The working frequency of an induction furnace is not a single value but falls into distinct ranges depending on the furnace's size, application, and the material being melted. While older and very large furnaces operate at line frequency (50/60 Hz), the vast majority of modern industrial furnaces operate in the medium frequency range, typically from 150 Hz to 10,000 Hz (10 kHz), with specialized smaller units using even higher frequencies.
The choice of operating frequency is a critical design decision that directly dictates the furnace's efficiency, melting speed, and the degree of metallurgical stirring in the molten metal. Lower frequencies penetrate deeper and stir more vigorously, making them suitable for large melts, while higher frequencies are better for small, precise applications.
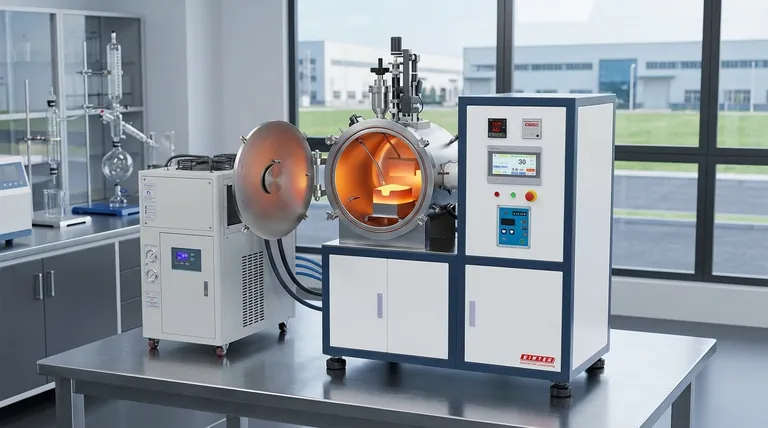

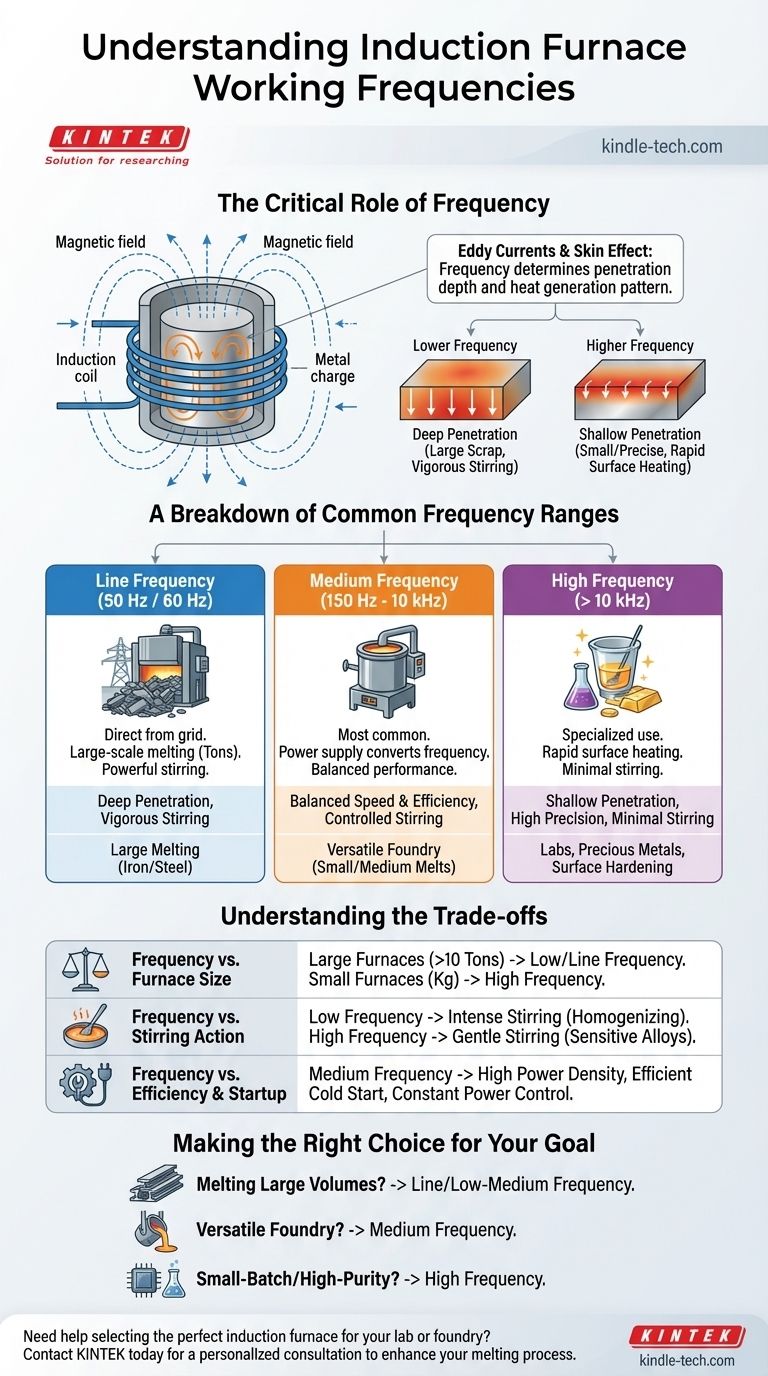
The Critical Role of Frequency in Induction Heating
To understand an induction furnace, you must understand the relationship between frequency and heating performance. The alternating current in the furnace's copper coil creates a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field. This field induces strong electrical currents, known as eddy currents, directly within the metal charge, generating immense heat through electrical resistance.
