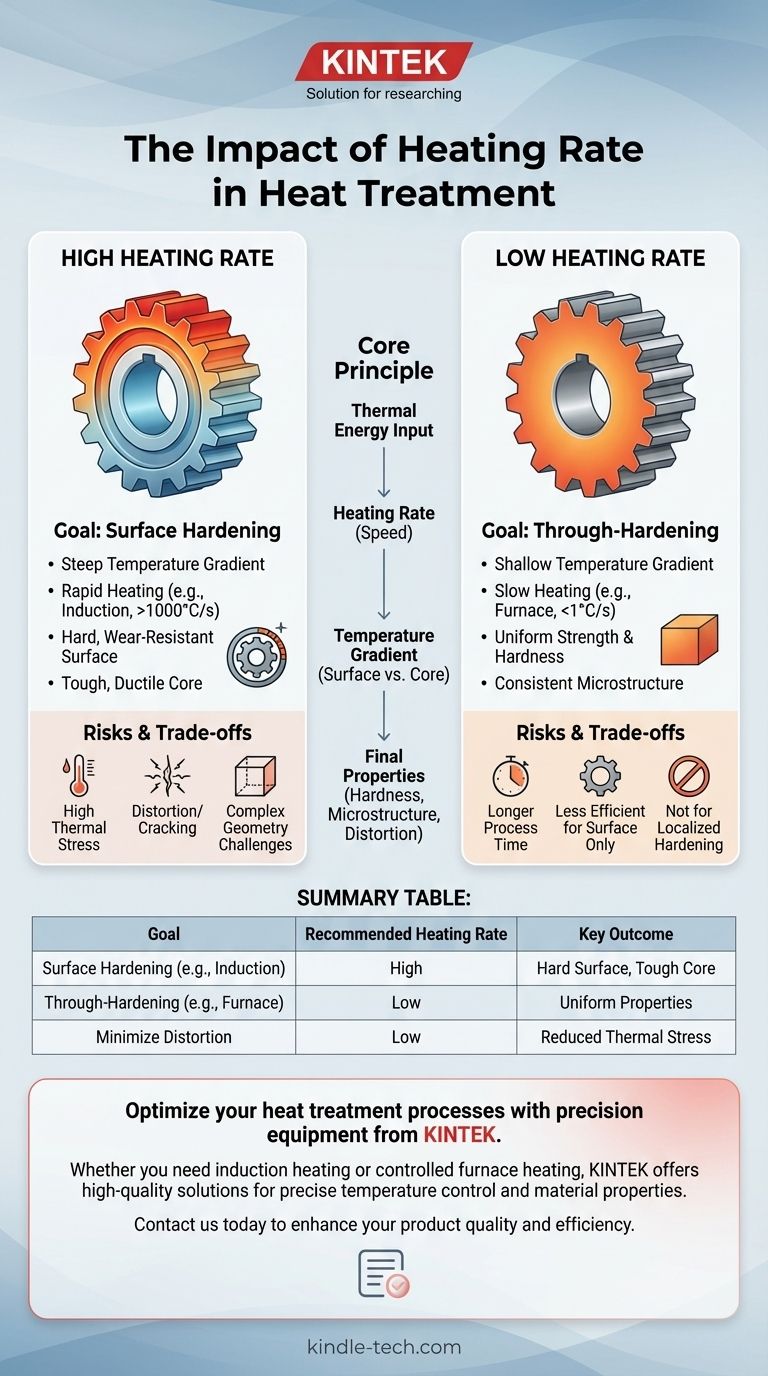
In heat treatment, the heating rate is a critical control lever. It directly determines the temperature difference between the surface and the core of a workpiece. This gradient dictates the final depth of hardness, the resulting microstructure, and the potential for distortion or cracking, making it one of the most important variables in the entire process.
Choosing the right heating rate is a fundamental trade-off. You are balancing the goal of achieving specific surface properties, like wear resistance, against the need to manage internal stresses and maintain the desired properties of the component's core.

The Core Principle: Temperature Gradients and Transformation
The effect of heating rate is fundamentally about how quickly you introduce thermal energy and how the material responds.
What is Heating Rate?
Heating rate is the speed at which a material's temperature increases, typically measured in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit per second (°C/s or °F/s). A rate can be very slow in a furnace (less than 1°C/s) or extremely fast with induction heating (over 1000°C/s).
The Impact on Temperature Gradient
A fast heating rate creates a steep temperature gradient. The surface of the part becomes extremely hot very quickly, while the core remains relatively cool. This is the key principle behind surface hardening.
