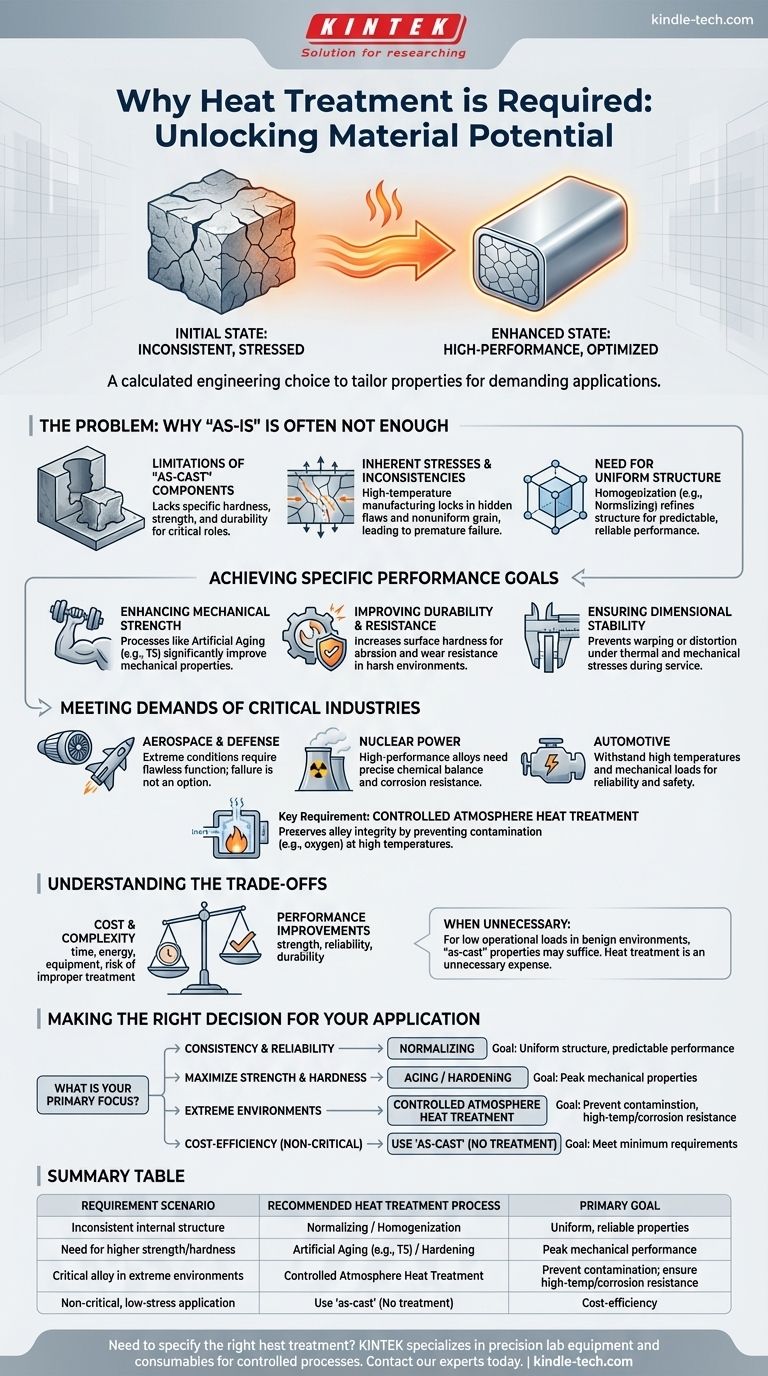
At its core, the requirement for heat treatment arises when a material's natural, or "as-is," properties are insufficient for its intended application. It is a controlled process of heating and cooling used to deliberately alter a material's internal structure, thereby enhancing specific characteristics like strength, hardness, or corrosion resistance to meet demanding engineering specifications.
The decision to use heat treatment is not a default step, but a calculated engineering choice. It is required when you must unlock a material's hidden potential, precisely tailoring its properties to survive the stresses and environment of its specific function.
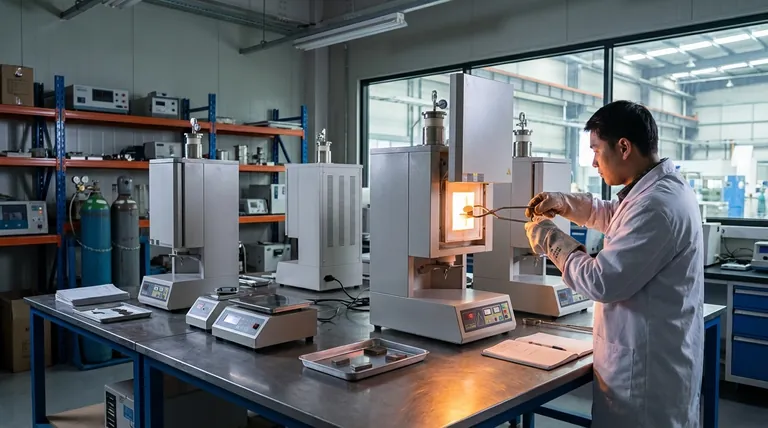

Why a Material's Initial State Is Often Not Enough
Many components, particularly those produced through casting or extrusion, are not ready for high-performance use immediately after they are formed. Their internal structure can be inconsistent and contain stresses that compromise their integrity.
