At their core, electric furnaces are used to deliver highly controlled and precise heat for processing a vast range of materials. Their applications span heavy industry, such as melting scrap steel in foundries and heating metal billets for forging, to advanced scientific processes like developing battery materials and annealing delicate sapphire wafers for electronics.
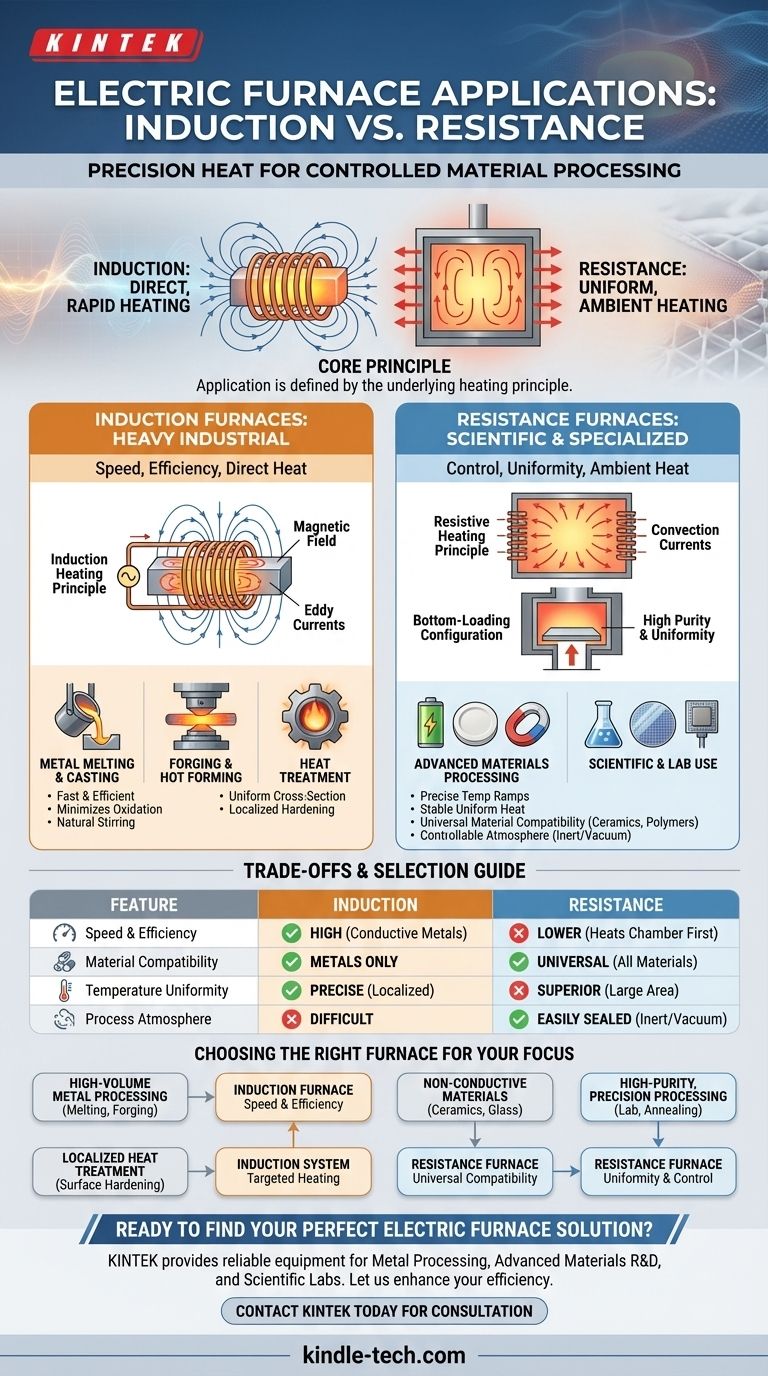
The specific application of an electric furnace is determined not by its name, but by its underlying heating principle. Understanding whether a process requires direct, rapid heating (induction) or uniform, ambient heating (resistance) is the key to selecting the right tool.

Heavy Industrial Applications: Induction Furnaces
Induction furnaces are the workhorses of the modern metalworking industry. They are valued for their speed, efficiency, and ability to generate intense heat directly within the material itself.
The Principle of Induction Heating
An induction furnace uses a powerful alternating current passed through a copper coil. This creates a strong, fluctuating magnetic field that induces electrical currents (eddy currents) directly within the conductive material placed inside. The material's own resistance to these currents generates rapid and precise heat from the inside out.
Application: Metal Melting and Casting
In the foundry industry, the medium frequency melting furnace is essential for melting raw materials, scrap metal, and alloys for casting. Because heat is generated within the metal, melting is extremely fast and efficient, minimizing metal loss due to oxidation. The electromagnetic forces also create a natural stirring action, improving the homogeneity of the final molten metal.
