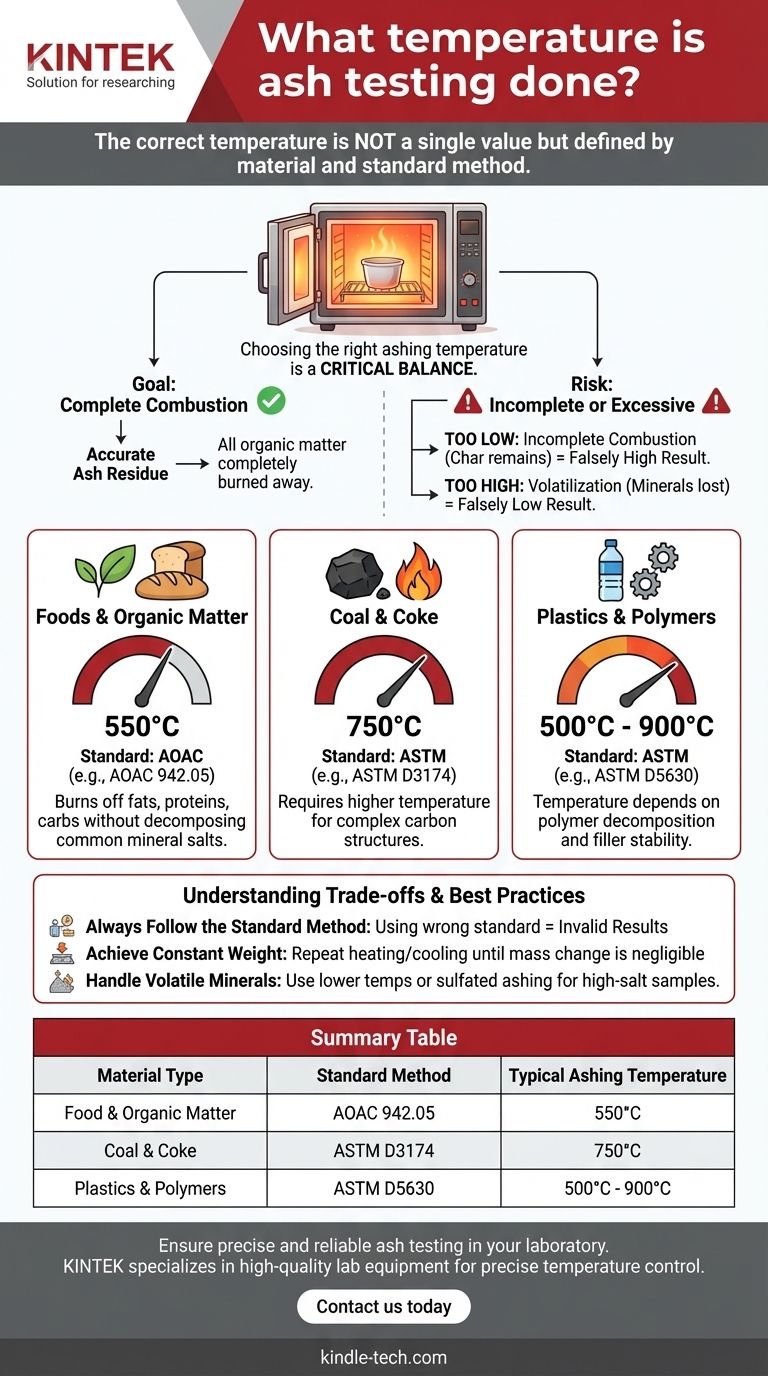
In ash testing, the correct temperature is not a single value but is strictly defined by the material being analyzed and the official standard method being followed. For most food and organic materials, the standard is 550°C, while for coal it is 750°C, and for plastics, it can range from 500°C to 900°C.
Choosing the right ashing temperature is a critical balance. The goal is to completely burn away all organic matter without causing the inorganic ash residue to decompose or vaporize, which would compromise the accuracy of the result.

Why Temperature is the Critical Factor in Ash Testing
Ash content analysis, or "ashing," is a method of gravimetric analysis that quantifies the total amount of inorganic mineral residue in a sample. The procedure involves heating a sample at a specific high temperature to incinerate all organic matter, leaving only the non-combustible ash.
The Goal: Complete Combustion
The fundamental purpose of the high temperature is to ensure complete oxidation of all organic components—primarily carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen—into gaseous products like carbon dioxide and water vapor.
This process must be thorough. Any remaining organic material that fails to combust will be weighed along with the ash, leading to an artificially high and incorrect result.
