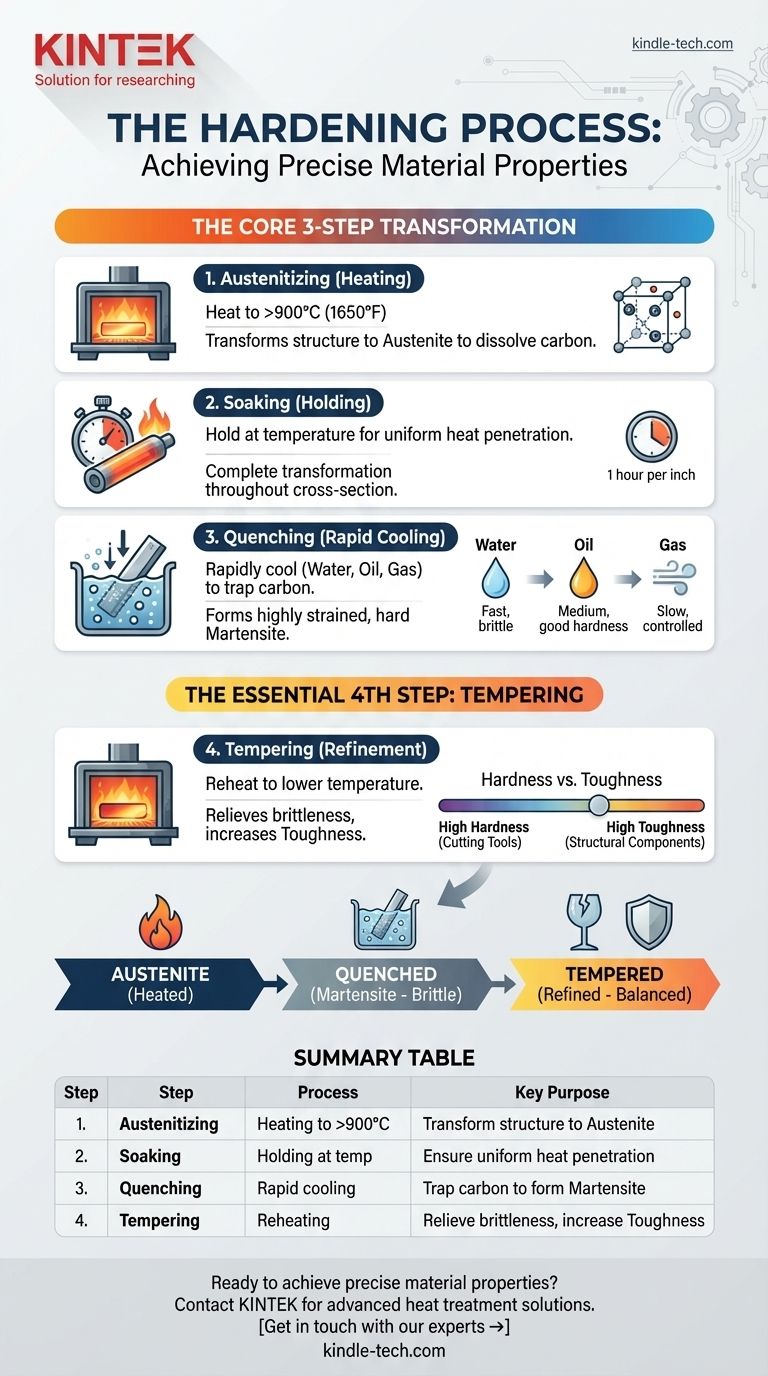
In essence, the hardening process consists of three core steps. It begins with heating the metal to a specific transformation temperature, holding it there to ensure a uniform internal structure, and then rapidly cooling it (quenching) to lock in that new structure. However, a critical fourth step, tempering, is almost always required to refine the final properties of the material.
The goal of hardening is not simply to make a metal harder; it is a controlled thermal process designed to manipulate a material's internal crystalline structure. The key is understanding that rapid cooling creates extreme hardness but also extreme brittleness, which must then be managed through tempering to achieve a useful balance of strength and toughness.

The Core Hardening Process: A Three-Step Transformation
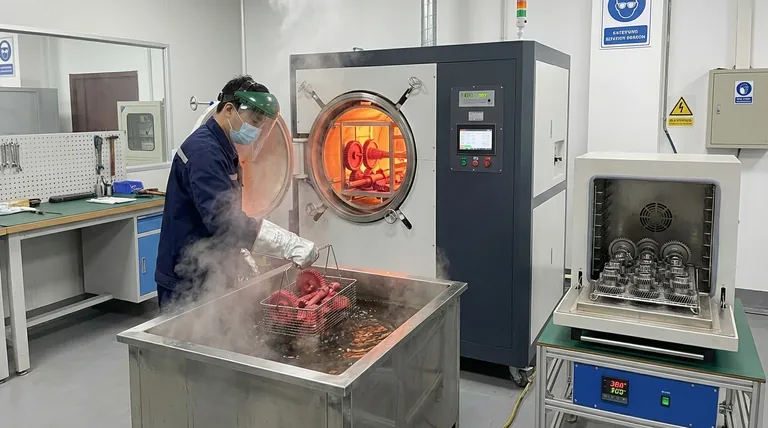
Hardening is a fundamental heat treatment that fundamentally alters the physical properties of steel and certain other alloys. Each step serves a precise metallurgical purpose.
