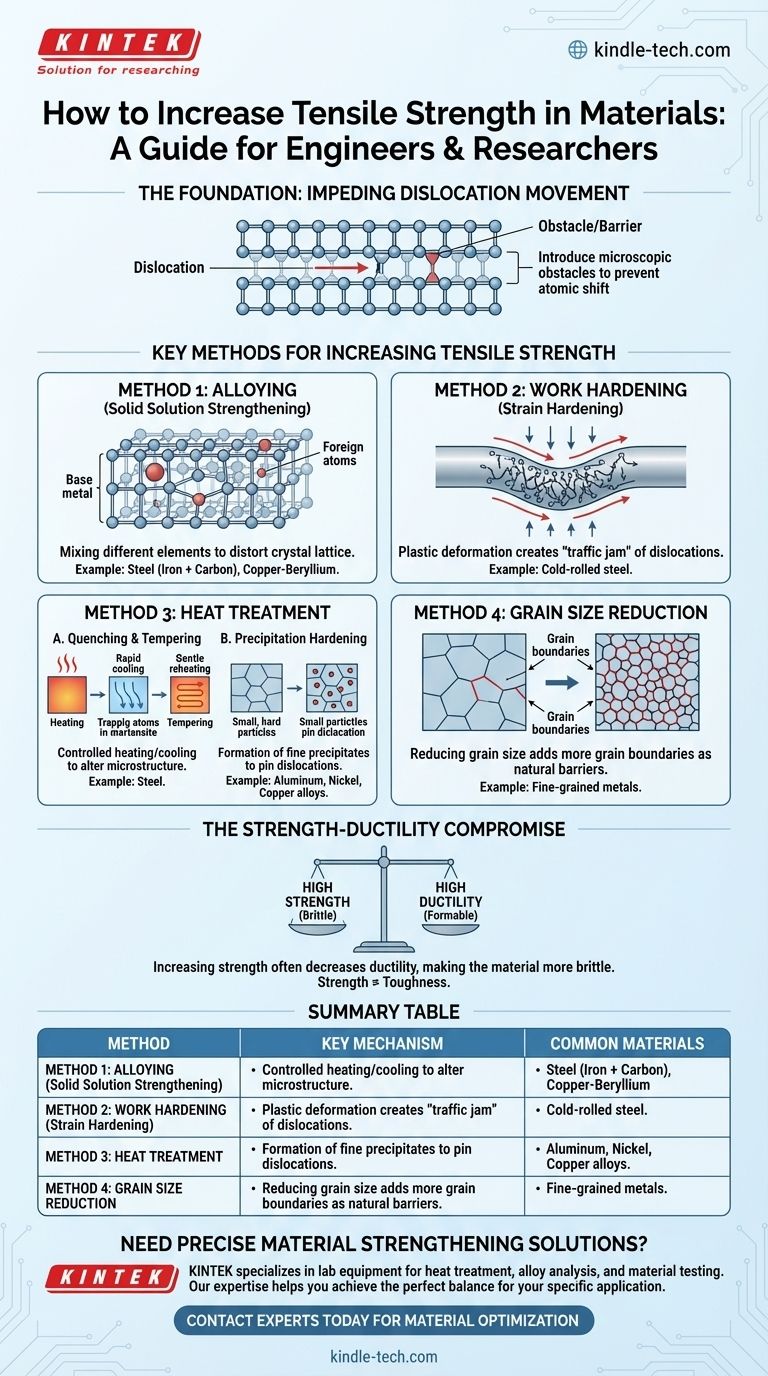
At its core, tensile strength is increased by introducing microscopic obstacles that prevent the internal crystal structure of a material from shifting under load. The most common methods for creating these obstacles are alloying the material with other elements, deforming it through work hardening, and altering its crystal structure with precise heat treatments.
The central challenge in material science is not merely increasing strength, but managing the inherent trade-off. Almost every method that increases a material's tensile strength will decrease its ductility, making it more brittle.

The Foundation: How Materials Resist Force
Understanding the Crystal Lattice
Most metals are crystalline, meaning their atoms are arranged in a highly organized, repeating grid called a lattice. This structure is what gives metals their fundamental properties.
The Role of Dislocations
Within this perfect lattice, there are always imperfections known as dislocations. You can visualize a dislocation as an extra half-plane of atoms inserted into the crystal structure.