The Risk of Insufficient Temperature
Using a temperature that is too low for the material is a common error. This results in incomplete combustion, where traces of carbon (char) remain in the crucible.
This residual carbon inflates the final weight, making the calculated ash content falsely high.
The Risk of Excessive Temperature
Conversely, using a temperature that is too high can be equally detrimental. Certain inorganic minerals present in the ash can decompose or volatilize at excessive temperatures.
For example, chlorides, carbonates, and some metal oxides can be lost as vapor, leading to a lower final weight. This makes the calculated ash content falsely low.
Standard Ashing Temperatures by Material
Official methods from organizations like AOAC International and ASTM International define the precise temperatures and procedures to ensure results are accurate and repeatable across different labs.
Foods and Organic Matter (AOAC): 550°C
For general food products, animal feeds, and most biological samples, the standard method (e.g., AOAC 942.05) specifies ashing in a muffle furnace at 550°C.
This temperature is effective at burning off fats, proteins, and carbohydrates without significantly decomposing the common mineral salts found in food. For high-sugar or high-fat products, a gentle pre-heating step may be used to prevent spattering.
Coal and Coke (ASTM): 750°C
Solid fuels like coal and coke have a much denser, more complex carbon structure that requires a higher temperature for complete combustion.
The standard method, ASTM D3174, mandates a final ashing temperature of 750°C. The procedure often involves a slower, initial heating stage to drive off volatile matter before reaching the final temperature.
Plastics and Polymers (ASTM): 500°C to 900°C
For plastics, the goal of ash testing is typically to determine the content of inorganic fillers or reinforcements, such as glass fiber or calcium carbonate.
The standard method, ASTM D5630, specifies a wide temperature range, typically between 500°C and 900°C. The exact temperature depends on the decomposition temperature of the polymer and the thermal stability of the filler being measured. The objective is to remove the polymer matrix completely without altering the filler.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Best Practices
Simply setting the furnace is not enough. Achieving an accurate result requires adherence to a rigorous procedure that accounts for potential errors.
Always Follow the Standard Method
Applying a standard from one industry to another will produce invalid results. For example, ashing coal at the food-grade temperature of 550°C would result in incomplete combustion and a grossly overestimated ash content.
The Concept of "Constant Weight"
The ashing process is complete only when the sample has been heated to constant weight. This involves heating for a set period, cooling the sample in a desiccator (to prevent moisture absorption), and weighing it.
The process is repeated in cycles of heating, cooling, and weighing until two consecutive measurements show a negligible change in mass. This confirms that all organic matter has been burned off.
Handling Volatile Minerals
For samples known to contain high levels of volatile minerals (e.g., high-salt foods), a lower temperature (around 500°C) may be specified in the method to prevent their loss. In other cases, a process called sulfated ashing is used, where sulfuric acid is added to convert minerals into more stable sulfates before heating.
Selecting the Correct Temperature for Your Analysis
Your choice of temperature must be dictated by the official standard for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is food or biological samples: Start with the standard 550°C as specified by AOAC methods, unless you have a high-salt product that requires a documented modification.
- If your primary focus is coal or other solid fuels: You must follow the ASTM D3174 standard, which mandates a final temperature of 750°C for accurate proximate analysis.
- If your primary focus is analyzing filled polymers: Refer to the specific ASTM method (like D5630) for your polymer type, as the correct temperature is chosen to burn the polymer without degrading the inorganic filler.
- If you are analyzing a novel or non-standard material: Always begin by searching for an established ISO or ASTM standard for that material class to ensure your results are valid and defensible.
Selecting the correct, standardized temperature is the foundation for obtaining accurate and repeatable ash content results.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Standard Method | Typical Ashing Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Food & Organic Matter | AOAC 942.05 | 550°C |
| Coal & Coke | ASTM D3174 | 750°C |
| Plastics & Polymers | ASTM D5630 | 500°C - 900°C |
Ensure precise and reliable ash testing in your laboratory. The correct temperature is critical for valid results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including muffle furnaces with precise temperature control, to meet your specific ashing needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your analytical accuracy and efficiency. Get in touch →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the parts of a muffle furnace? Uncover the Core Components for Precision Heating
- How do you calibrate a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise Temperature Control for Your Lab
- What is a muffle furnace used for? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between a lab furnace and a lab oven? Choose the Right Heating Tool for Your Lab
- What is a muffle furnace used in determination of? Precise Ash Content and Material Composition



















