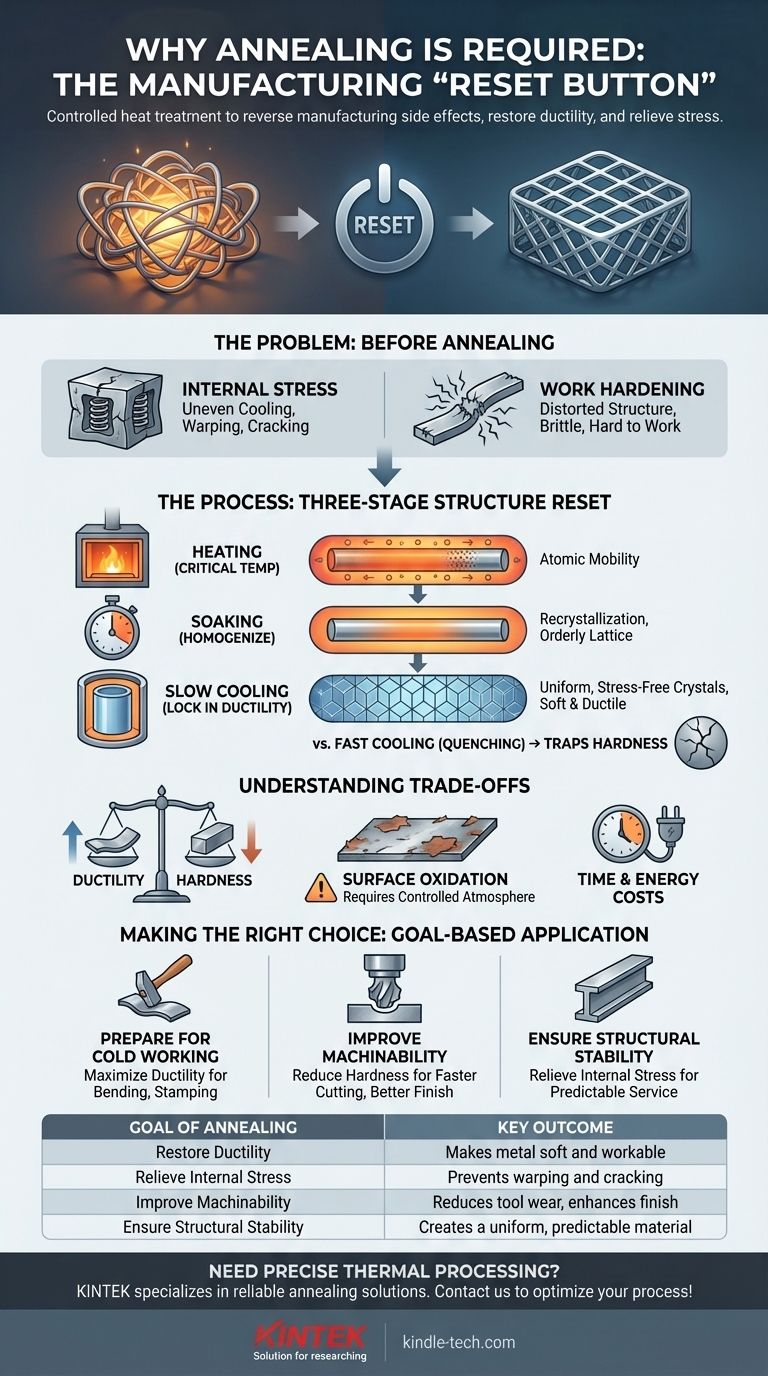
At its core, the annealing process is required to reverse the negative side effects of manufacturing. Processes like casting, forging, or cold working can leave a metal hard, brittle, and full of internal stress. Annealing is a controlled heat treatment that systematically removes these issues, reducing hardness, relieving stress, and restoring ductility to make the material more workable and stable.
Annealing should be understood not as a strengthening process, but as a critical "reset button." It sacrifices hardness to gain ductility and relieve internal stresses, transforming a brittle, unpredictable material into a uniform and workable one.

