Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF): For High-Quality Steel
An electric arc furnace offers significant technological flexibility and is a cornerstone of modern steelmaking, especially for recycling scrap metal.
EAFs excel at removing impurities like sulphur and phosphorus and allow for precise temperature control. This makes them ideal for smelting high-quality and specialized alloy steels.
Precision and Purity: The Role of Induction Furnaces
When the goal shifts from sheer volume to purity, efficiency, and control, induction technology becomes the superior choice.
How Induction Furnaces Work
An induction furnace uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to heat and melt metal. An electric current passed through a coil generates a magnetic field, which in turn creates powerful electrical currents within the metal itself, generating intense heat.
This method provides uniform temperature throughout the molten metal and allows for highly automated and controlled operations.
The Advantage in Precious Metals
Induction furnaces are exceptionally well-suited for smelting precious metals like gold. They offer high efficiency, accelerate the melting process, and can be completely emptied to minimize waste.
The precise temperature control also reduces oxidation, which improves the quality of the final purified metal.
Vacuum Induction: For Ultimate Purity
For the most demanding applications, smelting is performed inside a vacuum induction furnace. By removing the air from the melting chamber, this process prevents any contamination from atmospheric gases.
This technology is essential for producing the ultra-pure, high-performance alloys required in aerospace and other advanced industries.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a smelting furnace requires a clear understanding of the fundamental compromises between different technologies. Your material and goals will dictate the correct path.
Scale vs. Precision
Blast furnaces are built for one purpose: massive, continuous output of a base metal. In contrast, induction furnaces offer a highly controlled, batch-based process where precision is more important than sheer volume.
Refining Capability vs. Raw Material Purity
This is a critical distinction. An EAF has a strong refining capacity, meaning it can effectively remove impurities from lower-quality raw materials.
An induction furnace has a limited refining capacity. This is its primary weakness, meaning it requires very pure and carefully controlled raw materials to produce a high-quality final product.
The Critical Role of Refractory Linings
For induction furnaces, the health of the refractory lining—the heat-resistant material protecting the furnace structure—is paramount. Any failure in the lining directly impacts the furnace's reliability, operational efficiency, and the quality of the metal being produced.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision must be based on the specific outcome you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial production of base metals like iron: A blast furnace is the established technology designed for this purpose.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality, specialized alloy steel with flexibility: An Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) is the superior choice due to its refining capabilities.
- If your primary focus is smelting precious metals or materials where purity and minimal waste are paramount: An induction furnace offers the best control, efficiency, and quality for the task.
- If your primary focus is creating advanced alloys for critical applications: A specialized process like vacuum induction smelting is necessary to prevent any atmospheric contamination.
Understanding these core differences allows you to select the precise smelting technology that aligns perfectly with your material, scale, and quality requirements.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Blast Furnace | Large-scale iron production | Massive, continuous output |
| Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) | High-quality steel & alloys | Strong impurity refining |
| Induction Furnace | Precious metals & high purity | Precise control & minimal waste |
| Vacuum Induction Furnace | Ultra-pure aerospace alloys | Contamination-free melting |
Ready to select the perfect smelting furnace for your lab's needs? KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment, including induction furnaces ideal for precise, high-purity metal smelting. Our experts will help you choose the right technology to maximize efficiency, purity, and yield. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a sputtering system? Achieve Unmatched Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is a sputtering machine? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is RF magnetron sputtering? A Guide to Depositing Insulating Thin Films
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials



