Step 1: Austenitizing (Heating)
The process begins by heating the steel in a furnace to a temperature above its upper critical point, typically over 900°C (1650°F).
This high temperature causes the steel's crystalline structure to transform into a state known as austenite, which has the unique ability to dissolve a significant amount of carbon into its matrix.
Step 2: Soaking (Holding)
Once the transformation temperature is reached, the material is held, or "soaked," for a specific duration.
A common rule of thumb is to soak the part for one hour for every inch of thickness. This ensures the heat penetrates fully and the austenitic transformation is complete throughout the entire cross-section of the component.
Step 3: Quenching (Rapid Cooling)
Following the soak, the material is rapidly cooled by immersing it in a quenching medium. This extremely fast cooling does not give the carbon atoms time to move out of the crystal structure as they would during slow cooling.
This process "traps" the carbon, forcing the formation of a new, highly strained, and very hard crystal structure called martensite. The choice of medium—such as water, brine, oil, or gas—determines the cooling rate and the final hardness.
Why Hardening is Rarely the Final Step
Creating martensite achieves the goal of making the steel extremely hard, but it comes at a cost. The resulting material is often too brittle for most practical applications.
The Problem of Brittleness
A fully hardened, un-tempered piece of steel has properties similar to glass. It possesses very high compressive strength and wear resistance but is susceptible to shattering under sharp impact or shock loading.
The internal stresses created by the rapid quench make the part unstable and unreliable.
Step 4: Tempering (The Essential Refinement)
To solve the problem of brittleness, a secondary heat treatment called tempering is performed.
The hardened part is reheated to a much lower temperature (below the critical transformation range) and held for a set time. This process relieves the internal stresses and allows the crystal structure to relax slightly, trading a small amount of hardness for a significant gain in toughness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The relationship between hardening and tempering is a balancing act. The specific temperatures and timings used are dictated by the final properties required for the component.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Spectrum
The temperature used during the tempering phase directly controls the final balance of properties.
A low tempering temperature results in very high hardness but limited toughness, suitable for cutting tools. A higher tempering temperature produces a tougher, more ductile part at the expense of some hardness, ideal for structural components.
The Impact of Quenching Medium
The speed of the quench is a critical variable.
- Water/Brine: Provide the fastest cooling rates, achieving maximum hardness but with the highest risk of distortion or cracking.
- Oil: Offers a slower, less severe quench, reducing the risk of cracking while still achieving good hardness.
- Gas: Used in vacuum furnaces, gas quenching (often with nitrogen) provides the most controlled and slowest cooling, ideal for complex geometries and minimizing distortion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific parameters of the hardening and tempering process must be tailored to the intended application of the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance and cutting ability: Use a process that achieves high hardness, followed by a low-temperature temper to relieve stress without significantly reducing that hardness.
- If your primary focus is strength and impact resistance: Tempering is the most critical step; a higher tempering temperature will be necessary to impart the toughness required to prevent catastrophic failure in parts like gears, shafts, and axles.
- If your primary focus is maintaining tight dimensional tolerances: A less severe quenching medium, such as oil or gas in a vacuum furnace, is essential to minimize the risk of warping and distortion.
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment is about precisely controlling a material's internal structure to deliver the exact performance characteristics an application demands.
Summary Table:
| Step | Process | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Austenitizing | Heating to >900°C (1650°F) | Transform structure to austenite to dissolve carbon |
| 2. Soaking | Holding at temperature | Ensure uniform heat penetration and complete transformation |
| 3. Quenching | Rapid cooling (water, oil, gas) | Trap carbon to form hard martensite structure |
| 4. Tempering | Reheating to lower temperature | Relieve brittleness and increase toughness |
Ready to achieve precise material properties for your components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to master heat treatment processes like hardening and tempering. Whether you're developing cutting tools requiring maximum hardness or structural parts needing superior impact resistance, our solutions ensure controlled, repeatable results.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can help you optimize your heat treatment workflow and deliver the exact performance characteristics your application demands.
Get in touch with our experts →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- Why do you vacuum for heat treatment? Achieve Flawless, High-Performance Metal Components
- What is vacuum furnace high temperature? Unlock the Range for Your Material Processing
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance



















