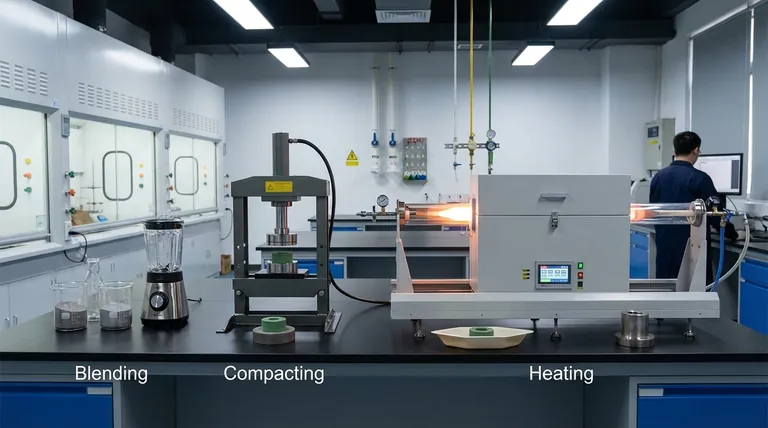
In powder metallurgy, the three-step sintering process refers to the fundamental manufacturing stages of Blending, Compacting, and Heating. This sequence transforms loose powders into a solid, high-density component. By applying pressure and then heat at a temperature below the material's melting point, the individual particles are forced to bond and fuse, drastically reducing the porous space between them.
While often described as a three-stage manufacturing process (Blending, Compacting, Heating), the true transformation occurs during the heating stage itself, which involves its own distinct physical phases. Understanding both the high-level workflow and the micro-level physics is key to controlling the final properties of a sintered part.
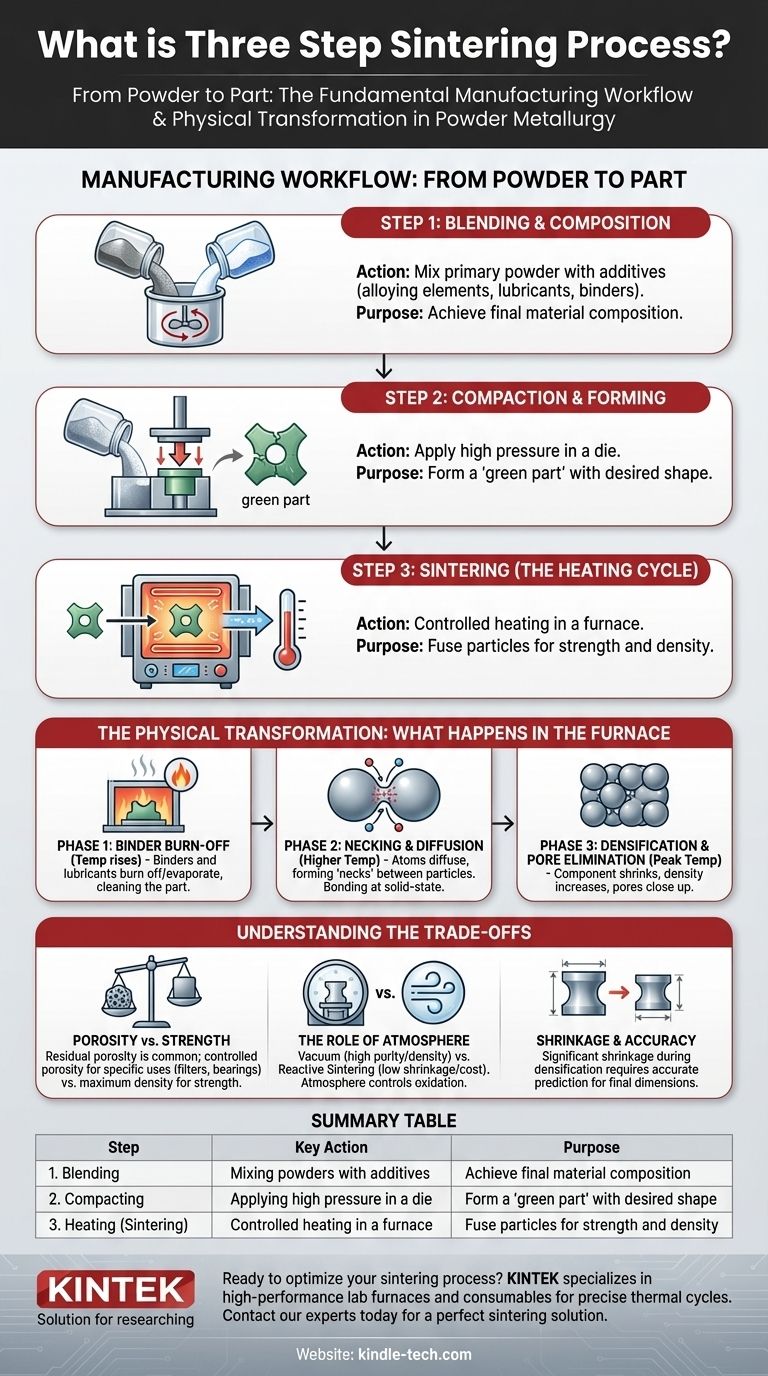
The Manufacturing Workflow: From Powder to Part
The most common way to describe the sintering process is as a three-step manufacturing workflow. This perspective focuses on the practical actions required to turn raw powder into a finished component.