The "Skin Effect" and Penetration Depth
Frequency governs how deeply these eddy currents penetrate the metal—a phenomenon known as the skin effect.
A lower frequency results in a deeper penetration depth. This allows the magnetic field to "grip" and heat larger pieces of scrap metal from the core outwards, making it effective for large-capacity furnaces.
A higher frequency results in a very shallow penetration depth. The heating is concentrated near the surface of the material, which allows for extremely rapid heating of smaller pieces or powders.
A Breakdown of Common Frequency Ranges
Induction furnaces are generally categorized into three main frequency bands, each suited for different tasks.
Line Frequency (50 Hz / 60 Hz)
These are the original induction furnaces, operating directly from the grid's mains frequency. They are typically very large, used for melting tons of iron or holding molten metal. The deep energy penetration is ideal for large-diameter scrap, and the powerful magnetic field creates a very strong, turbulent stirring action in the molten bath.
Medium Frequency (150 Hz to 10 kHz)
This is the most common and versatile range for modern foundries. As mentioned in the technical descriptions, these units use a medium frequency power supply to convert line frequency into a more optimal range. This provides an excellent balance of melting speed, energy efficiency, and controlled stirring for small to medium-sized furnaces.
High Frequency (Above 10 kHz)
High-frequency furnaces are used for specialized applications. This includes laboratory furnaces for developing new alloys, melting small quantities of precious metals, or industrial processes like surface hardening where only the outer "skin" of a metal part needs to be heated. The stirring action is minimal, which is ideal for applications where gas inclusion is a concern.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a frequency involves balancing several interconnected factors. There is no single "best" frequency; there is only the right frequency for the job.
Frequency vs. Furnace Size
There is a direct correlation here. Very large furnaces (over 10 tons) almost always use low or line frequencies to effectively heat the massive volume of metal. Small, tabletop furnaces (a few kilograms) require high frequencies to efficiently couple with the small charge.
Frequency vs. Stirring Action
This is a critical metallurgical consideration. The intense stirring of a low-frequency furnace is excellent for homogenizing alloys and melting down fine metal chips that might otherwise float. However, this same turbulence can increase oxidization and damage refractories. The much gentler stir of a high-frequency furnace is better for sensitive alloys.
Frequency vs. Efficiency and Startup
Modern medium-frequency systems offer significant advantages. They have a higher power density, leading to faster melting times. As the references note, their sophisticated control systems with automatic frequency scanning and constant power circuits allow them to start efficiently with a cold charge and maintain high efficiency throughout the melt cycle, unlike older line-frequency units which often required a molten "heel" to start.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's primary objective will determine the ideal frequency range.
- If your primary focus is melting large volumes of iron and steel scrap: A line-frequency or low-end medium-frequency furnace is the most effective choice for its deep penetration and powerful stirring.
- If your primary focus is operating a versatile, general-purpose foundry: A medium-frequency furnace offers the best combination of melting speed, efficiency, and operational flexibility for a wide range of metals and melt sizes.
- If your primary focus is small-batch, high-purity metals or laboratory work: A high-frequency furnace provides the rapid heating and precise control necessary for these specialized tasks.
Ultimately, the operating frequency is the core parameter that defines how an induction furnace performs its task.
Summary Table:
| Frequency Range | Primary Applications | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Line Frequency (50/60 Hz) | Large-scale melting of iron/steel (tons) | Deep penetration, powerful stirring, ideal for large scrap |
| Medium Frequency (150 Hz - 10 kHz) | Versatile foundry work (most common) | Balanced speed, efficiency, and control for small/medium melts |
| High Frequency (>10 kHz) | Labs, precious metals, surface hardening | Rapid surface heating, minimal stirring, high precision |
Need help selecting the perfect induction furnace for your lab or foundry?
The working frequency is just one critical factor in achieving optimal melting performance. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing laboratory equipment and consumables, including induction furnaces tailored to your specific materials, batch sizes, and metallurgical goals.
Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between frequency, efficiency, and stirring action to ensure you get a system that delivers the results you need.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover how our solutions can enhance your melting process, improve your productivity, and ensure the highest quality results for your laboratory or production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of an induction melting furnace? Achieving Homogeneity in Fe-Cr-Ni Alloys
- What is the raw material of induction furnace? Metal, Refractory Lining, and More
- What is the benefit of induction heating? Unlock Unmatched Speed, Precision, and Cleanliness
- What is the primary purpose of using a high-temperature melting furnace for Chromel-TaC? Achieve Superior Homogeneity
- What is high frequency induction heating? Master Precision Surface Hardening & Brazing
- What is the capacity of an induction furnace? Find the Right Size for Your Lab or Foundry
- What frequency is required for induction heating? Match Frequency to Your Heating Depth
- What is the purpose of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Unmatched Metal Purity and Performance



















