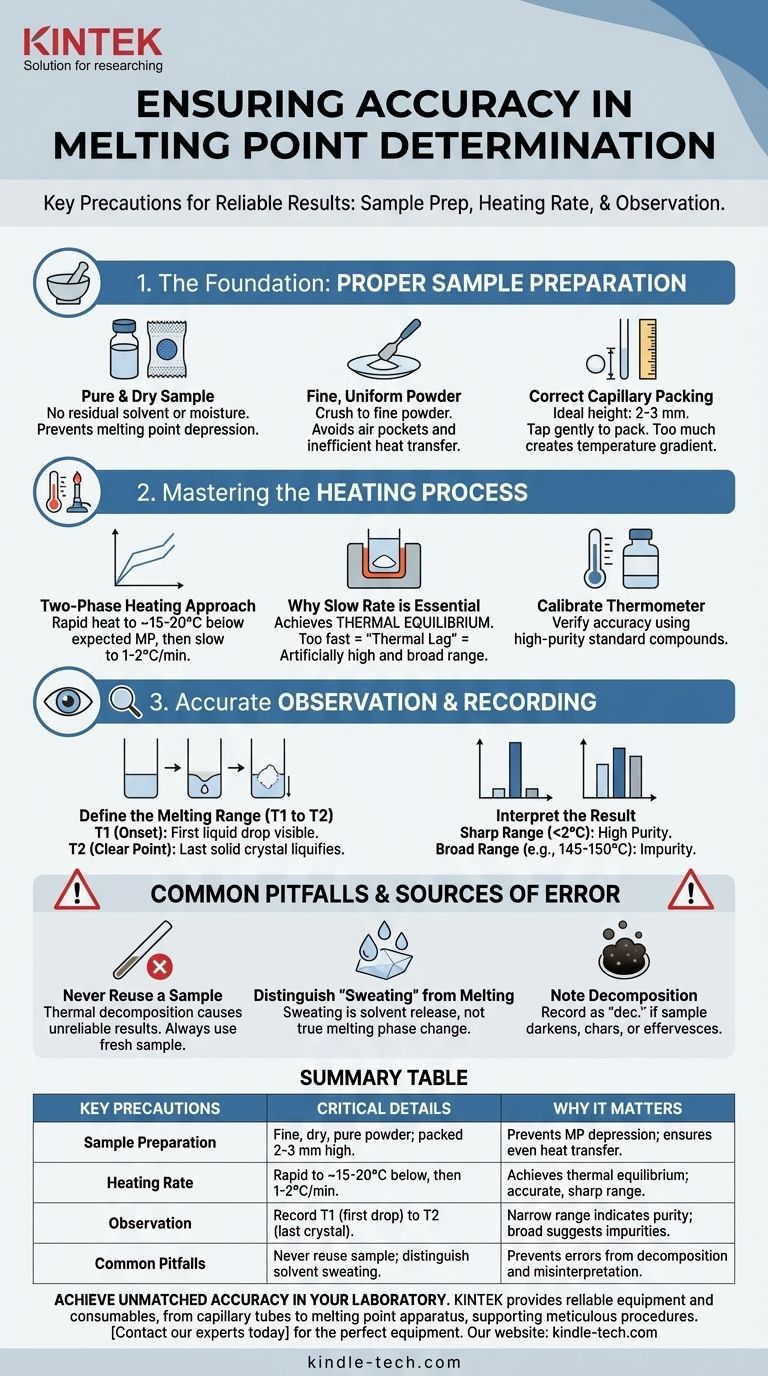
To ensure accuracy when determining a melting point, you must focus on three critical areas: meticulous sample preparation, precise control over the heating rate, and careful observation of the phase change. The most common errors arise from heating the sample too quickly, which prevents thermal equilibrium, and from improper packing of the capillary tube, which leads to uneven heat transfer.
The core principle of an accurate melting point determination is to ensure the sample and the thermometer are in perfect thermal equilibrium. This is achieved by heating the sample very slowly (1-2 °C per minute) so the thermometer reading accurately reflects the temperature at which the solid and liquid phases coexist.
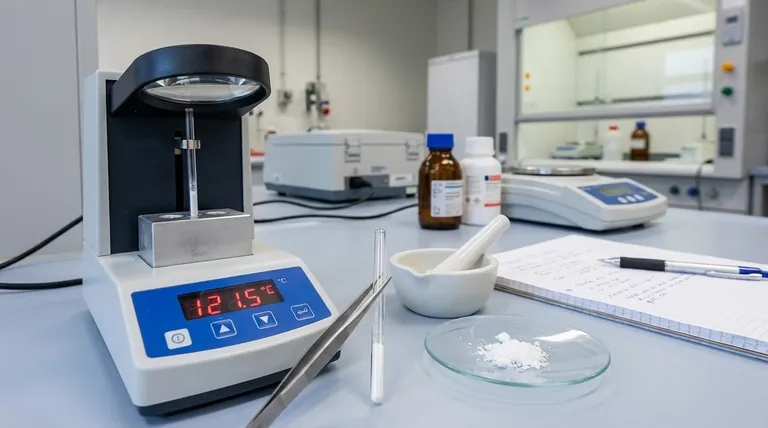

The Foundation: Proper Sample Preparation
Before you even turn on the heating apparatus, the state of your sample dictates the quality of your result. Errors introduced at this stage cannot be corrected later.