Application: Forging and Hot Forming
Before a metal part can be forged or shaped, it must be heated to a specific, uniform temperature. An induction diathermy furnace or medium frequency heating furnace excels at this, rapidly heating metal blanks through their entire cross-section. This speed reduces the formation of surface scale and ensures the part is at the optimal temperature for forming.
Application: Heat Treatment
Induction heating is also widely used for surface hardening, quenching, and tempering of metal parts like steel bars. The process is highly controllable, allowing heat to be applied to very specific areas of a component, resulting in a hardened surface layer with a more ductile core.
Specialized and Scientific Applications: Resistance Furnaces
Where induction furnaces are defined by speed and direct heating, resistance furnaces are defined by control and uniform ambient temperature. They function more like a highly precise conventional oven.
The Principle of Resistive Heating
Resistance furnaces use heating elements made from materials with high electrical resistance. When current is passed through these elements, they become extremely hot and transfer this heat to the furnace chamber and the material inside via convection and radiation.
The Bottom-Loading Configuration
A bottom-loading furnace is a common configuration for high-purity applications. In this design, the hearth (or floor) of the furnace is raised into the insulated heating chamber. This prevents contamination from falling particles and ensures extremely uniform heating, as the product is perfectly centered within the heating elements.
Application: Advanced Materials Processing
These furnaces are critical for developing and processing materials where precise temperature ramps and stable, uniform heat are paramount. This includes processing battery materials, electronic ceramics, and magnetic materials, where slight temperature deviations can ruin the final product's properties.
Application: Scientific and Lab Use
In university labs and research centers, resistance furnaces are used for a wide range of experiments and treatments. Their precision is ideal for sapphire wafer annealing and the heat treatment of components like zirconia sensors, where purity and repeatable thermal cycles are non-negotiable.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Induction vs. Resistance
Choosing between these furnace types involves clear and significant trade-offs tied directly to their heating mechanisms.
Speed and Efficiency
Induction is significantly faster and more energy-efficient for processing conductive metals because it heats the material directly. Resistance heating is slower, as it must first heat the entire furnace chamber before heating the product.
Material Compatibility
This is a critical distinction. Induction only works on electrically conductive materials like metals. Resistance heating is universal and can heat any material, including ceramics, polymers, and composites.
Temperature Uniformity
While induction heating is precise, resistance furnaces generally offer superior temperature uniformity across a large area. This is vital for processes like annealing, where the entire part must be heated and cooled under identical conditions.
Process Atmosphere
Resistance furnaces are more easily sealed to control the internal atmosphere (e.g., using inert gas or a vacuum). This is difficult to achieve in many induction furnace designs, making resistance furnaces better for processes sensitive to oxidation.
Choosing the Right Furnace for Your Process
Matching the heating principle to your primary objective is the most important step in selecting the correct furnace technology.
- If your primary focus is high-volume metal processing (melting, forging): An induction furnace is your default choice due to its unmatched speed and efficiency for conductive materials.
- If your primary focus is localized heat treatment (surface hardening): An induction system provides the precise, targeted heating necessary for creating specific metallurgical properties on a component's surface.
- If your primary focus is processing non-conductive materials (ceramics, glass): A resistance furnace is your only option, as the induction principle will not work.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, precision processing (lab research, wafer annealing): A resistance furnace, often in a bottom-loading or tube configuration, provides the superior temperature uniformity and atmospheric control required.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental heating principle is the key to selecting the right technology for your application.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Heating Principle | Ideal For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Induction Furnace | Direct, internal heating via magnetic fields | Melting metals, forging, surface hardening | High speed, energy-efficient, material-specific (conductive metals) |
| Resistance Furnace | Ambient, uniform heating via resistive elements | Lab research, battery materials, ceramics, annealing | Superior temperature control, universal material compatibility, atmosphere control |
Ready to Find Your Perfect Electric Furnace Solution?
Whether your process demands the high-speed melting of an induction furnace or the precise, uniform heat of a resistance furnace for your lab, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your needs.
We specialize in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables for:
- Metal Processing & Foundries: Achieve efficient melting and forging.
- Advanced Materials R&D: Develop battery materials, ceramics, and more with precise thermal cycles.
- Scientific Laboratories: Ensure purity and repeatability for annealing and heat treatment applications.
Let us help you select the right technology to enhance your efficiency and results.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and let our experts guide you to the optimal solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the use of a digital muffle furnace? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the thermal debinding process? A Guide to Safe Binder Removal for MIM & Ceramics
- What is the purpose of a laboratory furnace? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between a furnace and an oven in a laboratory? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Heat Needs
- What is the use of furnace in laboratory? Unlock Material Transformation for Your Research



















