At its core, heat treatment is a highly controlled industrial process that alters a metal's physical and sometimes chemical properties. It involves a precise sequence of heating, holding at a specific temperature (soaking), and cooling to achieve a desired internal structure and, consequently, characteristics like hardness or softness. This allows engineers to tailor a single metal alloy for many different applications.
The fundamental principle of heat treatment is not just to heat and cool metal, but to deliberately manipulate its internal crystalline structure—its microstructure—to achieve specific, predictable engineering properties.
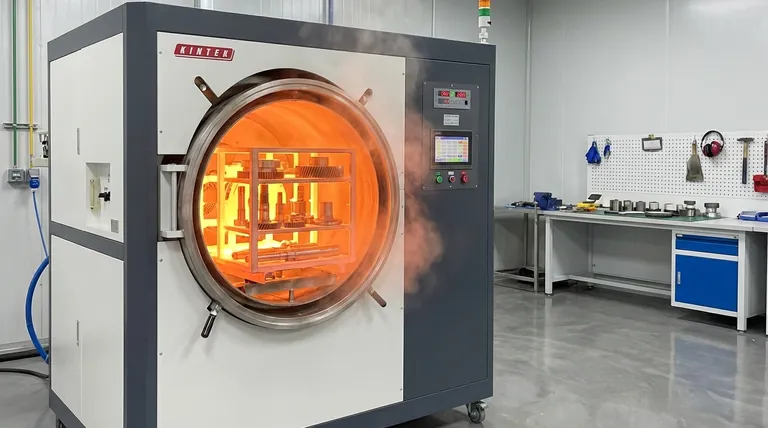

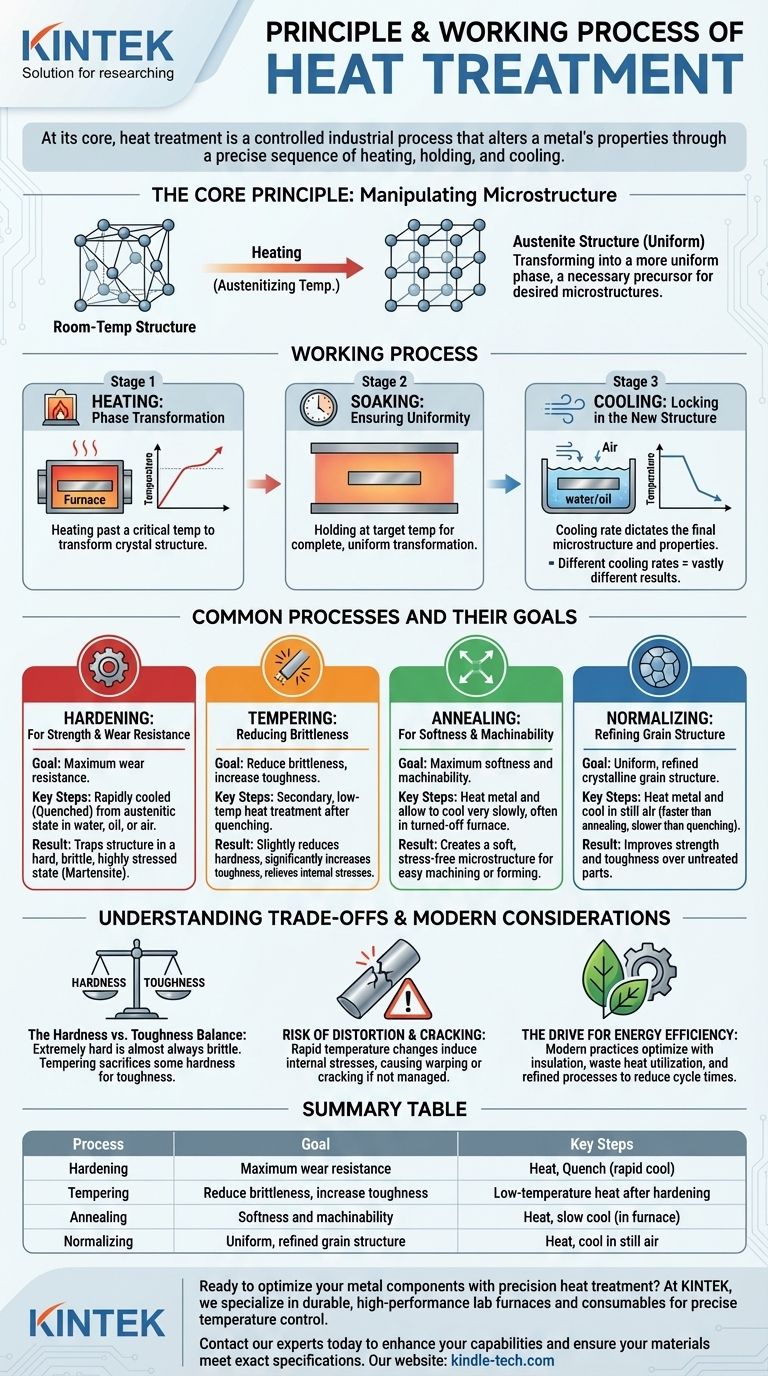
The Core Principle: Manipulating Microstructure
A metal's properties are determined by the arrangement of its atoms in a crystal lattice. Heat treatment works by changing this arrangement, or microstructure, into a more desirable state and then "locking" it in place.