The Problem: Why Metals Need to Be Annealed
Before a metal is annealed, it often exists in a state that is difficult or risky to work with. This is a direct consequence of previous manufacturing steps.
The Impact of Internal Stress
Processes like casting, welding, or forging cool unevenly, creating microscopic tension and compression zones within the material. These internal stresses are like tightly coiled springs hidden inside the metal, which can lead to warping or spontaneous cracking over time or during subsequent machining.
The Challenge of Work Hardening
When a metal is bent, stretched, or shaped at room temperature (a process called cold working), its internal crystal structure becomes distorted and tangled. This makes the metal harder and stronger, but also significantly more brittle and prone to fracture if further work is attempted.
The Goal: Restoring Workability
The primary driver for annealing is to make the material suitable for the next stage of production. A hard, brittle material is difficult to machine, impossible to form, and unreliable in service. Annealing restores its ductility (the ability to deform without breaking) and machinability.
How Annealing Resets the Material's Structure
Annealing is a precise, three-stage process designed to systematically rearrange the metal's internal crystal lattice, effectively repairing the damage from previous work.
Step 1: Heating to a Critical Temperature
The metal is heated in a furnace to a specific temperature, which is always below its melting point. This heat provides the atomic energy necessary for the crystal structure to become mobile and begin correcting itself. Different alloys have different optimal annealing temperatures.
Step 2: Soaking to Homogenize the Structure
The material is held at this high temperature for a set period. During this "soaking" phase, the atoms migrate into a more orderly and stable lattice. This process, known as recrystallization, eliminates the majority of the crystal defects (dislocations) that cause hardness and brittleness.
Step 3: Slow Cooling to Lock in Ductility
This is the most critical step for achieving softness and ductility. The material is cooled very slowly, often by leaving it in the insulated furnace to cool over many hours. This slow rate allows large, uniform, and stress-free crystals to form, resulting in a soft and highly ductile final state. Fast cooling (quenching), by contrast, would trap a hard, brittle structure.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
While essential, annealing is not without its compromises. Understanding these trade-offs is key to using the process effectively.
The Primary Trade-off: Hardness for Ductility
Annealing fundamentally reduces the hardness and tensile strength of a material. You are intentionally making the metal softer. If the final application requires high strength, another heat treatment (like hardening and tempering) may be necessary after the forming and machining operations are complete.
The Risk of Surface Oxidation
Heating metals to high temperatures in the presence of oxygen will cause a layer of scale or oxide to form on the surface. To prevent this, annealing is often performed in a furnace with a controlled, protective atmosphere (such as nitrogen or argon) that is chemically inert.
Time and Energy Costs
Annealing is an energy-intensive process that can take many hours from start to finish. The heating and slow cooling cycles tie up furnace capacity and consume significant power, adding to the overall cost of manufacturing a component.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Annealing is not a single solution but a tool to achieve a specific outcome. You should apply it based on what you need to do next with the material.
- If your primary focus is preparing for cold working: Anneal to maximize ductility, allowing the metal to be bent, stamped, or drawn into complex shapes without fracturing.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability: Anneal to reduce hardness, which results in less tool wear, faster cutting speeds, and a better surface finish.
- If your primary focus is ensuring structural stability: Anneal to relieve internal stresses from casting or welding, preventing dimensional changes or failure in service.
Ultimately, annealing provides the control to transform a stressed, brittle material into a predictable and reliable foundation for your final product.
Summary Table:
| Goal of Annealing | Key Outcome | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Restore Ductility | Makes metal soft and workable | Cold working, forming, bending |
| Relieve Internal Stress | Prevents warping and cracking | After casting, welding, or machining |
| Improve Machinability | Reduces tool wear, enhances finish | Pre-machining preparation |
| Ensure Structural Stability | Creates a uniform, predictable material | Critical components for service |
Need precise thermal processing for your materials? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for all your annealing and heat treatment requirements. Our expertise ensures your materials achieve the perfect balance of ductility and stability. Contact us today to optimize your manufacturing process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Hot Zone Materials and Processed Metals
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment



