The Limitations of 'As-Cast' Components
While some parts can be used "as-cast" for less demanding roles, this is often not the case for critical components. The raw material may lack the specific hardness, strength, or durability needed for its job.
Inherent Stresses and Inconsistencies
Manufacturing processes that involve high temperatures and rapid cooling, such as casting, can create an inconsistent grain structure and lock in internal stresses. These hidden flaws can lead to premature failure under load.
The Need for a Uniform Structure
To ensure predictable and reliable performance, the material's internal structure must be consistent throughout the entire component. This process, known as homogenization, is a primary reason for heat treatment.
One of the most common methods to achieve this is normalizing, which refines the grain structure to ensure consistent mechanical properties across the part.
Achieving Specific Performance Goals
Heat treatment is not a single process but a suite of techniques, each designed to produce a specific outcome. The requirement is dictated by the desired end-state property.
Enhancing Mechanical Strength
Processes like artificial aging (as seen in the T5 condition) are applied after a component is fabricated. This treatment accelerates the aging process to significantly improve mechanical properties and strength.
Improving Durability and Resistance
If an application demands high resistance to abrasion or wear, heat treatment is required to increase the surface hardness of the material. This makes the component more durable in its working environment.
Ensuring Dimensional Stability
Beyond just adding strength, some heat treatment processes are required to ensure the component remains dimensionally stable over its service life. This prevents warping or distortion when subjected to thermal cycles or mechanical stress.
Meeting the Demands of Critical Industries
Industries like aerospace, automotive, and nuclear power operate under extreme conditions where component failure is not an option. This makes highly controlled heat treatment an absolute requirement.
Preserving Alloy Integrity
High-performance alloys used in these sectors derive their special properties from a precise chemical balance. Controlled atmosphere heat treatment is required to prevent contamination from oxygen or other elements during the heating process, which would compromise the alloy's integrity.
Withstanding Extreme Environments
Components in jet engines or chemical reactors must function flawlessly at extreme temperatures and in corrosive environments. Heat treatment is the only way to impart the necessary high-temperature and corrosion resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is a powerful tool, but its application must be justified. It is an additional step that adds both cost and complexity to the manufacturing process.
When Heat Treatment is Unnecessary
If a component's operational loads are low and its environment is benign, the properties of the 'as-cast' material may be perfectly adequate. In these cases, heat treatment is an unnecessary expense.
Cost vs. Performance
The central trade-off is always cost versus performance. The decision to heat treat hinges on whether the required performance improvements justify the investment in time, energy, and equipment.
The Risk of Improper Treatment
A poorly executed heat treatment can do more harm than good. It can introduce new problems like cracking or warping, turning a usable component into scrap. This makes precise process control essential.
Making the Right Decision for Your Application
Choosing whether to specify heat treatment depends entirely on the functional requirements of the component.
- If your primary focus is consistency and reliability: Normalizing is often required to ensure a uniform internal structure and predictable performance.
- If your primary focus is maximizing strength or hardness: An aging or hardening process is necessary to achieve the material's peak mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is survival in extreme environments: Controlled atmosphere heat treatment is non-negotiable for critical alloys used in high-stress or high-temperature applications.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for a non-critical part: Using the component 'as-cast' is the right choice, provided its inherent properties meet the minimum design requirements.
Ultimately, heat treatment is the essential bridge between a standard material and a high-performance engineered component.
Summary Table:
| Requirement Scenario | Recommended Heat Treatment Process | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Inconsistent internal structure | Normalizing / Homogenization | Uniform, reliable properties |
| Need for higher strength/hardness | Artificial Aging (e.g., T5) / Hardening | Peak mechanical performance |
| Critical alloy in extreme environments | Controlled Atmosphere Heat Treatment | Prevent contamination; ensure high-temp/corrosion resistance |
| Non-critical, low-stress application | Use 'as-cast' (No treatment) | Cost-efficiency |
Need to specify the right heat treatment for your components? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for controlled heat treatment processes. Whether you're developing materials for aerospace, automotive, or industrial applications, our solutions help you achieve consistent, high-performance results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and ensure your materials meet the most demanding specifications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout



















