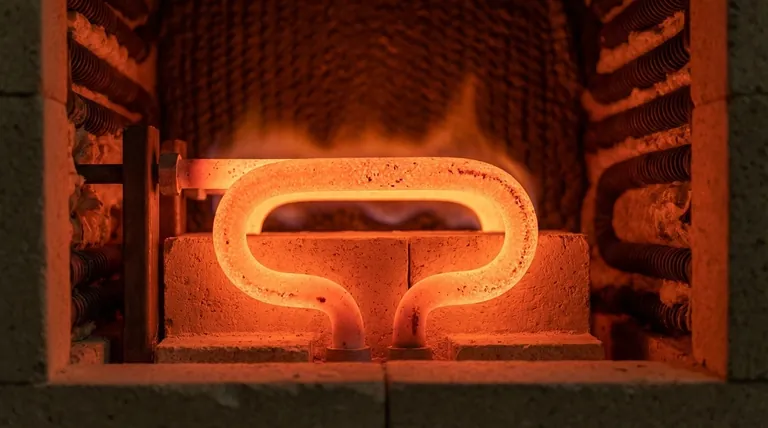
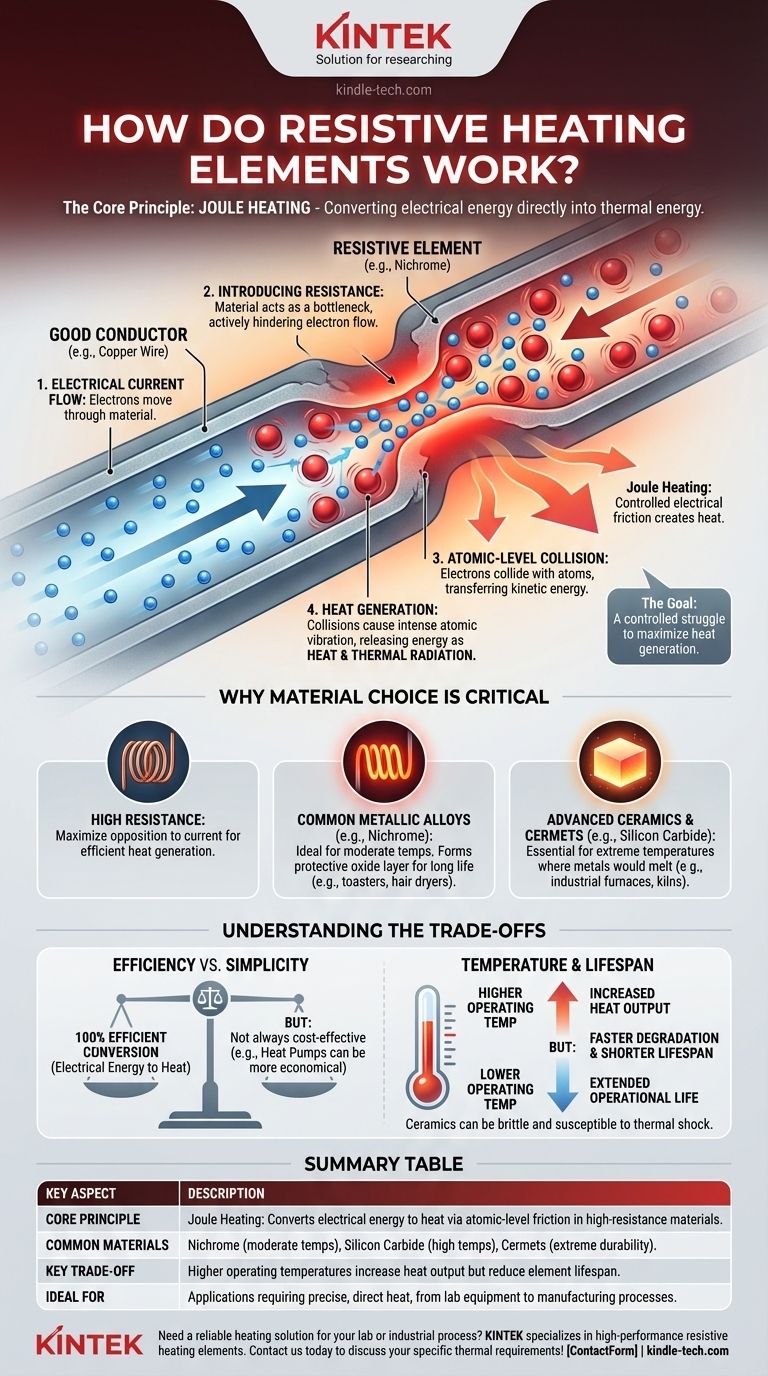
At its core, a resistive heating element works by converting electrical energy directly into thermal energy. This happens when an electrical current is passed through a material specifically chosen for its high electrical resistance. This opposition to the flow of electricity causes friction on an atomic scale, releasing energy in the form of heat in a process known as Joule heating.
