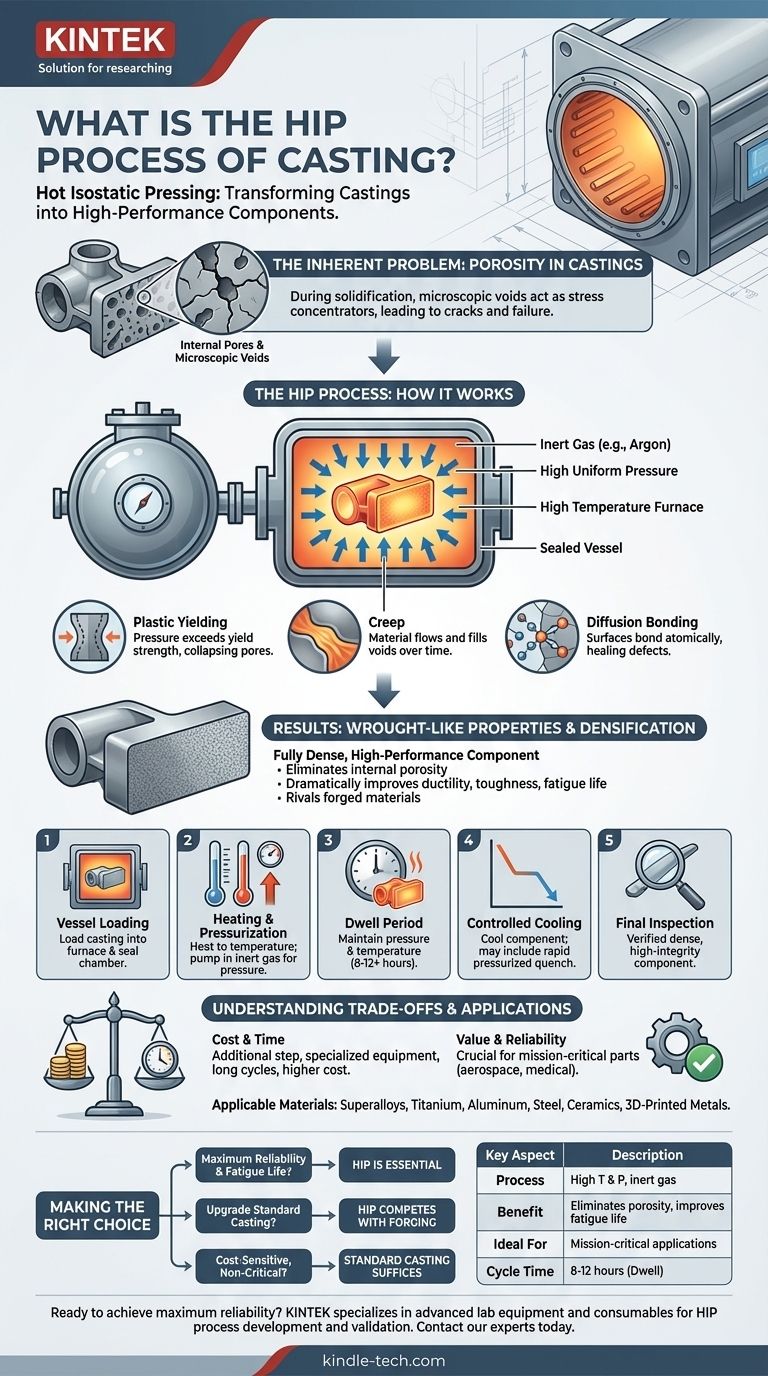
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is a post-casting manufacturing process that uses high temperature and uniform high pressure to eliminate internal porosity in metal components. By subjecting a casting to this environment inside a sealed vessel with an inert gas like argon, the material plastically deforms and creeps on a microscopic level, forcing internal voids and defects to collapse and fully weld shut. This densification process dramatically improves the mechanical properties and reliability of the final part.
HIP is not a method of casting itself, but rather a critical secondary treatment. It transforms a standard casting with potential internal flaws into a fully dense, high-performance component with mechanical properties that can rival those of more expensive forged materials.

The Core Purpose: Why Castings Need HIP
The Inherent Problem of Porosity
During the solidification process, microscopic voids or pores can form within a metal casting. These defects are often undetectable by surface inspection.
