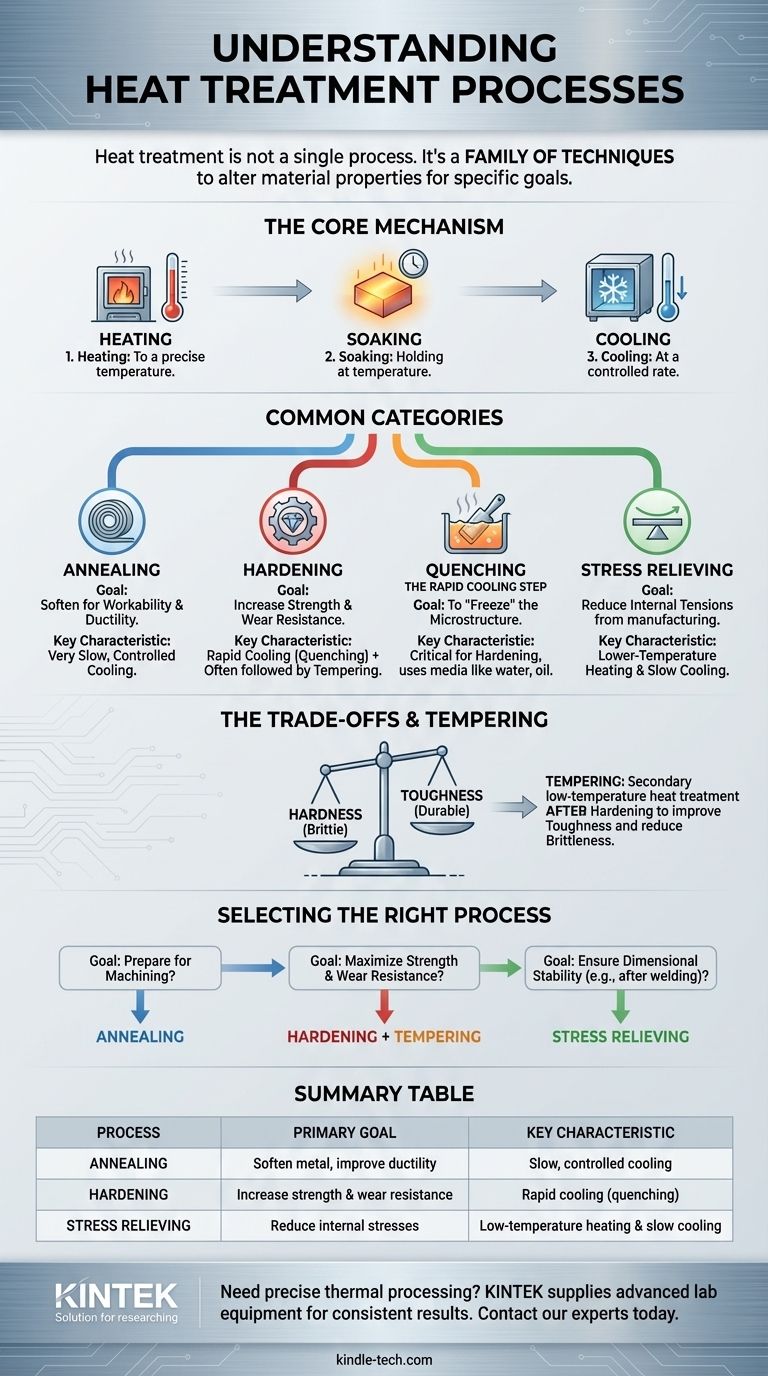
Heat treatment is not a single process but a broad category of industrial thermal processes used to intentionally alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a material. The specific process is named based on its intended outcome, with common examples including annealing, hardening, quenching, and stress relieving.
The core misunderstanding is searching for a single name for "heat treatment." The key is to recognize that heat treatment is a family of techniques, and the correct term depends entirely on your engineering goal—whether you need to soften a metal, make it harder, or stabilize it.

The Purpose of Heat Treatment: Why We Alter Metals
Heat treatment is a fundamental tool in metallurgy and manufacturing. It gives engineers precise control over a material's mechanical properties to match the demands of a specific application.
Controlling Material Properties
The primary goal of any heat treatment process is to manipulate a material's microstructure. This internal arrangement of crystals determines its hardness, toughness, ductility, and strength.
The Core Mechanism: Heating and Cooling
All heat treatment processes involve three basic stages:
- Heating the material to a specific, predetermined temperature.
- Soaking or holding the material at that temperature for a set duration.
- Cooling the material back to room temperature at a controlled rate.
The temperatures and, most critically, the rate of cooling dictate the final properties of the component.
Common Categories of Heat Treatment
While there are many specialized processes, most fall into a few key categories defined by their function.
Annealing: Softening for Workability
Annealing is a process used to make a metal softer and more ductile. This is often done to relieve internal stresses, improve machinability, or prepare the material for further cold working processes like stamping or drawing. The key is a very slow, controlled cooling rate.
Hardening: Increasing Strength and Wear Resistance
Hardening does the opposite of annealing. It involves heating a metal to a critical temperature and then cooling it rapidly to lock in a very hard, brittle microstructure. This process significantly increases strength and resistance to wear and abrasion.
Quenching: The Rapid Cooling Step
Quenching is not a full process in itself, but rather the critical rapid cooling step used in hardening. The material is quickly submerged in a medium like water, oil, or forced air to "freeze" its internal structure in the hardest possible state.
Stress Relieving: Reducing Internal Tensions
Stress relieving is a lower-temperature process used to reduce internal stresses that may have been introduced during manufacturing processes like welding, casting, or heavy machining. By gently heating the part and allowing it to cool slowly, these stresses are relaxed, preventing future distortion or cracking.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heat treatment process always involves balancing competing properties. No single process can optimize for every characteristic.
Hardness vs. Brittleness
The most fundamental trade-off in heat treatment is between hardness and brittleness. A fully hardened steel part is extremely strong but so brittle that it can shatter under impact.
The Role of Tempering
To solve this, a hardened part is almost always tempered. Tempering is a secondary, lower-temperature heat treatment performed after hardening and quenching. It slightly reduces the hardness but dramatically increases the material's toughness, making it durable and resistant to fracture.
Time and Cost Implications
Generally, processes that require very slow, controlled cooling (like annealing) or multiple steps (hardening and tempering) are more time-consuming and costly than simpler processes like stress relieving.
Selecting the Right Process for Your Goal
The correct process is dictated entirely by the final application of the component.
- If your primary focus is to prepare a metal for machining or forming: Annealing is the correct choice to increase ductility and reduce hardness.
- If your primary focus is to maximize strength and wear resistance for a finished part: Hardening (via quenching) followed by tempering is the standard procedure to achieve a balance of strength and toughness.
- If your primary focus is to ensure dimensional stability after welding or heavy machining: Stress relieving is used to prevent the part from warping or cracking over time.
Understanding these distinct processes allows you to precisely engineer the material properties required for any application.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Soften metal, improve ductility | Slow, controlled cooling |
| Hardening | Increase strength and wear resistance | Rapid cooling (quenching) |
| Stress Relieving | Reduce internal stresses from manufacturing | Low-temperature heating & slow cooling |
Need precise thermal processing for your materials? The right heat treatment is critical for achieving the perfect balance of hardness, strength, and durability in your components. At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for controlled heating and cooling processes. Whether you're in R&D or production, our solutions help you achieve consistent, reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific heat treatment needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- Can I vacuum the inside of my furnace? A Guide to Safe DIY Cleaning vs. Professional Service
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Hot Zone Materials and Processed Metals
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing



















