In short, Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is a high-pressure thermal treatment used to improve material properties and manufacture components for the most demanding applications. It is primarily applied in the aerospace, medical, automotive, and energy industries to create parts like jet engine turbines, medical implants, and high-performance engine components by eliminating internal defects and increasing density.
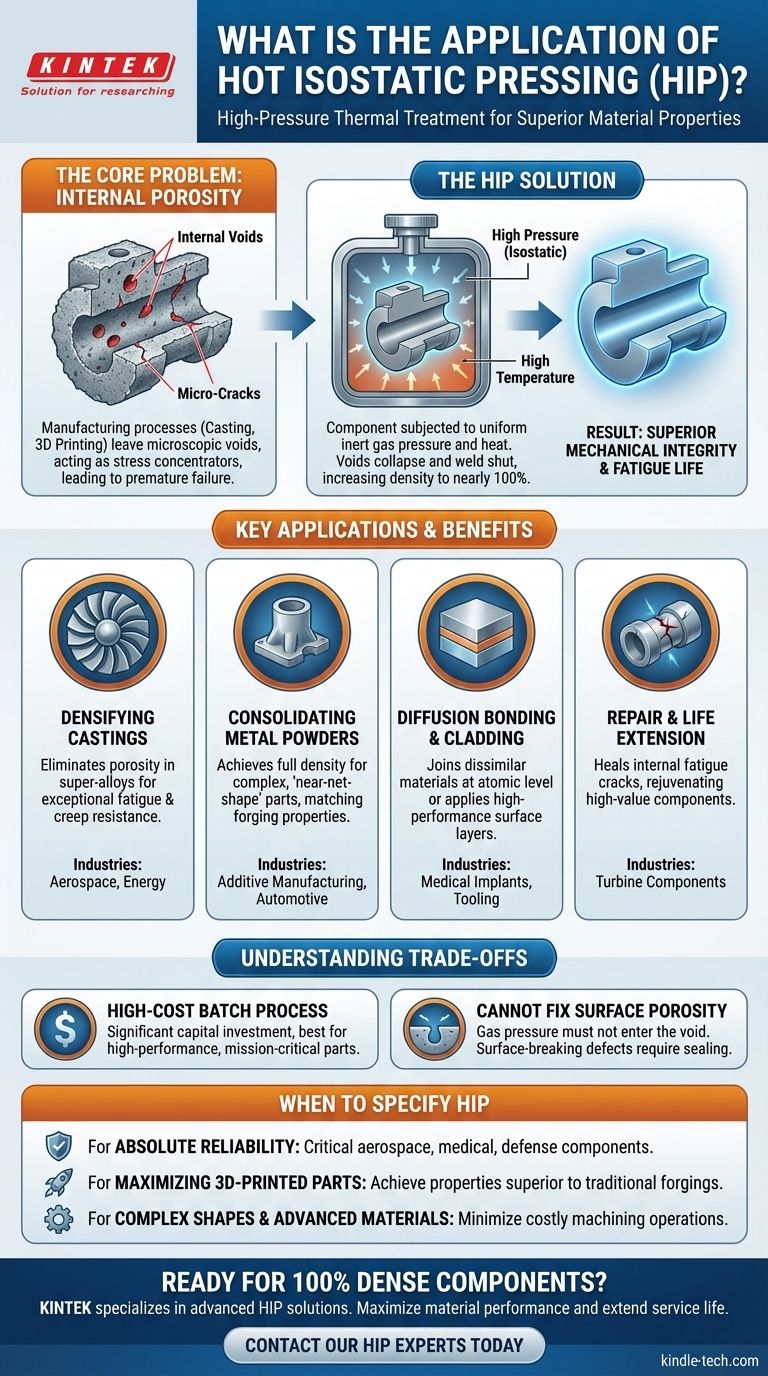
The core problem HIP solves is the presence of microscopic internal voids, or porosity, left behind by manufacturing processes like casting or 3D printing. By subjecting a part to immense, uniform pressure at high temperatures, HIP effectively collapses these voids, creating a fully dense material with superior mechanical integrity.

The Fundamental Problem: Internal Porosity
Manufacturing components, especially those with complex geometries, is an imperfect science. Processes like metal casting, powder metallurgy, and even additive manufacturing (3D printing) can leave behind tiny internal voids.
Why Internal Voids Are Critical Failures
These microscopic pores and cavities act as stress concentrators. Under operational loads, cracks can initiate at these voids and propagate through the material, leading to premature fatigue and catastrophic failure.
For a component like an aircraft turbine blade or a surgical implant, such a failure is not an option. This is the precise problem HIP was developed to solve.