These internal pores act as stress concentrators, becoming the initiation points for cracks and ultimate component failure, especially under fatigue or high-stress conditions.
Achieving Wrought-Like Properties
By eliminating this internal porosity, the HIP process significantly improves a casting's mechanical properties, including ductility, toughness, and fatigue life.
The resulting dense, uniform material structure allows HIPed castings to challenge the performance of parts made from wrought or forged stock, which are traditionally considered superior.
How Defects Are Eliminated
The process relies on a combination of three mechanisms at high temperature and pressure:
- Plastic Yielding: The pressure exceeds the material's yield strength, causing it to deform and collapse pores.
- Creep: Over the long cycle time, the material slowly flows or "creeps" to fill remaining voids.
- Diffusion Bonding: At the atomic level, the collapsed surfaces of the former void bond together, completely healing the defect and leaving no trace it was ever there.
How the HIP Process Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The HIP Vessel
The entire process takes place inside a specialized piece of equipment that combines a high-temperature furnace with a high-pressure containment vessel.
Loading and Heating
The castings are loaded into the vessel's furnace chamber. The chamber is sealed, and the temperature is raised to a specific point, which is below the material's melting point but high enough to make it malleable.
Pressurization with Inert Gas
Simultaneously, an inert gas—typically argon—is pumped into the vessel, creating immense, uniform pressure. This pressure is "isostatic," meaning it is applied equally from all directions on the part's surface.
The Dwell or "Soak" Period
The casting is held at the target temperature and pressure for a specified duration, often lasting 8 to 12 hours or more. This extended "soak" time is what allows the creep and diffusion mechanisms to fully densify the material.
Controlled Cooling
After the cycle is complete, the parts are cooled in a controlled manner. Some HIP units can perform a pressurized rapid cool, which acts as a quenching step and can be integrated into the component's overall heat treatment plan.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Cost and Cycle Time
HIP is an additional manufacturing step that requires specialized equipment and significant time. This adds cost and lead time, making it unsuitable for every application.
Application Specificity
The process provides the most value for mission-critical components where failure is unacceptable, such as in aerospace, power generation, and medical implants. For less demanding applications, the cost may not be justified.
Broad Material Applicability
While it is an added expense, a key advantage of HIP is its versatility. It can be applied to a wide range of materials, including nickel-based superalloys, titanium, aluminum, steel, and even ceramics and 3D-printed metals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to specify HIP is a matter of balancing performance requirements against cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum reliability and fatigue life (e.g., aerospace turbine blades): HIP is an essential processing step to guarantee material integrity and eliminate internal defects.
- If your primary focus is upgrading the performance of a standard casting: HIP can elevate its mechanical properties to be competitive with more expensive forged components.
- If your primary focus is on cost-sensitive, non-critical components: The added expense and time of HIP are likely unnecessary, and a standard casting will suffice.
Ultimately, Hot Isostatic Pressing is a powerful tool for transforming good components into exceptional ones by ensuring they are free from internal flaws.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | High temperature and uniform isostatic pressure applied via inert gas (e.g., argon). |
| Primary Benefit | Eliminates internal porosity and voids, dramatically improving fatigue life and toughness. |
| Ideal For | Mission-critical components in aerospace, medical implants, and power generation. |
| Cycle Time | Typically 8-12 hours for the high-pressure, high-temperature "soak" period. |
Ready to achieve maximum reliability and performance for your critical metal components?
The HIP process is essential for eliminating internal defects and ensuring material integrity in demanding applications. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for developing and validating these high-performance manufacturing processes.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how our solutions can support your materials testing and processing needs, helping you transform good components into exceptional ones.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Why is Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) Required for Additive Inconel 718? Achieve 100% Theoretical Density
- How long is hot isostatic pressing? Unlocking the Variables That Control Cycle Time
- What is the principle of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve 100% Density and Superior Performance
- How does Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) enhance CuNiCoZnAlTi properties? Achieve Theoretical Density & Maximum Strength
- What is HIP in material processing? Achieve Near-Perfect Density for Critical Components
- What is the meaning of Hot Isostatic Pressing? Achieve 100% Density and Superior Material Integrity
- What is the primary function of an industrial Hot Isostatic Press (HIP)? Maximize Powder Alloy Densification Today
- Why are Warm Isostatic Presses (WIP) necessary for solid-state batteries? Achieve Atomic-Level Contact



