Step 1: Blending and Composition
This initial stage is where the material science happens. The primary metal or ceramic powder is precisely mixed with other elements.
These additions can include alloying elements to enhance strength or corrosion resistance, lubricants to aid in the compaction process, or a temporary binder to hold the shape together before heating. The final composition of this blend dictates the properties of the finished part.
Step 2: Compaction and Forming
The blended powder is placed into a die or mold and subjected to high pressure. This compaction process forces the particles into close contact, forming a fragile object known as a "green part."
This green part has the desired shape and dimensions but possesses very low mechanical strength. It is dense enough to be handled but requires the final heating step to achieve its intended durability.
Step 3: Sintering (The Heating Cycle)
The green part is placed into a controlled-atmosphere furnace and heated. The temperature is raised to a specific point below the material's melting point but high enough to initiate atomic bonding.
During this thermal cycle, the particles fuse together, the part shrinks, and its density increases significantly, resulting in a solid, strong final component.
The Physical Transformation: What Happens in the Furnace
While heating is a single manufacturing "step," it involves several distinct physical phases. Understanding these phases is critical for controlling the outcome.
Phase 1: Binder Burn-Off
As the furnace temperature initially rises, any temporary binders (like wax or polymers) or lubricants mixed into the powder are burned away or evaporated.
This step cleans the part, leaving behind only the primary metallic or ceramic particles. The atmosphere in the furnace is controlled to ensure this process happens without negatively impacting the material.
Phase 2: Necking and Diffusion
As the temperature climbs higher, the atoms at the contact points between powder particles become highly mobile. This mobility allows atoms to diffuse across the boundaries, forming small bridges or "necks" between adjacent particles.
This is the core of the sintering process. The material does not melt into a liquid; instead, it bonds at a solid-state level, much like two soap bubbles merging at their point of contact.
Phase 3: Densification and Pore Elimination
As the necks grow, they pull the particles closer together, causing the entire component to shrink and become more dense. The small voids or pores between the original powder particles gradually close up.
The duration and peak temperature of the heating cycle determine the extent of this densification. Longer times or higher temperatures result in a denser, stronger part, but also greater shrinkage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sintering is a powerful process, but it involves critical trade-offs that engineers must manage.
Porosity vs. Strength
While sintering dramatically reduces porosity, it rarely eliminates it completely. A small amount of residual porosity is common in sintered parts. This can be a weakness, but in some applications like self-lubricating bearings or filters, controlled porosity is a desired feature.
The Role of Atmosphere
The process is highly sensitive to the furnace atmosphere. Sintering in a vacuum removes gases and prevents oxidation, leading to high-purity, high-density products. In contrast, reaction sintering uses a reactive gas to form a new compound during heating, which can offer benefits like low shrinkage and lower production cost.
Shrinkage and Dimensional Accuracy
Because sintering involves densification, the part will shrink during the heating cycle. This shrinkage must be accurately predicted and accounted for in the initial mold design to achieve the desired final dimensions.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of process parameters depends entirely on the goals for your final component.
- If your primary focus is creating complex shapes at a low cost: Standard press-and-sinter methods are highly effective, but you must carefully manage binder burn-off and predict shrinkage.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum purity and density: Vacuum sintering is the superior choice, as it prevents oxidation and helps remove trapped gases from the part's interior.
- If your primary focus is final part strength: Pay close attention to the heating cycle, as time and temperature directly control the atomic diffusion and densification that build strength.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering process means controlling the interplay between powder composition, compaction pressure, and the precise thermal cycle to engineer the exact material properties required.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Blending | Mixing powders with additives | Achieve final material composition |
| 2. Compacting | Applying high pressure in a die | Form a 'green part' with the desired shape |
| 3. Heating (Sintering) | Controlled heating in a furnace | Fuse particles for strength and density |
Ready to optimize your sintering process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and consumables for precise thermal cycles. Whether you need a vacuum furnace for maximum purity or a controlled-atmosphere model for reaction sintering, our equipment ensures consistent, high-quality results for your laboratory. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect sintering solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- Why are quartz tubes preferred for chromium powder combustion? Superior Heat Resistance & Optical Clarity
- What is the function of quartz tubes and vacuum sealing systems? Secure Your High-Purity Solid Solution Synthesis
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What are the primary functions of high-precision tube furnaces in graphene growth? Achieve Defect-Free GS Synthesis
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results



