How HIP Provides the Solution
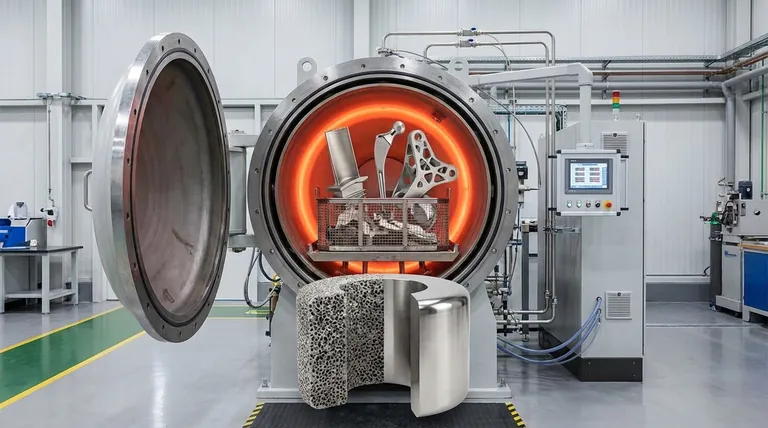
The HIP process places a component inside a sealed, high-pressure vessel. The vessel is then filled with an inert gas, typically argon, and heated.
As the temperature rises, the material becomes more plastic or malleable. Simultaneously, the immense, uniform (isostatic) pressure from the gas acts on the component from all directions. This pressure differential between the outside and the inside of the internal voids causes them to collapse and weld shut on an atomic level.
The result is a component that is theoretically 100% dense, with its internal structure and mechanical properties dramatically improved.
Key Applications of HIP
The ability to eliminate internal defects makes HIP a critical finishing step or a primary manufacturing method across several high-value industries.
Densifying High-Performance Castings
Many critical components, such as super-alloy gas turbine blades or titanium structural airframe parts, are initially created by investment casting. HIP is applied after casting to remove any resulting porosity.
This densification step is what gives these parts their exceptional resistance to fatigue, creep, and extreme temperatures, ensuring reliability in service.
Consolidating Metal Powders
HIP is fundamental to powder metallurgy (PM) and additive manufacturing (AM). It can take a part made of loosely bonded metal powder and consolidate it into a fully solid, high-performance component.
This allows for the creation of complex, "near-net-shape" parts that require very little final machining, reducing waste and cost for materials that are difficult to work with.
Diffusion Bonding and Cladding
HIP provides the perfect environment—high heat and pressure—to bond dissimilar materials together at an atomic level without melting them.
This process, known as diffusion bonding or HIP cladding, is used to create bimetallic parts or apply a high-performance surface layer (e.g., for wear or corrosion resistance) onto a less expensive substrate.
Repair and Service Life Extension
High-value components that develop internal micro-cracks from operational fatigue, such as turbine blades, can be rejuvenated using HIP.
The process can heal these internal fatigue cracks, effectively resetting the component's service life and saving significant replacement costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, HIP is not a universal solution. Its application involves specific considerations and limitations.
It Is a High-Cost Batch Process
HIP equipment is a significant capital investment, and the process treats parts in batches within a chamber. This makes it less suitable for high-volume, low-cost commodity parts and best reserved for components where performance and reliability justify the cost.
It Cannot Fix Surface-Connected Porosity
The HIP process relies on gas pressure acting on the exterior of the part. If a pore is connected to the surface, the pressurized gas will simply fill the void, creating equilibrium and preventing it from collapsing.
Parts with surface-breaking defects must be sealed, often by canning them in a disposable metal container, before undergoing HIP.
When to Specify HIP for Your Project
Choosing to use HIP is a strategic decision based on the final requirements of your component.
- If your primary focus is absolute reliability and fatigue life: HIP is essential for critical components in aerospace, medical, and defense applications where material failure would be catastrophic.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the performance of 3D-printed metal parts: Use HIP as a post-processing step to achieve mechanical properties that are comparable to or exceed those of traditional forgings.
- If your primary focus is creating complex shapes from advanced materials: Leverage HIP to consolidate powdered metals into near-net-shape components, minimizing difficult and costly machining operations.
Ultimately, applying HIP is a strategic decision to trade upfront process costs for unparalleled material integrity and in-service performance.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Benefit | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Densifying Castings | Eliminates porosity, improves fatigue life | Aerospace, Energy |
| Consolidating Metal Powders | Creates fully dense, near-net-shape parts | Additive Manufacturing, Automotive |
| Diffusion Bonding | Joins dissimilar materials without melting | Medical Implants, Tooling |
| Repair & Life Extension | Heals internal fatigue cracks | Turbine Components, High-Value Parts |
Ready to achieve 100% dense, high-performance components?
KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions, including Hot Isostatic Pressing systems and services. Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables helps manufacturers in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries eliminate internal defects and maximize material performance.
Contact our HIP experts today to discuss how we can enhance your component reliability and extend service life.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve 100% Density and Superior Performance
- How much energy does hot isostatic pressing consume? Unlock Net Energy Savings in Your Process
- What are the components of a hot isostatic pressing system? A Guide to Core HIP Equipment
- What pressure is hot isostatic press? Achieve Full Density & Superior Material Performance
- What is the historical background of the Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) process? From Nuclear Roots to Industry Standard



