A slow heating rate creates a shallow temperature gradient. The entire part, both surface and core, heats up more uniformly, minimizing the temperature difference across its cross-section. This is essential for through-hardening.
How Rate Affects Austenitization
For steel, heat treatment involves transforming the initial microstructure into a phase called austenite before quenching. The heating rate affects this transformation. A slower rate provides more time for carbon atoms to dissolve evenly into the austenite, leading to a more uniform structure. Extremely rapid heating can result in a finer austenite grain size and potentially incomplete carbon dissolution if not controlled properly.
High vs. Low Heating Rates: Practical Applications
Different heating rates are chosen to achieve specific, often opposite, engineering goals.
High Heating Rates: The Goal of Surface Hardening
The primary application for high heating rates is surface hardening, also known as case hardening. The goal is to create a component with a very hard, wear-resistant surface while maintaining a softer, tougher, and more ductile core.
A perfect example is induction heating. By applying a high-frequency alternating current, heat is generated rapidly and concentrated only on the surface of the part. As the reference material notes, a higher frequency creates a thinner heated layer, allowing for precise control over the case depth.
This rapid surface heating followed by a fast quench transforms only the outer layer to hard martensite, leaving the core unaffected and tough.
Low Heating Rates: The Goal of Through-Hardening
Low heating rates are used when the objective is to achieve uniform properties throughout the entire component. This process is called through-hardening or quench and tempering.
By heating the part slowly in a furnace, thermal energy soaks through the entire cross-section. This ensures the core reaches the same austenitizing temperature as the surface. When the entire part is then quenched, it hardens uniformly from surface to core, maximizing overall strength and hardness.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
The choice of heating rate is not without consequences. Each approach has inherent risks and benefits that must be carefully managed.
The Risk of Distortion and Cracking
The most significant risk associated with high heating rates is thermal stress. The steep temperature gradient between the hot surface and cool core causes the surface to expand rapidly, creating immense internal stress. In parts with complex geometries, sharp corners, or thin sections, this stress can cause warping (distortion) or even cracking.
The Challenge of Microstructure Control
While fast heating is effective, if the rate is excessive or the time at temperature is too short, the transformation to austenite may be incomplete. Not all the carbon may dissolve and diffuse properly, which can result in a lower-than-expected hardness after quenching.
The Cost and Process Factor
High-rate processes like induction heating require specialized equipment and tooling, which can be a significant capital investment. However, they are extremely fast and energy-efficient for high-volume production. Furnace heating is slower and less efficient for surface treatments but is more versatile for a wide range of part sizes and for achieving through-hardening.
Selecting the Right Heating Rate for Your Goal
Your choice of heating rate must be driven by the final performance requirements of the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum surface wear resistance: Opt for a high heating rate process like induction or flame hardening to create a hard case with a tough, ductile core.
- If your primary focus is achieving uniform strength and hardness throughout a component: Use a slow, controlled heating rate in a furnace to ensure even temperature distribution and transformation before quenching.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion in a complex part: A slower heating rate is generally safer, as it reduces the thermal gradients that cause internal stress during the heating cycle.
Ultimately, mastering the heating rate allows you to precisely engineer the material properties to match the part's intended function.
Summary Table:
| Goal | Recommended Heating Rate | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Hardening (e.g., induction) | High | Hard, wear-resistant surface; tough, ductile core |
| Through-Hardening (e.g., furnace) | Low | Uniform strength and hardness throughout the component |
| Minimize Distortion | Low | Reduced thermal stress and warping in complex parts |
Optimize your heat treatment processes with precision equipment from KINTEK.
Whether you require the rapid, localized heating of induction for surface hardening or the uniform, controlled heating of a furnace for through-hardening, the right equipment is critical to achieving your desired material properties and avoiding costly defects like distortion.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab and industrial equipment, including furnaces and heating systems, designed to provide the precise temperature control your applications demand. Our experts can help you select the ideal solution to master heating rates for your specific materials and components.
Contact us today to discuss your heat treatment challenges and discover how our solutions can enhance your product quality and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance
- What is vacuum furnace high temperature? Unlock the Range for Your Material Processing
- What are the uses of vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance
- How does a vacuum heat treatment work? Achieve Superior Material Properties in a Pristine Environment
- Why do you vacuum for heat treatment? Achieve Flawless, High-Performance Metal Components



















