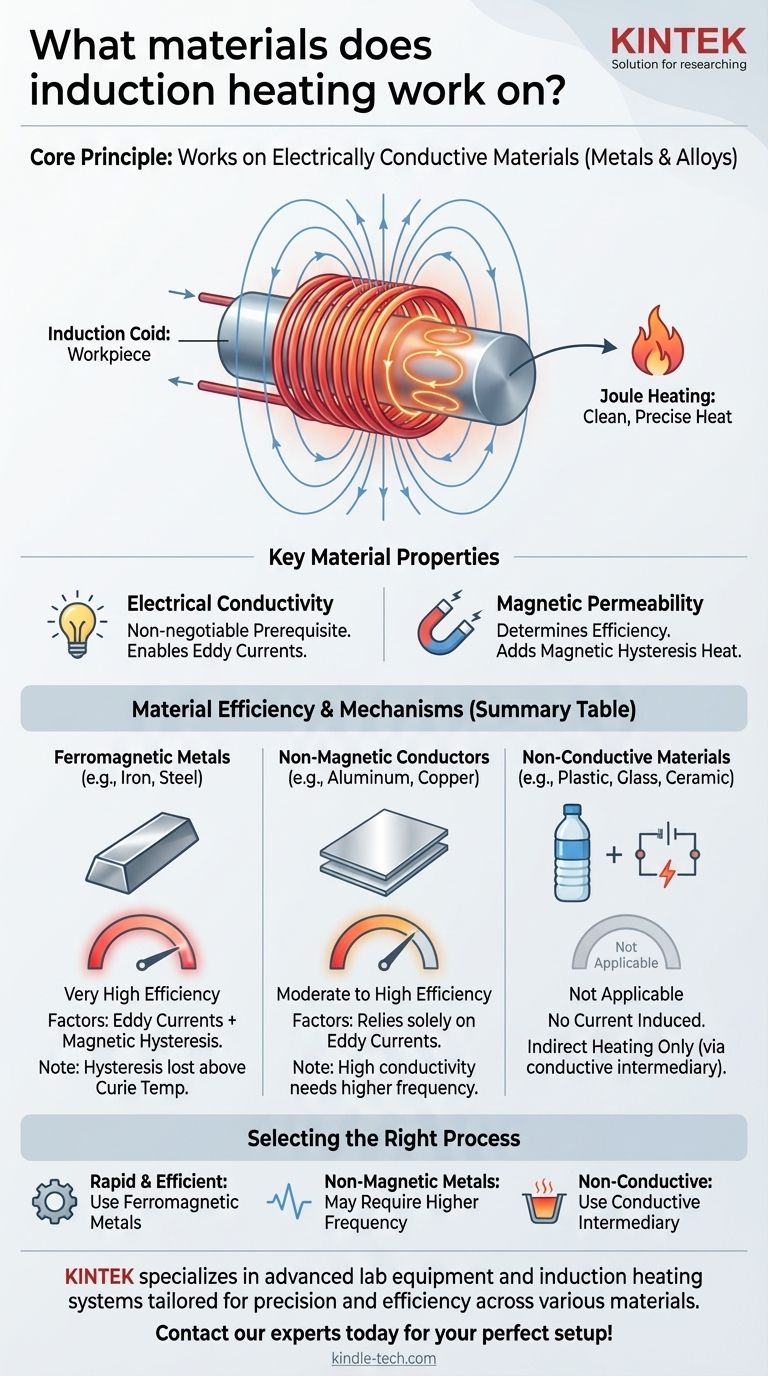
At its core, induction heating works on electrically conductive materials. This process is most effective with metals and their alloys, including common materials like iron, steel, stainless steel, copper, aluminum, and brass. The principle relies on generating electrical currents directly within the material itself to produce clean, precise heat.
The essential requirement for induction heating is electrical conductivity. However, a material's magnetic properties and electrical resistance are the two factors that determine how quickly and efficiently it will heat.
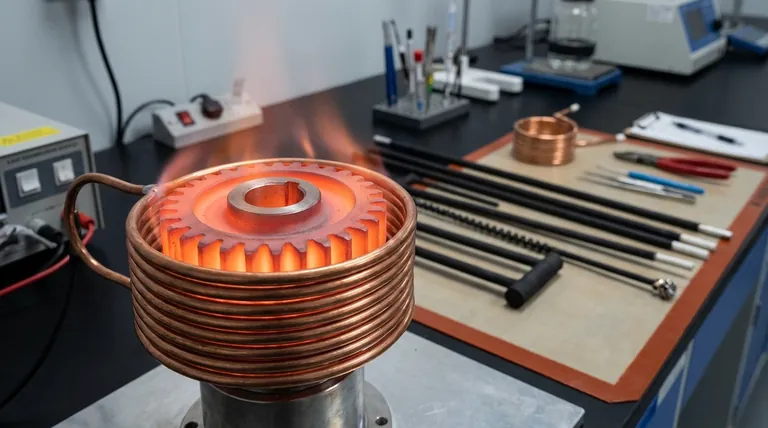
The Fundamental Principle: How Induction Heating Works
Induction is a non-contact heating method. It uses electromagnetic energy to generate heat inside a target material, rather than applying heat from an external source like a flame or heating element.