Ensure the Sample is Pure and Dry
Any residual solvent or moisture in your sample acts as an impurity. This will invariably lead to melting point depression, causing the substance to melt at a lower temperature and over a broader range than its pure form.
Create a Fine, Uniform Powder
Large crystals do not pack well and trap air pockets, leading to inefficient and uneven heat transfer. You must crush the sample into a fine, homogenous powder using a mortar and pestle or by crushing it on a watch glass with a spatula.
Pack the Capillary Tube Correctly
This is a frequent source of error. Press the open end of a capillary tube into your powdered sample. Invert the tube and tap it gently on the benchtop, or drop it down a long glass tube, to shake the powder to the bottom.
The ideal sample height in the tube is 2-3 mm. Too little sample is difficult to observe, while too much creates a significant temperature gradient within the sample itself, resulting in a broad melting range.
Mastering the Heating Process
The control you exert during heating is the single most important factor in obtaining an accurate reading.
Use a Two-Phase Heating Approach
Do not heat at a single, slow rate from room temperature. This is inefficient.
First, heat rapidly to about 15-20 °C below the expected melting point. Then, dramatically reduce the rate of heating to a slow, steady 1-2 °C per minute.
Why a Slow Rate is Essential
The goal is to maintain thermal equilibrium. If you heat too quickly, the temperature of the heating block will rise faster than the sample can absorb the heat. This "thermal lag" means your thermometer will read a higher temperature than the actual temperature of the sample, giving you an artificially high and broad melting range.
Calibrate Your Thermometer
For research-grade work, the accuracy of your thermometer must be verified. This is done by measuring the melting points of several high-purity standard compounds with well-known melting points that span a wide temperature range.
Accurate Observation and Recording
A melting point is not a single number but a range. How you define this range is critical for interpreting the result.
Define the Melting Range (T1 to T2)
The measurement consists of two temperatures.
- T1 is the onset point: The temperature at which the very first drop of liquid becomes visible within the sample.
- T2 is the clear point: The temperature at which the last solid crystal liquefies completely.
How to Interpret the Result
The recorded value is always presented as this range, for example, 121-122.5 °C. For a highly pure organic compound, this range should be very sharp and narrow, typically less than 2 °C. A broad melting range (e.g., 145-150 °C) is a strong indication that the sample is impure.
Common Pitfalls and Sources of Error
Even with careful technique, certain issues can arise that require correct interpretation.
Never Reuse a Sample
Once a sample has been melted, it may have undergone some thermal decomposition. Allowing it to re-solidify and re-melting it will often give a different, unreliable result. Always use a fresh sample in a new capillary tube for every measurement.
Distinguish "Sweating" from Melting
Sometimes, crystalline solids that are not perfectly dry will show droplets of liquid well before true melting begins. This is often solvent "sweating" from the crystal lattice. True melting begins when you see the solid phase itself begin to collapse into a liquid.
Note Any Decomposition
Some compounds decompose at or near their melting point. This is usually visible as the sample darkening, charring, or effervescing. If this occurs, the melting point should be recorded with the note "d" or "dec." for decomposition (e.g., 251 °C dec.).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The level of precision required depends on your objective.
- If your primary focus is identifying an unknown compound: Absolute accuracy is paramount for comparing your result to literature values. Meticulous sample preparation and a slow heating rate of 1°C/minute are non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is assessing the purity of a known compound: The sharpness and narrowness of the range are more indicative than the absolute number. A broad range is a clear sign of impurity, even if the thermometer is slightly uncalibrated.
- If your primary focus is a quick preliminary check: A faster heating rate can provide a rough estimate, but you must recognize this value will likely be inaccurate and should not be reported as a definitive result.
Mastering this fundamental technique provides a powerful and immediate insight into the identity and purity of your substance.
Summary Table:
| Key Precautions | Critical Details | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Preparation | Use a fine, dry, pure powder packed 2-3 mm high in a capillary tube. | Prevents melting point depression and ensures even heat transfer. |
| Heating Rate | Heat rapidly to ~15-20°C below expected MP, then slow to 1-2°C/min. | Achieves thermal equilibrium for an accurate, sharp melting range. |
| Observation | Record the range from the first liquid drop (T1) to the last crystal melting (T2). | A narrow range (<2°C) indicates high purity; a broad range suggests impurities. |
| Common Pitfalls | Never reuse a melted sample; distinguish solvent 'sweating' from true melting. | Prevents errors from decomposition and misinterpretation of the phase change. |
Achieve Unmatched Accuracy in Your Laboratory
Mastering melting point determination is fundamental for reliable results in compound identification and purity assessment. The precision of your equipment is just as critical as your technique.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. We provide the reliable tools—from high-quality capillary tubes to precisely calibrated melting point apparatus—that support the meticulous procedures outlined in this guide.
Ready to enhance your analytical capabilities? Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your specific application and ensure your measurements are consistently accurate and trustworthy.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Lab Electrochemical Workstation Potentiostat for Laboratory Use
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity















