The most suitable material for a heating element is determined almost entirely by its required operating temperature and environment. For lower temperatures, metallic alloys like nickel-chromium are standard, while high-temperature industrial applications rely on materials like silicon carbide, graphite, molybdenum, and for extreme heat, refractory metals like tungsten or advanced ceramics like molybdenum disilicide.
The search for a single "best" material is misleading. The critical task is to match the material's properties—primarily its temperature limit and atmospheric reactivity—to the specific demands of the heating application.
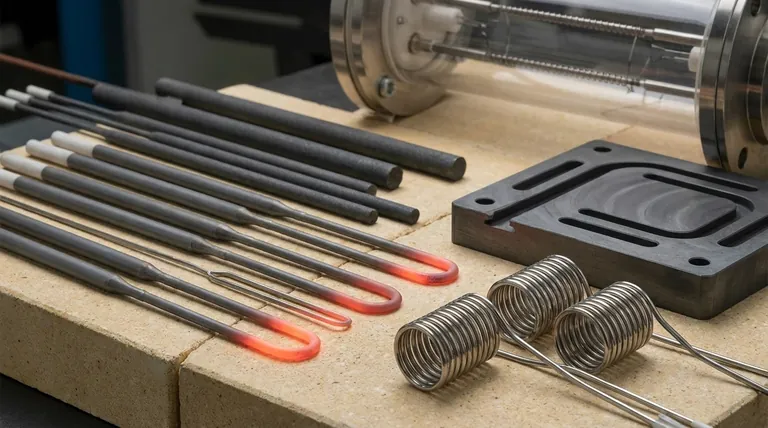

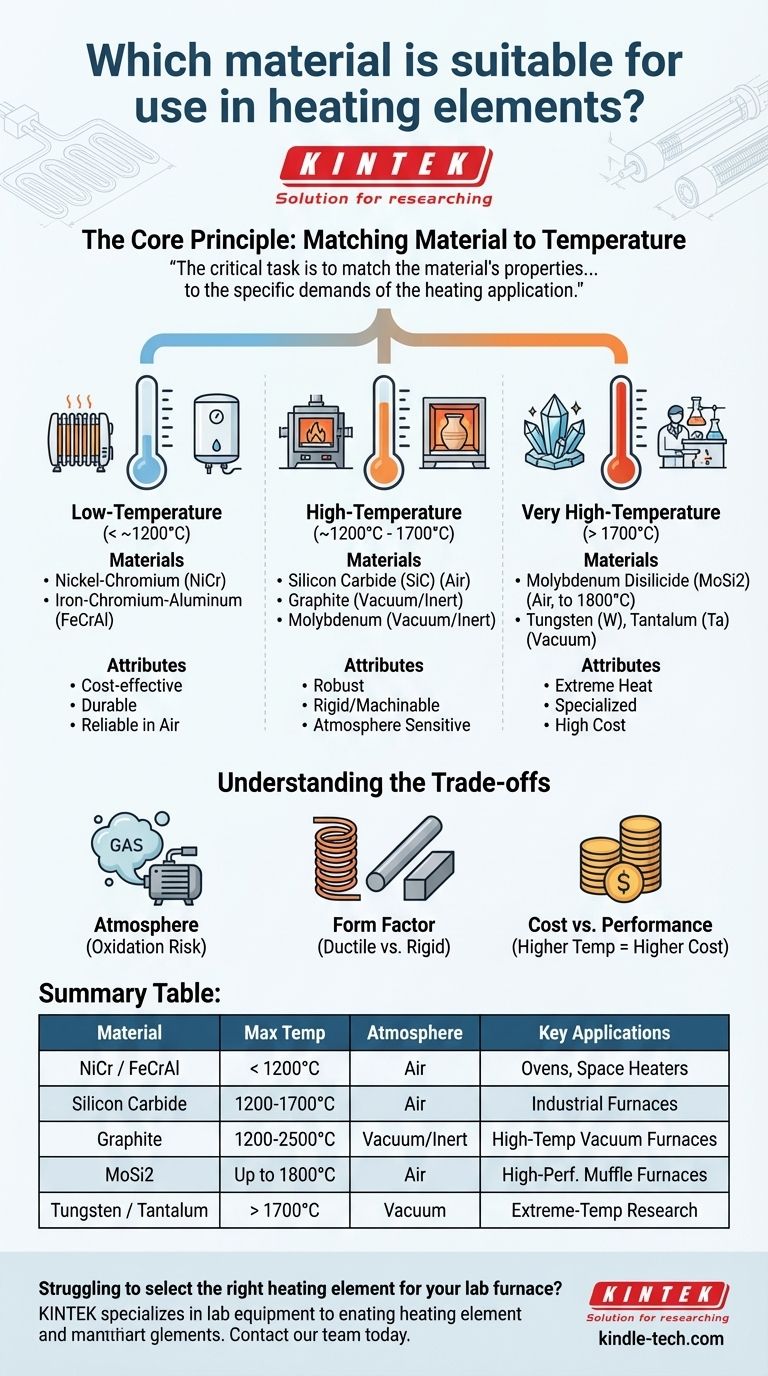
The Core Principle: Matching Material to Temperature
The single most important factor in selecting a heating element material is the maximum temperature it needs to achieve and sustain. Materials behave very differently as they get hotter, defining their operational limits.