The central principle is not just about using electricity, but about forcing that electricity through a material designed to intentionally impede its flow. This controlled struggle is what reliably and efficiently converts electrical energy into heat.

The Fundamental Principle: Joule Heating
To truly understand how this works, we need to look at the flow of electricity at a microscopic level. It's a simple but powerful concept.
The Flow of Electrons
An electric current is simply the movement of electrons through a material. In a good conductor, like a copper wire, electrons flow very easily with minimal obstruction.
Introducing Resistance
A resistive heating element, however, is made from a material that acts like a bottleneck for electrons. It has a high electrical resistance, meaning it actively hinders the flow of current.
Imagine trying to force a large amount of water through a very narrow, rough pipe. The friction between the water and the pipe walls would generate heat. This is a powerful analogy for what happens inside a resistive element.
The Atomic-Level Collision
As electrons are forced through the resistive material, they repeatedly collide with the atoms of that material. Each collision transfers kinetic energy from the electron to the atom, causing the atom to vibrate more intensely.
This widespread, intense vibration of the material's atoms is what we perceive and measure as heat. The element gets hot, glows, and radiates that thermal energy outward.
Why Material Choice is Critical
The specific material used for a heating element is the most important factor in its design. The goal is to select a material that not only has high resistance but can also survive extreme operating conditions.
High Resistance is the Goal
Materials like copper are excellent for wires because they have low resistance, minimizing energy loss. For a heating element, we want the exact opposite. We need a material that fights the current to maximize heat generation.
Common Metallic Alloys
The most common material is an alloy of nickel and chromium called Nichrome. It is ideal for many applications because it has high resistance and, crucially, forms a stable layer of chromium oxide on its surface when heated. This protective layer prevents it from oxidizing further and burning out, giving it a long service life in devices like toasters and hair dryers.
Advanced Ceramic Materials
For applications requiring much higher temperatures, such as industrial furnaces or kilns, metallic alloys would melt. Here, ceramic-based elements are used. Materials like silicon carbide or molybdenum disilicide can operate at extreme temperatures where metals would fail.
Ceramic Metals (Cermets)
Cermets are composite materials that combine the high-temperature resistance of a ceramic with some of the properties of a metal. They are engineered for specialized, high-performance heating applications that demand extreme durability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While resistive heating is a straightforward technology, it comes with practical limitations and design considerations that are important to understand.
Efficiency vs. Simplicity
Resistive heating is 100% efficient at converting electrical energy into heat. No energy is lost in the conversion process itself. However, this does not always make it the most cost-effective heating method. For heating a room, for example, a heat pump can be far more economical because it moves existing heat rather than generating it from scratch.
Temperature and Lifespan
There is a direct trade-off between an element's operating temperature and its lifespan. Running an element at its maximum rated temperature will generate the most heat, but it will also cause the material to degrade much faster, leading to premature failure.
Brittleness and Mechanical Stress
Many materials that excel at high temperatures, particularly ceramics, are often very brittle. They can be susceptible to cracking or breaking if subjected to physical shock or rapid, repeated temperature changes (thermal shock).
Matching the Element to the Application
The right choice of heating element is entirely dependent on the intended use case and required operating conditions.
- If your primary focus is common household appliances (toasters, space heaters): Metallic alloys like Nichrome are the standard, offering a superb balance of cost, performance, and durability for moderate temperatures.
- If your primary focus is industrial furnaces or semiconductor manufacturing: Advanced ceramic or cermet elements are the only viable choice to withstand the extreme and controlled temperatures required.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability at a moderate temperature: Designing the system to run a metallic element well below its maximum temperature rating will dramatically extend its operational life.
Ultimately, understanding this principle of controlled electrical friction is the key to engineering reliable and effective thermal systems.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Joule Heating: Converts electrical energy to heat via atomic-level friction in high-resistance materials. |
| Common Materials | Nichrome (moderate temps), Silicon Carbide (high temps), Cermets (extreme durability). |
| Key Trade-off | Higher operating temperatures increase heat output but reduce element lifespan. |
| Ideal For | Applications requiring precise, direct heat, from lab equipment to manufacturing processes. |
Need a reliable heating solution for your lab or industrial process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including durable resistive heating elements designed for precision and longevity. Whether you require standard metallic alloys or advanced ceramics for extreme conditions, our experts can help you select the ideal element to maximize efficiency and lifespan. Contact us today to discuss your specific thermal requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- What are the properties of molybdenum heating element? Choose the Right Type for Your Furnace Atmosphere



















