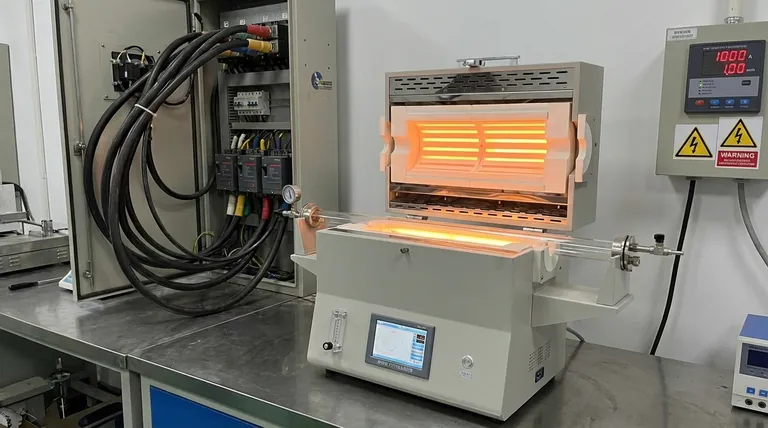
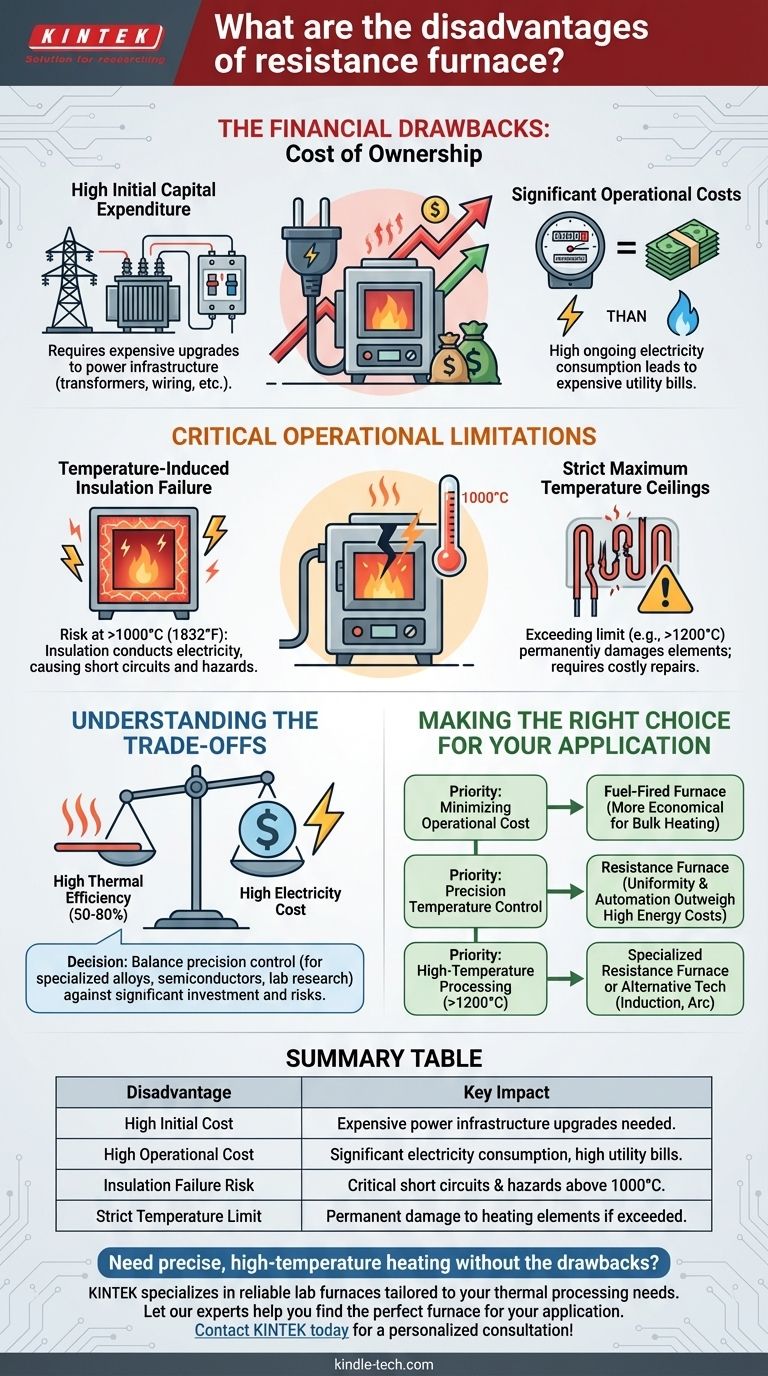
The primary disadvantages of a resistance furnace are its high economic costs and specific operational limitations. These include significant initial investment for power infrastructure, high ongoing electricity consumption, and a critical risk of insulation failure when operating at temperatures above 1000°C.