Low-Temperature Applications (Below ~1200°C)
The vast majority of common heating applications fall into this category.
For applications like space heaters, ovens, and water heaters, nickel-chromium (NiCr) and iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloys are the dominant choice. They are cost-effective, durable, and perform reliably within their temperature range.
High-Temperature Applications (~1200°C to 1700°C)
Industrial furnaces for processes like metal treatment and ceramics firing require more robust materials.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) is a common choice here. It is a rigid ceramic material often formed into rods or spirals, capable of operating at high temperatures in air.
Graphite is another popular option, especially for vacuum or inert-atmosphere furnaces. It has excellent thermal shock resistance and is easily machined into complex shapes, but it will oxidize (burn away) if used in an oxygen-rich environment at high temperatures.
Molybdenum is a refractory metal used for high-temperature vacuum furnace elements. Like graphite, it must be protected from oxygen at high temperatures to prevent rapid failure.
Very High-Temperature Applications (Above 1700°C)
Reaching extreme temperatures for research, crystal growth, or specialized manufacturing requires exotic materials.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) is an advanced ceramic composite that can operate in air at temperatures up to 1800°C. These elements are a modern solution for high-performance muffle furnaces.
Refractory metals like Tungsten (W) and Tantalum (Ta) have exceptionally high melting points and are used for the most demanding high-temperature vacuum applications. Platinum is also used for its high-temperature stability and resistance to oxidation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material is never just about the maximum temperature; it involves balancing performance, cost, and environmental constraints.
The Critical Impact of Atmosphere
A material's suitability can change completely based on the atmosphere it operates in.
Elements like graphite and molybdenum offer superb high-temperature performance but will be destroyed by oxidation. They are therefore restricted to vacuum or inert gas environments. In contrast, silicon carbide and molybdenum disilicide can operate in air.
Form Factor and Mechanical Properties
The physical shape of the element also dictates material choice.
Metallic alloys like nickel-chromium are ductile and can be easily formed into coils. Graphite is valued for its machinability, allowing for custom-designed heating elements. Ceramics like SiC are more rigid and typically supplied in standard shapes like rods or tubes.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between temperature capability and cost.
NiCr and FeCrAl alloys are relatively inexpensive. Materials like silicon carbide and molybdenum represent a significant step up in cost and performance. The most extreme-temperature materials, such as tungsten, platinum, and molybdenum disilicide, are the most expensive and reserved for applications where their performance is non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your selection must be guided by your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating below 1200°C: Choose a Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) or Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) alloy for the best balance of cost and performance.
- If your primary focus is a high-temperature furnace operating in air: Select Silicon Carbide (SiC) or, for even higher temperatures, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2).
- If your primary focus is a high-temperature furnace under vacuum: Use Graphite for its excellent thermal properties and machinability, or Molybdenum for metallic element requirements.
- If your primary focus is extreme-temperature performance in a vacuum: Your application demands a refractory metal like Tungsten or Tantalum.
Ultimately, understanding these key trade-offs empowers you to select a material that provides reliable and efficient heat for your specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temp Range (°C) | Ideal Atmosphere | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| NiCr / FeCrAl Alloys | < 1200°C | Air | Ovens, Space Heaters |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | 1200°C - 1700°C | Air | Industrial Furnaces |
| Graphite | 1200°C - 2500°C | Vacuum / Inert | High-Temp Vacuum Furnaces |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Up to 1800°C | Air | High-Performance Muffle Furnaces |
| Tungsten / Tantalum | > 1700°C | Vacuum | Extreme-Temp Research |
Struggling to select the right heating element for your lab furnace? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you match the perfect material—whether it's cost-effective NiCr for standard ovens or high-performance MoSi2 for advanced research—to your specific temperature, atmosphere, and application requirements. Contact our team today to ensure reliable, efficient heating for your laboratory processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Infrared Heating Quantitative Flat Plate Press Mold
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
People Also Ask
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere
- What function do molybdenum disilicide heating elements perform? Precision Heat for Pulverized Coal Research
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab



