When a force is applied, it is the movement of these dislocations through the lattice that allows the material to deform permanently, rather than snapping like glass.
The Goal: Impeding Dislocation Movement
To increase a material's tensile strength, you must make it more difficult for these dislocations to move. The entire science of strengthening metals revolves around creating barriers and "pinning" these dislocations in place.
Key Methods for Increasing Tensile Strength
Method 1: Alloying (Solid Solution Strengthening)
This involves mixing different elements into the base metal. The added atoms distort the crystal lattice, creating stress fields that act as roadblocks for dislocation movement.
The provided reference highlights this perfectly: adding carbon to iron disrupts its lattice to create steel, a material vastly stronger than pure iron. Similarly, adding beryllium to copper creates an alloy with exceptional strength.
Method 2: Work Hardening (Strain Hardening)
This method involves strengthening a metal by plastically deforming it at a temperature below its recrystallization point. Bending, rolling, or drawing a metal creates a high density of new dislocations.
These new dislocations become tangled and interfere with one another, effectively creating a "traffic jam" that makes further movement—and thus further deformation—much more difficult. This is why a paperclip becomes harder to bend after you've bent it back and forth a few times.
Method 3: Heat Treatment
Heat treatment modifies a material’s strength by controlling heating and cooling rates to produce different microscopic structures (phases).
Quenching and Tempering are common for steel. Rapidly cooling (quenching) steel from a high temperature traps its atoms in a very strong but brittle structure called martensite. Subsequent, gentler heating (tempering) relieves some internal stress, sacrificing a small amount of strength to regain crucial toughness.
Precipitation Hardening is used for aluminum, nickel, and copper alloys. This process involves a heat treatment that causes extremely small, hard particles (precipitates) to form within the material's grain structure. These particles are powerful obstacles that effectively pin dislocations.
Method 4: Grain Size Reduction
Metals are made of many individual crystals, or "grains." The boundary where two grains meet acts as a natural barrier to dislocation movement.
By reducing the average grain size, you increase the total area of these grain boundaries. More boundaries mean more obstacles, which results in a higher tensile strength. Grain size is typically controlled during the casting or heat treatment process.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Strength-Ductility Balance
The Inevitable Compromise
Increasing tensile strength is not a "free lunch." As you make it harder for dislocations to move, you also reduce the material's ability to deform before it fractures. This property is known as ductility.
A highly strengthened material is often more brittle. It can withstand a greater load, but it will fail with little to no warning or visible deformation.
Strength vs. Toughness
It's also critical to distinguish strength from toughness. Toughness is a material's ability to absorb energy and resist fracture, especially in the presence of a flaw.
Making a material extremely strong can sometimes lower its toughness, making it more susceptible to catastrophic failure from a small crack or notch. This is a primary concern in structural and aerospace engineering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a strengthening strategy depends entirely on the intended application and its specific performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength at any cost: You will likely use a heavily alloyed material combined with an aggressive heat treatment, but you must design for the resulting low ductility and potential brittleness.
- If your primary focus is formability during manufacturing: You might start with a softer, more ductile material and use the work hardening from the forming process itself to achieve the final desired strength in the finished part.
- If your primary focus is a balance of strength, toughness, and reliability: You will likely choose a well-understood alloy and a standard heat treatment protocol, such as quenching and tempering for steel, to achieve proven, predictable properties.
Ultimately, mastering material strength lies in controlling its microscopic structure to achieve your specific engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Mechanism | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Alloying | Distorts crystal lattice with foreign atoms | Steel (Iron + Carbon), Copper-Beryllium |
| Work Hardening | Increases dislocation density through deformation | Metals (e.g., cold-rolled steel) |
| Heat Treatment | Alters microstructure via controlled heating/cooling | Steel (Quenching/Tempering), Aluminum alloys |
| Grain Size Reduction | Adds grain boundaries as dislocation barriers | Fine-grained metals and alloys |
Need precise material strengthening solutions for your lab or production? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for heat treatment, alloy analysis, and material testing. Our expertise helps you achieve the perfect balance of strength, ductility, and toughness for your specific application. Contact our experts today to optimize your material performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tube Racks
People Also Ask
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification


