Heating: The Phase Transformation
When a metal like steel is heated past a critical temperature (the austenitizing temperature), its crystal structure transforms. The rigid room-temperature structure rearranges into a different, more uniform phase known as austenite.
This transformation is the essential first step, as the austenitic structure is the necessary precursor for achieving other desired microstructures upon cooling.
Soaking: Ensuring Uniformity
Once the metal reaches the target temperature, it is held there for a specific period. This step, called soaking, ensures that the phase transformation is complete and uniform throughout the entire volume of the part.
Insufficient soaking can lead to an inconsistent microstructure, resulting in unreliable performance with hard and soft spots.
Cooling: Locking in the New Structure
The cooling phase is the most critical part of the process, as the cooling rate dictates the final microstructure and properties of the metal.
Different cooling rates produce vastly different results from the same initial austenitic state, giving engineers precise control over the final outcome.
Common Processes and Their Goals
The combination of heating temperature, soaking time, and cooling rate defines the specific heat treatment process. Each is designed to achieve a different engineering goal.
Hardening: For Strength and Wear Resistance
To make steel hard, it is rapidly cooled or quenched from its austenitic state, typically in water, oil, or air.
This rapid cooling traps the crystal structure in a hard, brittle, and highly stressed state known as martensite.
Tempering: Reducing Brittleness
A part that has been hardened is often too brittle for practical use. Tempering is a secondary, low-temperature heat treatment applied after quenching.
It slightly reduces the hardness but significantly increases the metal's toughness (its ability to absorb impact without fracturing), relieving internal stresses.
Annealing: For Softness and Machinability
To make a metal as soft and ductile as possible, annealing is used. This involves heating the metal and then allowing it to cool very slowly, often by leaving it inside the turned-off furnace.
This slow cooling process creates a soft, stress-free microstructure, making the metal easy to machine, form, or stamp.
Normalizing: Refining Grain Structure
Normalizing involves heating the metal and then letting it cool in still air. This cooling rate is faster than annealing but slower than quenching.
The goal is not maximum softness or hardness but to create a more uniform and refined crystalline grain structure, which improves both strength and toughness over an untreated part.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Modern Considerations
Heat treatment is a powerful tool, but it is governed by fundamental trade-offs and practical constraints. Understanding these is key to successful application.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Balance
The most critical trade-off in heat treatment is between hardness and toughness. A material that is extremely hard is almost always brittle.
Processes like tempering are specifically designed to sacrifice some hardness to regain essential toughness, finding the optimal balance for the part's intended function.
Risk of Distortion and Cracking
The rapid temperature changes, especially during quenching, induce significant internal stresses in the material.
If not managed properly through process control and part geometry, these stresses can cause the part to warp, distort, or even crack.
The Drive for Energy Efficiency
Traditional heat treatment is energy-intensive. Modern practices focus heavily on optimization by using new insulation materials in furnaces and utilizing waste heat from one process to preheat parts for another.
Manufacturers also refine processes to reduce cycle times, replacing long, energy-consuming treatments with shorter, more efficient alternatives without compromising quality.
Matching the Process to the Application
The correct heat treatment process is entirely dependent on the final goal for the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance: A hardening (quenching) process, often followed by a low-temperature temper, is the necessary path.
- If your primary focus is preparing a material for machining or forming: Annealing will soften the metal, reducing tool wear and making it easier to work.
- If your primary focus is a balance of strength and impact resistance: The classic combination of hardening followed by tempering to a specific toughness level is the standard approach.
- If your primary focus is creating a uniform material after a process like forging: Normalizing is used to refine the grain structure for predictable mechanical properties.
Ultimately, heat treatment transforms a simple piece of metal into a high-performance component engineered for a specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Process | Goal | Key Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening | Maximum wear resistance | Heat, Quench (rapid cool) |
| Tempering | Reduce brittleness, increase toughness | Low-temperature heat after hardening |
| Annealing | Softness and machinability | Heat, slow cool (in furnace) |
| Normalizing | Uniform, refined grain structure | Heat, cool in still air |
Ready to optimize your metal components with precision heat treatment? The right laboratory equipment is crucial for achieving consistent, high-quality results. At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying durable, high-performance lab furnaces and consumables that provide the precise temperature control required for processes like hardening, annealing, and tempering. Whether you're in R&D or quality control, our solutions help you achieve the perfect balance of hardness and toughness for your specific application. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your heat treatment capabilities and ensure your materials meet exact specifications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Materials
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Control, Cleanliness, and Quality



