While resistance furnaces offer exceptional temperature control and high thermal efficiency, these benefits come at a direct cost. Decision-makers must weigh the need for precision against the significant financial investment and inherent high-temperature operational risks.

The Financial Drawbacks: Cost of Ownership
The most immediate and persistent disadvantages of a resistance furnace are financial. The total cost of ownership extends far beyond the price of the unit itself.
High Initial Capital Expenditure
A resistance furnace consumes a large amount of power. This often requires you to upgrade your facility's electrical infrastructure, including transformers, circuit breakers, and wiring, to handle the high load. This "power distribution equipment" represents a significant and often overlooked upfront cost.
Significant Operational Costs
These furnaces convert electrical energy directly into heat. While they are efficient at this conversion, electricity is frequently a more expensive energy source compared to alternatives like natural gas. This results in high utility bills, making them costly for continuous or large-scale heating operations.
Critical Operational Limitations
Beyond cost, resistance furnaces have inherent physical and material limitations that dictate their use.
Temperature-Induced Insulation Failure
This is the most critical safety and operational risk. At temperatures exceeding 1000°C (1832°F), the refractory materials used for insulation can begin to conduct electricity. This compromises the furnace's electrical insulation, creating a severe risk of short circuits, equipment damage, and electrical shock hazards.
Strict Maximum Temperature Ceilings
Every resistance furnace is designed with a maximum operating temperature determined by its heating elements and structural materials. Exceeding this limit, even for short periods, can cause permanent damage to the elements, leading to costly repairs and downtime. Most common box-type furnaces, for example, are rated for operation below 1200°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a resistance furnace involves balancing its unique advantages against its clear disadvantages.
The Efficiency Paradox
Resistance furnaces boast high thermal efficiency, often between 50% and 80%. This means a large percentage of the electricity consumed is successfully converted into useful heat within the chamber. However, this efficiency does not necessarily translate to low cost. The high price of electricity can make a highly efficient resistance furnace more expensive to run than a less efficient but fuel-fired alternative.
When Control Justifies the Cost
The primary reason to accept the high costs is for process control. Resistance furnaces allow for extremely precise, uniform, and easily automated temperature management. For applications like treating specialized metal alloys, manufacturing semiconductors, or conducting sensitive lab research, this level of control is non-negotiable and justifies the expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision depends on your specific operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational cost: A resistance furnace may be unsuitable for bulk heating; a fuel-fired furnace is likely more economical.
- If your primary focus is precision temperature control: The unparalleled uniformity and automation of a resistance furnace often outweigh its high energy costs.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing (above 1200°C): You must select a specially designed furnace and remain vigilant about insulation integrity, or consider alternative technologies like induction or arc furnaces.
Understanding these economic and operational limitations is the key to correctly leveraging the precision and control that a resistance furnace offers.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| High Initial Cost | Requires expensive power infrastructure upgrades (transformers, wiring). |
| High Operational Cost | Significant electricity consumption leads to expensive utility bills. |
| Insulation Failure Risk | Critical risk of short circuits and hazards above 1000°C (1832°F). |
| Strict Temperature Limit | Exceeding the maximum rating can permanently damage heating elements. |
Need precise, high-temperature heating without the drawbacks?
While resistance furnaces have limitations, selecting the right lab equipment is crucial for your budget, safety, and process success. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab furnaces and equipment tailored to your specific thermal processing needs, whether you require exceptional control for research or a cost-effective solution for production.
Let our experts help you find the perfect furnace for your application. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How does a quartz tube facilitate fractional condensation in a horizontal tube vacuum gasification furnace? Expert Guide
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process



