Generating a Magnetic Field
The process begins with an induction coil, typically made of copper tubing. A high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil. This flow of electricity generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space around the coil.
Creating Internal Electrical Currents
When an electrically conductive workpiece is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces electrical currents within the material. These are known as eddy currents. They are similar to the swirling eddies you see in a river.
The Role of Electrical Resistance
As these eddy currents flow through the material, they encounter electrical resistance. This resistance to the current's flow generates intense, localized heat through a process called Joule heating. It's the same fundamental principle that makes a stove's heating element glow red.
Key Material Properties for Effective Heating
While all conductive materials can be heated, some respond far better than others. The efficiency of the process is dictated by two primary material properties.
Electrical Conductivity
This is the non-negotiable prerequisite. If a material cannot conduct electricity, eddy currents cannot be induced, and no heating will occur. This is why metals are the primary candidates for induction.
Magnetic Permeability
For ferromagnetic materials like iron and many types of steel, an additional heating mechanism comes into play. These materials strongly resist the rapid changes in the magnetic field, creating internal friction. This effect, known as magnetic hysteresis, generates significant extra heat, making them heat up much faster than non-magnetic materials.
A Quick Comparison: Iron vs. Aluminum
Both iron and aluminum are excellent electrical conductors. However, iron is ferromagnetic while aluminum is not.
When placed in an induction coil, iron heats dramatically faster, especially at lower temperatures. This is because it benefits from both Joule heating (from eddy currents) and the powerful secondary effect of magnetic hysteresis. Aluminum relies only on Joule heating.
Understanding the Limitations and Nuances
The effectiveness of induction heating is not uniform across all conductive materials. Understanding the trade-offs is crucial for any practical application.
Why Non-Conductive Materials Don't Work
Materials like plastic, glass, wood, and ceramics are electrical insulators. Because they do not conduct electricity, an induction field cannot generate eddy currents within them. Therefore, they cannot be heated directly by this method.
The Challenge with Highly Conductive Metals
It may seem counter-intuitive, but materials with very high conductivity (and thus low resistance), such as copper and aluminum, can be more challenging to heat. Their low resistance generates less friction-like heat from the eddy currents. To heat them effectively, induction systems must often use a higher frequency to generate more powerful currents.
The Role of Temperature
For ferromagnetic materials like steel, the magnetic hysteresis effect disappears once the metal is heated past a certain point, known as the Curie temperature (around 770°C for iron). Above this temperature, the steel loses its magnetic properties and heats only through the effect of eddy currents, just like aluminum or copper.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material—or the right process for a given material—depends entirely on your goal.
- If your primary focus is rapid, efficient heating: Ferromagnetic metals like carbon steel, cast iron, and certain stainless steels are the ideal choice, leveraging both eddy currents and magnetic hysteresis.
- If you need to heat non-magnetic metals: Materials like aluminum, brass, and copper can be heated effectively but may require higher frequency equipment to compensate for their low electrical resistance.
- If you must heat a non-conductive material: You cannot do so directly. The only solution is to use a conductive intermediary (like a graphite crucible or a steel plate) that is heated by induction and transfers its heat to the non-conductive material.
Ultimately, mastering the induction process comes from understanding a material's fundamental electrical and magnetic properties.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Examples | Heating Efficiency | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ferromagnetic Metals | Iron, Carbon Steel, Some Stainless Steels | Very High | High electrical resistance & magnetic hysteresis |
| Non-Magnetic Conductors | Aluminum, Copper, Brass | Moderate to High | Relies solely on eddy currents (Joule heating) |
| Non-Conductive Materials | Plastic, Wood, Ceramics, Glass | Not Applicable | Cannot conduct electricity; no eddy currents induced |
Need to heat a specific material with precision and efficiency? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction heating systems tailored for conductive metals and alloys. Whether you're working with ferromagnetic steels or challenging conductors like copper, our solutions deliver clean, controlled, and rapid heating for your laboratory applications. Contact our experts today to find the perfect induction heating setup for your material and process requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a silicon carbide heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat for Industrial Processes
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace
- What are the uses of silicon carbide rod? The Ultimate Heating Solution for Extreme Temperatures
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution
- What kind of metal is used in heating elements? A Guide to Materials for Every Temperature & Atmosphere












